Vous pouvez lire le billet sur le blog La Minute pour plus d'informations sur les RSS !
Canaux
8180 éléments (3914 non lus) dans 50 canaux
 Dans la presse
(3748 non lus)
Dans la presse
(3748 non lus)
-
 Cybergeo
(3683 non lus)
Cybergeo
(3683 non lus) -
 Mappemonde
(60 non lus)
Mappemonde
(60 non lus) -
 Dans les algorithmes
(5 non lus)
Dans les algorithmes
(5 non lus)
 Du côté des éditeurs
(28 non lus)
Du côté des éditeurs
(28 non lus)
-
 Toute l’actualité des Geoservices de l'IGN
(17 non lus)
Toute l’actualité des Geoservices de l'IGN
(17 non lus) -
 arcOpole - Actualités du Programme
arcOpole - Actualités du Programme
-
 arcOrama
(11 non lus)
arcOrama
(11 non lus) -
 Neogeo
Neogeo
 Toile géomatique francophone
(110 non lus)
Toile géomatique francophone
(110 non lus)
-
Géoblogs (GeoRezo.net) (5 non lus)
-
 UrbaLine (le blog d'Aline sur l'urba, la géomatique, et l'habitat)
UrbaLine (le blog d'Aline sur l'urba, la géomatique, et l'habitat)
-
 Séries temporelles (CESBIO)
(2 non lus)
Séries temporelles (CESBIO)
(2 non lus) -
 Datafoncier, données pour les territoires (Cerema)
Datafoncier, données pour les territoires (Cerema)
-
 Cartes et figures du monde
Cartes et figures du monde
-
 SIGEA: actualités des SIG pour l'enseignement agricole
SIGEA: actualités des SIG pour l'enseignement agricole
-
 Data and GIS tips
Data and GIS tips
-
 ReLucBlog
ReLucBlog
-
 L'Atelier de Cartographie
L'Atelier de Cartographie
-
My Geomatic
-
 archeomatic (le blog d'un archéologue à l’INRAP)
archeomatic (le blog d'un archéologue à l’INRAP)
-
 Cartographies numériques
Cartographies numériques
-
 Carnet (neo)cartographique
Carnet (neo)cartographique
-
 GEOMATIQUE
GEOMATIQUE
-
 Évènements – Afigéo
(12 non lus)
Évènements – Afigéo
(12 non lus) -
 Afigéo
(12 non lus)
Afigéo
(12 non lus) -
 Geotribu
(50 non lus)
Geotribu
(50 non lus) -
 Conseil national de l'information géolocalisée
(9 non lus)
Conseil national de l'information géolocalisée
(9 non lus) -
 Icem7
Icem7
-
Makina Corpus (1 non lus)
-
 Oslandia
(1 non lus)
Oslandia
(1 non lus) -
 CartONG
(2 non lus)
CartONG
(2 non lus) -
 GEOMATICK
(6 non lus)
GEOMATICK
(6 non lus) -
 Geomatys
(3 non lus)
Geomatys
(3 non lus) -
 Les Cafés Géo
(1 non lus)
Les Cafés Géo
(1 non lus) -
 L'Agenda du Libre
(3 non lus)
L'Agenda du Libre
(3 non lus) -
 Conseil national de l'information géolocalisée - Actualités
(3 non lus)
Conseil national de l'information géolocalisée - Actualités
(3 non lus)
 Géomatique anglophone
(16 non lus)
Géomatique anglophone
(16 non lus)
Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Membership approves OGC API – Maps – Part 1: Core as an official OGC Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Membership has approved OGC API – Maps – Part 1: Core as an official OGC Standard.
The OGC API – Maps – Part 1: Core Standard defines a web interface for portraying geographic information. One of the main benefits of this Standard is the ability to generate maps by combining data from one or more servers into a single view, ensuring fast and efficient cartographic portrayal.
Additional features include options for retrieving data layers within specific areas of interest (AOIs) as well as specifying transparency, styles, scales, and device display settings. The Standard also provides the ability to specify map orientation and supports multiple Coordinate Reference Systems (CRS).
The OGC API – Maps – Part 1: Core Standard is designed as a modern, API-based alternative to the Web Map Service (WMS) and Web Map Tile Service (WMTS) Standards. It can be integrated with the OGC API – Tiles – Part 1: Core Standard to support more advanced capabilities.
To help developers quickly implement products that support this standard, example API definitions and schemas are available on the OGC API – Maps webpage. These resources conform to OpenAPI Specification v3.0, making them easy to integrate into various Web APIs.
OGC API – Maps – Part 1: Core is the outcome of the work and dedication of the OGC API – Maps Standards Working Group. Development of the Standard was led by:
- Editors:
- Joan Masó, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (CREAF)
- Jérôme Jacovella-St-Louis, Ecere Corporation
- Submitters:
- Jeff Harrison, US Army Geospatial Center (AGC)
- Satish Sankaran, Esri
As with any OGC standard, the OGC API – Maps – Part 1: Core Standard is free to download and implement. Interested parties can learn more on the OGC API – Maps Standard webpage.
The post OGC Membership approves OGC API – Maps – Part 1: Core as an official OGC Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
- Editors:
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Membership approves OGC API – Features – Part 3: Filtering as an official OGC Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Membership has approved OGC API – Features – Part 3: Filtering as an official OGC Standard.
OGC API – Features defines a web interface for creating, modifying, and querying feature data. Part three of this standard is focused on defining query parameters and the Queryables resource, allowing users to specify filter criteria in API requests.
OGC API – Features – Part 3: Filtering extends the ability to extract data subsets that meet specific criteria beyond bounding boxes or date and time attributes. This enhanced query functionality is specified using the Common Query Language (CQL2) – a recently approved OGC Standard.
Part 3 is designed to extend and interoperate with other parts of the OGC API – Features Standard. It builds on Part 1, which defines basic server behavior and is compatible with Part 2, which extends support for different Coordinate Reference Systems.
To help developers quickly implement products that support this standard, example API definitions and schemas are available on the OGC API – Features webpage. These resources conform to the OpenAPI Specification v3.0, making them easy to integrate into various Web APIs.
OGC API – Features – Part 3: Filtering is the outcome of the work and dedication of the OGC API – Features Standards Working Group. Development of the standard was led by:
- Editors:
- Panagiotis (Peter) A. Vretanos, CubeWerx Inc.
- Clemens Portele, interactive instruments GmbH
- Submitters:
- Andrea Aime, GeoSolutions di Giannecchini Simone & C. s.a.s.
- Jeff Harrison, US Army Geospatial Center (AGC)
- Jérôme Jacovella-St-Louis, Ecere Corporation
As with any OGC Standard, the OGC API – Features – Part 3: Filtering Standard is free to download and implement. Interested parties can learn more on the OGC API – Features Standard webpage.
The post OGC Membership approves OGC API – Features – Part 3: Filtering as an official OGC Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
- Editors:
-
 17:00
17:00 Bentley Systems increases investment in OGC and reinforces commitment to Open Standards following Cesium acquisition
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is pleased to announce that infrastructure engineering software company Bentley Systems is increasing its investment and engagement in OGC—and further strengthening its commitment to growing an open ecosystem.
Bentley recently acquired Cesium, a fellow OGC member and the creator of 3D Tiles, an OGC Community Standard for massive heterogenous 3D geospatial content.
Bentley’s increased investment in OGC, coupled with its acquisition of Cesium, signals their commitment to a future built around open standards, data, and infrastructure. OGC’s trusted community of problem solvers leverages the power of geography, open standards, and interconnected systems to address real-world problems while opening up opportunities for commercial growth.
“We are pleased to see this increased investment in OGC by Bentley, and their support to us as a Principal member,” said Peter Rabley, Chief Executive Officer, OGC. “As a Principal Member of OGC, Bentley will play a significant role serving on OGC’s Executive Planning Committee and participating in final approval decisions for all OGC Standards and nominations to the Board of Directors.”
Patrick Cozzi, Chief Platform Officer, Bentley, and Cesium founder, commented, “The success and impact of 3D Tiles as an open standard reinforces our belief that openness and interoperability are essential to making the best use of location information to benefit society. We look forward to continuing to work within the OGC community as part of Bentley.”
“Bentley is a strong supporter of open data ecosystems,” added Julien Moutte, Chief Technology Officer, Bentley Systems. “As a principal member of OGC, we are committing further resources to accelerate the development and adoption of open standards that benefit applications for the built and natural environment.”
About OGC
The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is a membership organization dedicated to using the power of geography and technology to solve problems faced by people and the planet. OGC unlocks value and opportunity for its members through Standards, Innovation, and Policy & Advocacy. Our membership represents a diverse and active global community drawn from government, industry, academia, international development agencies, research & scientific organizations, civil society, and advocates.
Visit ogc.org for more information about our work.About Bentley Systems
Bentley Systems (Nasdaq: BSY) is the infrastructure engineering software?company. Bentley provides innovative software to advance the world’s infrastructure – sustaining both the global economy and environment. Bentley’s industry-leading software solutions are used by professionals, and organizations of every size, for the design, construction, and operations of roads and bridges, rail and transit, water and wastewater, public works and utilities, buildings and campuses, mining, and industrial facilities. Bentley’s offerings, powered by the iTwin?Platform for infrastructure digital twins, include MicroStation and Bentley Open?applications for modeling and simulation, Seequent’s software for geoprofessionals, and Bentley Infrastructure Cloud encompassing ProjectWise?for project delivery, SYNCHRO?for construction management, and AssetWise?for asset operations. Bentley Systems’ 5,200 colleagues generate annual revenues of more than $1 billion in 194 countries.About Cesium
Cesium is the open platform for 3D Geospatial. Cesium created 3D Tiles, the Open Geospatial Consortium community standard for streaming massive 3D geospatial datasets. Use Cesium ion to optimize, host, and combine your data with curated global 3D content and stream to any device. With unique expertise at the intersection of 3D geospatial and computer graphics, Cesium is deeply committed to openness and interoperability through open standards, open APIs, and open source offerings like CesiumJS, Cesium for Unreal, Cesium for Unity, and Cesium for Omniverse. Originally built for Aerospace, Cesium is now used to power thousands of applications in industries like Defense, Architecture, Engineering, Construction and Operations, Commercial real estate, urban planning, and more.The post Bentley Systems increases investment in OGC and reinforces commitment to Open Standards following Cesium acquisition appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Membership approves Common Query Language (CQL2) as an official OGC Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the OGC Membership has approved Version 1.0 of the Common Query Language (CQL2) for adoption as an official OGC Standard.
Filtering is a fundamental operation performed on feature data to obtain a subset that contains the geospatial information a user needs. CQL2 is a filter grammar that can be used to specify how features can be filtered to obtain a subset. The Standard supports both text and JSON encodings so can be easily integrated into a variety of software applications.
CQL2 is a revision of the original Common Query Language. While the language design is consistent with the original version, many changes and additions to improve consistency and capabilities have been made. Existing implementations of CQL will need to be updated to process filter expressions specified by CQL2.
The OGC API – Features Standard currently uses CQL2, and other Standards that require the ability to filter data are likely to adopt it as well. Example files and JSON, YAML, and BNF schemas have been published on the OGC schemas repository to enable software developers to rapidly implement CQL2.
The original Common Query Language (CQL) was created as a text encoding for use in the OGC Catalogue Service Implementation Specification. CQL is based on the capabilities in the OGC Filter Encoding (FE) Standard, which was originally part of the Web Feature Service (WFS) Standard.
CQL2 is the outcome of the work and dedication of the OGC API – Features Standards Working Group, which led the development of the Standard, including:
- Editors:
- Panagiotis (Peter) A. Vretanos, CubeWerx Inc.
- Clemens Portele, interactive instruments GmbH
- Submitters:
- Andrea Aime, GeoSolutions di Giannecchini Simone & C. s.a.s.
- Jeff Harrison, US Army Geospatial Center (AGC)
- Jérôme Jacovella-St-Louis, Ecere Corporation
As with any OGC Standard, CQL2 is free to download and implement. Interested parties can learn more on the OGC CQL2 Standard webpage.
The post OGC Membership approves Common Query Language (CQL2) as an official OGC Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
- Editors:
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Approves Model for Underground Data Definition and Integration as Official Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the OGC Membership has approved version 1.0 of the OGC Model for Underground Data Definition and Integration (MUDDI) Part 1: Conceptual Model for adoption as an official OGC Standard. MUDDI serves as a framework to make datasets that utilize different information for underground objects interoperable, exchangeable, and more easily manageable.
MUDDI represents real-world objects found underground. It was designed as a common basis to create implementations that make different types of subsurface data – such as those relating to utilities, transport infrastructure, soils, ground water, or environmental parameters – interoperable in support of a variety of use cases and in different jurisdictions and user communities. The case for better subsurface data and an explanation of the usefulness of the MUDDI data model is made in this MUDDI For Everyone Guide.
Certainly, a key focus application domain, and one of the main motivations for creating MUDDI, is utilities and the protection of utilities infrastructure. Indeed, OGC’s MUDDI Model was successfully used in pilot testing for the National Underground Asset Register (NUAR), a program led by the UK Government’s Geospatial Commission. More information on NUAR can be found here.
MUDDI aims to be comprehensive and provides sufficient level of detail to address many different application use cases, such as:
- Routine street excavations;
- Emergency response;
- Utility maintenance programs;
- Large scale construction projects;
- Disaster planning;
- Disaster response;
- Environmental interactions with infrastructure;
- Climate Change mitigation; or
- Smart Cities programs.
The MUDDI Conceptual Model provides the implementation community with the flexibility to tailor the implementations to specific requirements in a local, regional, or national context. The standardization targets are specific MUDDI implementations in one or more encodings such as GML (Geographic Markup Language), SFS (Simple Features SQL), Geopackage or JSON-FG encodings that are expected to be standards in future parts of the MUDDI standards family. Both GML and JSON-FG are supported by the OGC API – Features Standard. SFS is supported by a number of database systems.
MUDDI consists of a core of mandatory classes describing built infrastructure networks (such as utility networks) together with a number of optional feature classes, properties, and relationships related to the natural and built underground environment. The creation of implementations targeted to defined use cases and user communities also allows the extension of the concepts provided in MUDDI.
The early work for crafting this OGC Standard was undertaken in the OGC Underground Infrastructure Concept Study, sponsored by Ordnance Survey, Singapore Land Authority, and The Fund for the City of New York – Center for Geospatial Innovation.
The Concept Study was followed by the Underground Infrastructure Pilot and MUDDI ETL-Plugfest workshop, as well as close collaboration with early implementers of MUDDI, such as the UK Geospatial Commission. Several implementations of MUDDI were thoroughly tested in the OGC Open Standards Code Sprint in October/November 2023. The results are described in the OGC 2023 Open Standards Code Sprint Summary Engineering Report and a blog post entitled Going underground: developing and testing an international standard for subsurface data, which describes the experiences and lessons learned from the Geospatial Commission’s attendance at the Code Sprint.
Version 1.0 of the MUDDI Conceptual Model Standard is the outcome of those initiatives, as well as the work and dedication of the MUDDI Standards Working Group, which led the development of the Standard, including:
- Editors:
- Alan Leidner, New York City Geospatial Information System and Mapping Organization (GISMO)
- Carsten Roensdorf, Ordnance Survey
- Neil Brammall, Geospatial Commission, UK Government
- Liesbeth Rombouts, Athumi
- Joshua Lieberman
- Andrew Hughes, British Geological Survey, United Kingdom Research and Innovation
- Contributors:
- Dean Hintz, Safe Software
- Allan Jamieson, Ordnance Survey
- Chris Popplestone, Ordnance Survey
OGC Members interested in staying up to date on the progress of this Standard, or contributing to its development, are encouraged to join the MUDDI Standards Working Group via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about participating in this SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
As with any OGC standard, the open MUDDI Part 1: Conceptual Model Standard is free to download and implement. Interested parties can view and download the standard from OGC’s Model for Underground Data Definition and Integration (MUDDI) Standard Page.
The post OGC Approves Model for Underground Data Definition and Integration as Official Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 0:05
0:05 Public Services on the Map: A Decade of Success
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Netherlands’ Cadastre, Land Registry, and Mapping Agency (Kadaster) maintains the nation’s register of land and property rights, ships, aircraft, and telecom networks. It’s also responsible for national mapping and the maintenance of the nation’s reference coordinate system and serves as an advisory body on land-use issues and national spatial data infrastructures. In its public service role, Kadaster handles millions of transactions a day.
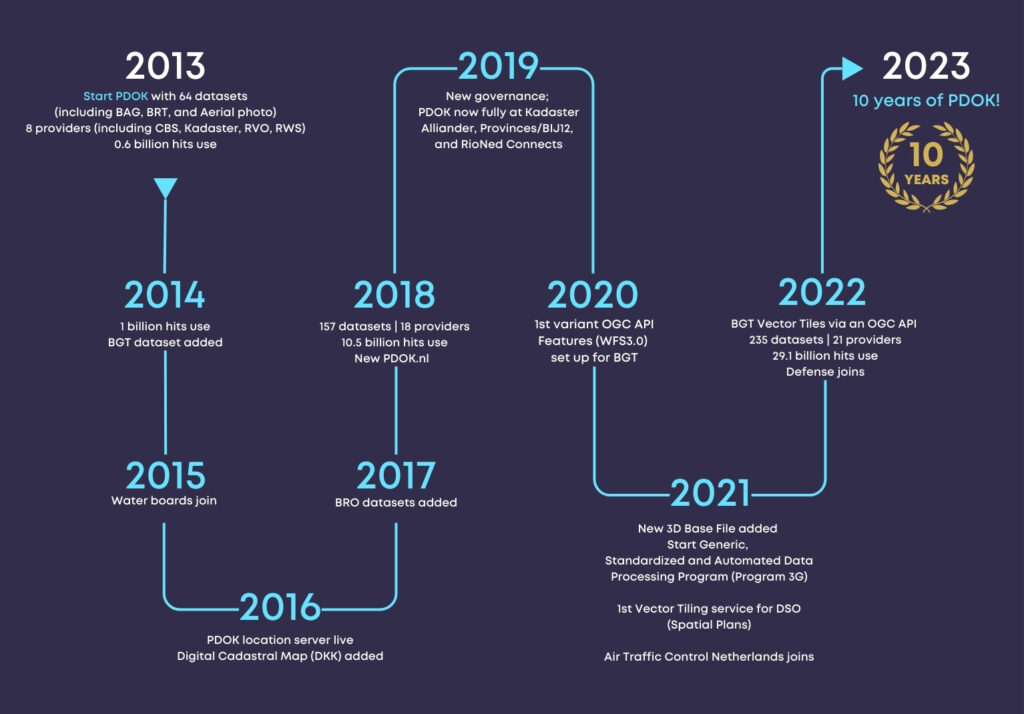 Celebrating 10 years: PDOK’s evolution. (click to enlarge)
Celebrating 10 years: PDOK’s evolution. (click to enlarge)
PDOK was launched in 2013 to make the Dutch government’s geospatial datasets Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR) as mandated by the EU’s INSPIRE Directive. OGC Standards have been foundational in ensuring that the country’s Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) is scalable, available, and responsive.
PDOK serves base maps and Earth Observation data for the whole country. It includes the Key Topography Register (Basisregistratie Topografie, BRT), aerial imagery (updated annually at 8 and 25 cm GSD), and the Large Scale Topography Register (Basisregistratie Grootschalige Topografie, BGT). The BGT is a detailed digital base map (between 1:500 and 1:5,000) that depicts building footprints, roads, water bodies, railways lines, agricultural land, and parcel boundaries. PDOK also serves a 3D dataset of buildings and terrain created from topography (BGT), building footprints (from the Building and Addresses Register or BAG), and height information (from aerial photography).
When PDOK was launched in 2013, it hosted 40 datasets and handled 580 million server requests annually. Today it hosts 210 datasets and handles 30 billion server requests annually—representing a 5,000% increase in service requests being handled by the platform.
 Examples of PDOK basemaps and imagery.
Standards Enabling Success
Examples of PDOK basemaps and imagery.
Standards Enabling Success
The majority of datasets on PDOK are made available using OGC’s popular Web Map Service (WMS) and Web Feature Service (WFS) standards. The BRT is available in three coordinate reference systems (EPSG 28992, EPSG 25831, and EPSG 3857) using the Web Map Tile Service (WMTS) standard.
Kadaster is in the process of transitioning to the newer OGC API Standards, including OGC API – Tiles and OGC API – Features. The most frequently used key registers, like the Building and Addresses Register (BAG), the Large Scale Topography Register (BGT), and the Key Topography Register (BRT) are in the process of being migrated to these newer OGC APIs. The focus is on using OGC API – Tiles, specifically Vector Tiles. For query services the OGC API – Features Standard is used. Although Earth Observation data doesn’t currently use the newer APIs, aerial imagery is available through WM(T)S services, stored as OGC Cloud Optimized GeoTiffs (CoG). 3D Building data is encoded as OGC 3D Tiles and served using the OGC API – 3D GeoVolumes standard.
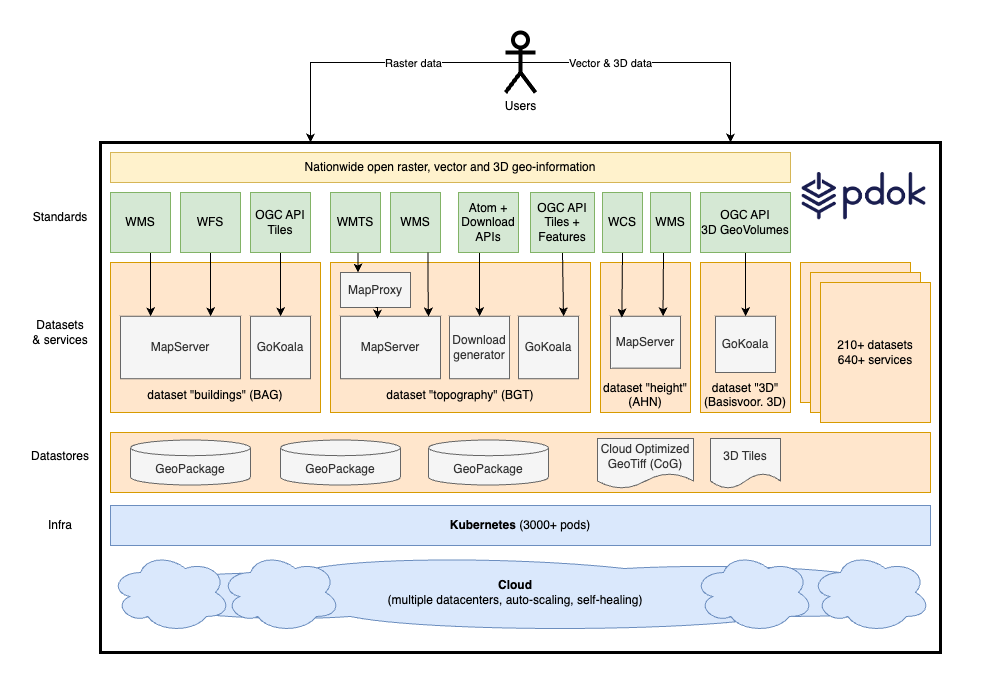 The PDOK architecture and OGC Standards. (click to enlarge)
The PDOK architecture and OGC Standards. (click to enlarge)
By using the newer OGC API Standards, Kadaster has found it significantly easier to handle the large volume of data in its national-scale 3D building dataset (which can be used between scales of 1:500 and 1:10,000) providing an unparalleled, high-resolution perspective of the country’s built environment.
OGC APIs also make it easier to track compute and memory usage on servers, allowing Kadaster to better realize platform scalability and optimize performance.
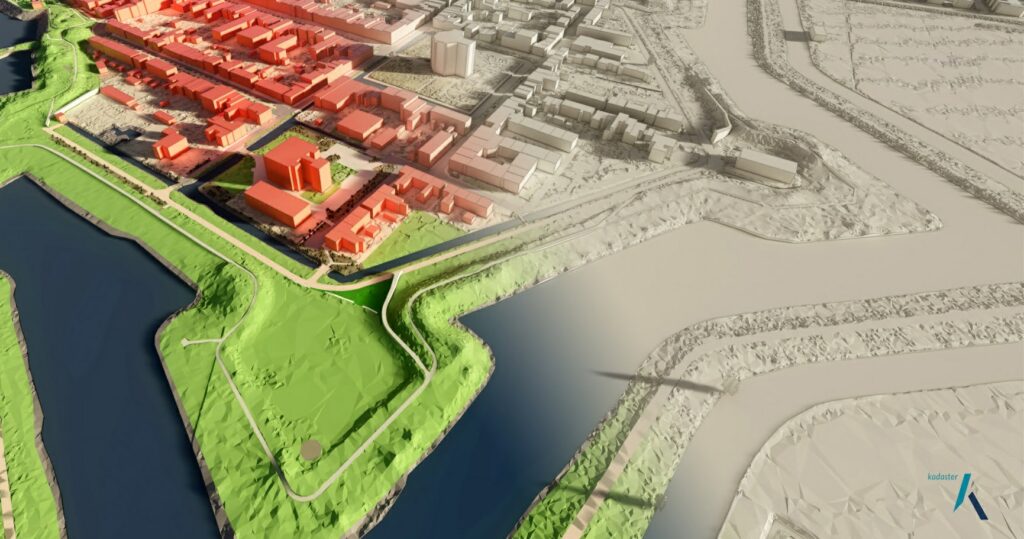 PDOK uses the OGC API – 3D GeoVolumes to serve the 3D building dataset. (click to enlarge)
A Smooth Transition to OGC APIs
PDOK uses the OGC API – 3D GeoVolumes to serve the 3D building dataset. (click to enlarge)
A Smooth Transition to OGC APIs
PDOK processes billions of user requests every month. Transitioning from OGC Web Services Standards to OGC APIs has meant Kadaster is able to efficiently handle the volume of requests it handles today – and can expect to handle in the future.
It took Kadaster little over a month to build their implementation of OGC API – Tiles. Following a short learning curve they were able to build out implementations of OGC API – Features and API – 3D GeoVolumes even faster. By making the move to deliver its geospatial tiles and feature data through an API conformant to the OGC API Standards, Kadaster continues to make government data Findable and Accessible.
PDOK implements what Kadaster calls the 3G principle—Generic (Generic), Geautomatiseerd (Automated) en Gestandaardiseerd (Standardized). This has led to simplified data processing, the automation of many manual processes, a standardization in services, and high standards in service design and operation – while at the same time remaining infrastructure independent. It has streamlined the adoption of new OGC Standards and made it better able to respond to changing user requirements.
Kadaster and OGCBeing an OGC Member allows Kadaster to leverage the collective knowledge of a global network of geospatial experts, while providing Kadaster with opportunities to contribute back to a community driven to use the power of geography and technology to solve problems faced by people and the planet.
Kadaster has recently contributed to the OGC Community by participating in an OGC Code Sprint. These hybrid online/in-person events give participants the opportunity to work on implementations of new or emerging OGC Standards.
Through OGC, Kadaster has also shared their experiences and challenges at OGC Member Meetings, contributing to the ongoing evolution of OGC Standards, Collaborative Solutions and Innovation (COSI) Program Initiatives, and, more broadly, advanced the “state of the art” of geospatial technologies.
The below video provides an overview of PDOK.
The post Public Services on the Map: A Decade of Success appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 20:13
20:13 OGC announces Christy Monaco as new Chief Operating Officer
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that Ms. Christy Monaco will soon join OGC’s senior leadership as the Consortium’s Chief Operating Officer (COO). Christy commences her new role on September 1, 2024.
Christy brings to OGC a deep understanding of the geospatial industry, including historical and current trends, gained from her experience leading operations, technological transformation, organizational change, and resource management in the government and non-profit sectors of the geospatial and intelligence communities.
“I am thrilled to be joining Peter and the amazing team at OGC,” commented Christy Monaco. “For thirty years, OGC has brought together the geospatial community to ensure interoperability of data and technology during a period of tremendous growth and change. In our increasingly interconnected world, new opportunities abound for OGC, its partners, and stakeholders to address rapidly evolving global challenges and drive innovation. I’m truly excited to take on this new role as we shape the future of geospatial technology together.”
As OGC’s COO, Christy will use her experience with federal agencies, partnership-building, event management, and member success to help grow and shape the Consortium as it looks to its next chapter and works with new and established partners and stakeholders to bring accelerated, practical, and implementable solutions to the world of geospatial.
“We are very excited to have Christy join our executive team,” commented Peter Rabley, OGC CEO. “Christy will work with me and the rest of the team to enhance and grow the support and value that OGC provides to our members through our Policy & Advocacy, Innovation, and Standards.”
Previous to her appointment at OGC, Christy was the Vice President of Programs at the U.S. Geospatial Intelligence Foundation (USGIF), where she led content development for the Foundation’s events and programs, including the Foundation’s annual GEOINT Symposium. Christy also oversaw the Foundation’s education & professional development initiatives and marketing & communication activities.
About Christy Monaco
Ms. Christy Monaco is the new Chief Operating Officer (COO) at the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), starting September, 2024. Previous to joining OGC, Christy was the Vice President of Programs at the U.S. Geospatial Intelligence Foundation (USGIF), a role she held since December of 2020. She previously served for over 30 years in the U.S. Intelligence Community, during which she held a number of positions including with the Office of Naval Intelligence (ONI), the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA), and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA). A government executive for over half of her federal career, in 2022 she was recognized by President Biden as a Meritorious Executive in the Defense Intelligence Senior Executive Service for her contributions at NGA. Christy currently resides in Alexandria, Virginia.The post OGC announces Christy Monaco as new Chief Operating Officer appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:00
16:00 A recap of the 129th OGC Member Meeting, Montreal, Canada
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The 129th OGC Member Meeting was held in Montreal, Canada, from June 17-21, 2024. The meeting was hosted by OGC Strategic Member Natural Resources Canada, with additional support from Esri Canada, CAE, Safe Software, and Bentley Systems. The week saw more than 200 leaders and experts from industry, academia, and government come together—with a further 100 online—to learn about the latest innovations from OGC Members, advance Standards, network, and shape the future of geospatial technology. The meeting was also notable as it marked the beginning of OGC’s 30 year anniversary celebrations, which will culminate at an event in Washington, D.C., this December.
Under the theme “Standards enabling collaboration for global challenges” the 129th Member Meeting focused on discussing, aligning, supporting, and promoting geospatial solutions that address challenges as far reaching as climate change and related disasters, and application domains as diverse as marine, Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML), and beyond.
Alongside the many OGC Standards and Domain Working Group meetings, there also included a Methane Summit, a Sensor Summit, a two-day meeting of the Canada Forum, a Quantum Computing ad hoc, a Metadata Workshop, and the kickoff of Testbed-20.
Friday’s OGC Executive Planning Committee Meeting was hosted by CAE at their nearby factory, and included a memorable tour of their factory floor. Social occasions included a Monday evening reception and a Wednesday night dinner was held at Northern Italian restaurant, Le Richmond. During the dinner, Andreas Matheus from Secure Dimensions GmbH was presented the 2024 Gardels Award for his persistent efforts to ensure best practices in security and API design in OGC. Congratulations, Andreas!
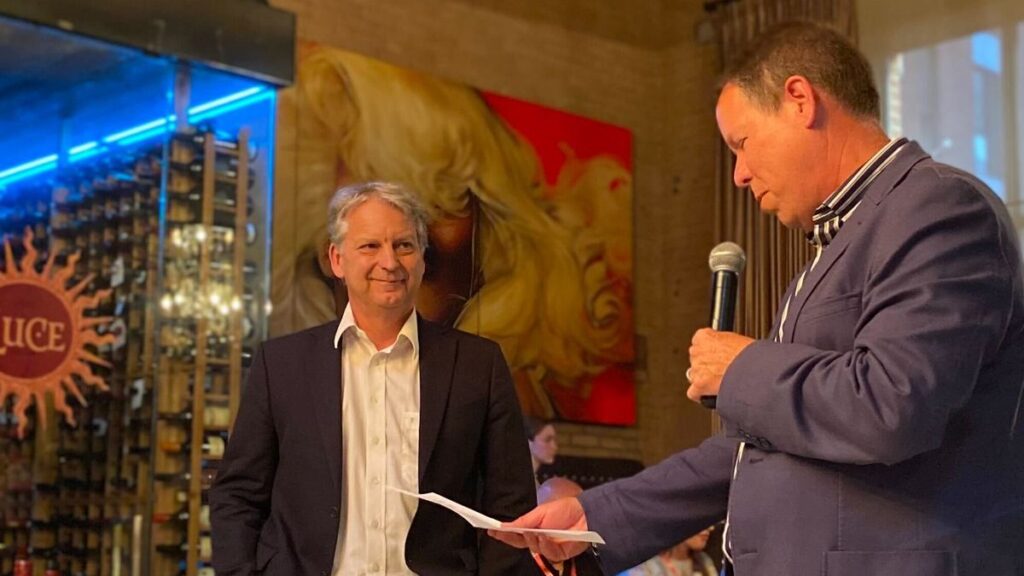 Andreas Matheus (L) is presented the 2024 Gardels Award by OGC Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons (R).
Andreas Matheus (L) is presented the 2024 Gardels Award by OGC Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons (R).
In addition to the challenges and domains covered by the meeting theme, two additional areas of discussion that stood out during the week: Digital Twins & Sensors, and Ethics in Geospatial.
Digital Twins & Sensors. OGC members are increasingly demonstrating the use of digital twins of the built environment (e.g., city and building models) as the context and framework in which sensors are managed. Sensed information in the real world can be displayed on digital representations of that digital reality to enable better understanding of environmental conditions, human activity, and system responses to those factors. The Urban Digital Twins DWG, 3D Information Management DWG, and the Autonomy, Sensors, Things, Robots, and Observations DWG are each actively discussing and collaborating on this integration.
Ethics in Geospatial. The OGC Executive Planning Committee has established a new subgroup on Ethics in Geospatial to set strategy for how OGC might address/respond to the ethical use of geospatial data or the use of those data for ethical purposes. The group will organize an initial meeting this July. If you would like to contribute to the conversation, you can sign up to the OGC Ethics in Geospatial email list here.
Building on the success of the demonstration at the 128th Member Meeting in Delft, The Netherlands, members of the OGC GeoPose and Points of Interest Standards Working Groups, in collaboration with the Open AR Cloud team, XR Masters, and Augmented City, expanded the GeoPose demonstration to include a native browser developed by OGC member Ethar, Inc. With the Ethar implementation, the team successfully demonstrated that a GeoPose can be encoded into a QR code. You can read more about the demonstration on the Open AR Cloud blog post, which includes a video showing how GeoPose can be used for anchoring content indoors and how it can be recognized by different Augmented Reality Clients.
Opening PlenaryThe Opening Plenary was hosted by OGC’s Dr. Rachel Opitz and featured a keynote presentation from Eric Loubier, Director General of the Canada Centre for Mapping and Earth Observation at Natural Resources Canada. Mr. Loubier highlighted the use of geospatial data and technologies to address the needs of Canadian citizens, with examples including flood and wildfire risk.
Introductory messages were then delivered by Louis-Martin Losier from Bentley Systems, Gordon Plunkett from Esri Canada, Hermann Brassard from CAE, and Dean Hintz from Safe Software. Finally, Prashant Shukle, Chair of the OGC Board of Directors, presented on “Canada and the OGC – 30 years of impact,” which reflected on the important parts that Canadian organizations have played in OGC’s 30 year history.
Special tribute was then paid to an instrumental figure in OGC’s history who sadly passed away in May this year, Dr. John Herring. John was OGC’s first Gardels Award recipient back in 1999, and also received an OGC Lifetime Achievement Award in 2021.
 Chair of the OGC Board of Directors, Prashant Shukle, presents “Canada and the OGC – 30 years of impact” during the opening session.
Future Directions
Chair of the OGC Board of Directors, Prashant Shukle, presents “Canada and the OGC – 30 years of impact” during the opening session.
Future Directions
This Meeting’s Future Directions session focused on Artificial Intelligence in Geoinformatics. Four presentations were made to provide updates since this topic was last addressed.
- Leveraging AI for Geospatial Reality Data: Louis-Martin Losier, Jeroen Vermeulen, Arnaud Durante (Bentley Systems)
- Spatial Web: AI agents operating in hyperspace: George Percivall (GeoRoundtable / IEEE GRSS)
- A User-Centric Process to Build AI-Powered Geospatial Applications: Pablo Fuentes (makepath)
- Bringing Geospatial Awareness to Large Language Models Using Spatial Knowledge Graphs: Nathan McEachen (TerraFrame)
The four presenters then engaged in a fascinating panel discussion moderated by Dr. Gobe Hobona of OGC. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
Meeting Special SessionsThe Methane Summit focused on the observation, measurement, monitoring, and spatial analysis of methane emissions. Consistent reporting of these emissions in a spatial context is key to effective decision making regarding reduction of emissions and their environmental consequences. Hence, the session also resulted in the proposal of a new OGC Standards Working Group (SWG) for EmissionML as a means to encode emission data. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
Directly following the Methane Summit was a linked Sensor Summit to talk more specifically about sensor model and data standardization. The focus of this Summit was on new and emerging Standards activities in OGC, including SensorThings API version 2.0, OGC API – Connected Systems and its dependent updates to the SensorWeb Standards, and the UK SAPIENT sensor architecture. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The OGC Canada Forum held sessions on both Monday and Tuesday. Day 1 included an opening and the Forum Overview, followed by a panel on “The Transformative Role of Industry in National Geospatial Strategy and Spatial Data Infrastructure.” Day 2 started with an Oxford debate on the impact of standards on innovation and then included a panel on “National Geospatial Strategy in a Time of Rapid Change and Growing Challenges.” The day wrapped up with a discussion on partnerships and a closing. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
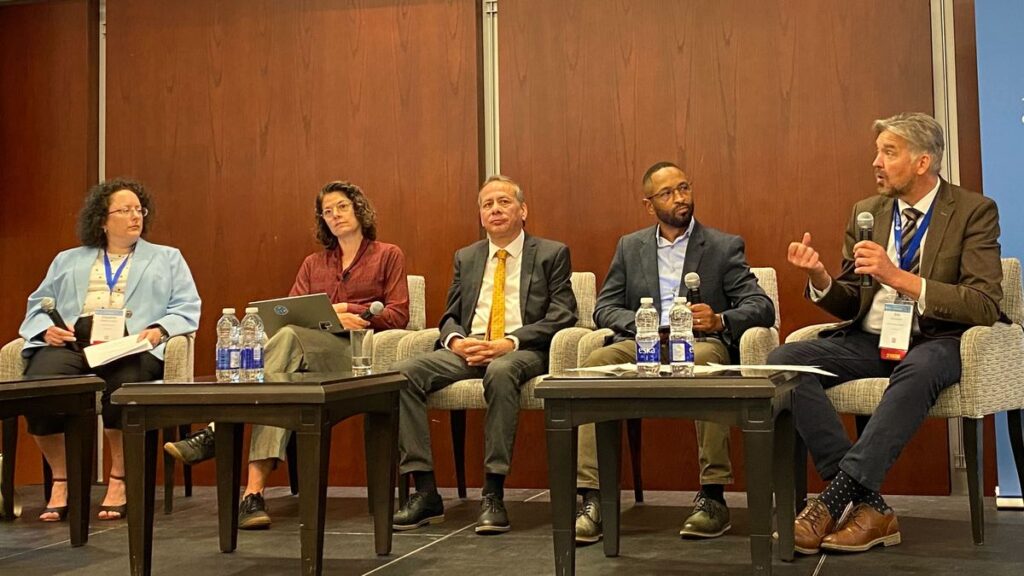 (L-R) Claudine Couture, Linda van den Brink, Bradford Dean, Eldrich Frazier, and Eric Loubier discussing “National Geospatial Strategy in a Time of Rapid Change and Growing Challenges” during the Canada Forum.
(L-R) Claudine Couture, Linda van den Brink, Bradford Dean, Eldrich Frazier, and Eric Loubier discussing “National Geospatial Strategy in a Time of Rapid Change and Growing Challenges” during the Canada Forum.
The Quantum Computing ad hoc session was a follow-up from the previous Member Meeting to assess whether a new OGC Working Group should be established to assess the geospatial role of quantum computing technologies. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
On Friday of the meeting week, a full-day Metadata Workshop was organized by the Metadata and Catalogs Domain Working Group (DWG). The first half of the workshop set the stage with presentations on current and emerging metadata Standards as well as their practical use. The second half of the summit was focused on the candidate OGC GeoDCAT Standard, how GeoDCAT fits within OGC’s building block approach to Standards, and preparation for a metadata-centric OGC Code Sprint later in 2024. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The next OGC Testbed has now begun! The Testbed-20 kickoff session helped participants better understand sponsor requirements and introduced both parties to the process by which OGC will manage the Testbed. As the largest Research & Development (R&D) Initiatives conducted under OGC’s COSI Program, OGC Testbeds exist at the cutting edge of technology, actively exploring and evaluating future geospatial technologies to solve today’s problems.
Testbeds provide an opportunity to engage with and lead the latest research on geospatial system design, concept development, and rapid prototyping. They also provide a business opportunity for stakeholders to mutually define, refine, and evolve service interfaces and protocols in the context of hands-on experience and feedback. The solutions developed in Testbeds eventually move into the OGC Standards Program, where they are reviewed, revised, and potentially approved as new international Open Standards that can reach millions of individuals.
Testbed-20 will drive innovation at the foundations of geospatial data ecosystems. While working across four tasks, participants will collaborate to create mechanisms that improve Integrity, Provenance, and Trust (IPT) in geospatial data systems and workflows; transform Standards for GEOINT Imagery Media for Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (GIMI); enhance the usability of, and investigate new applications for, GeoDataCubes; and explore options for High-Performance Geospatial Computing Optimized Formats.
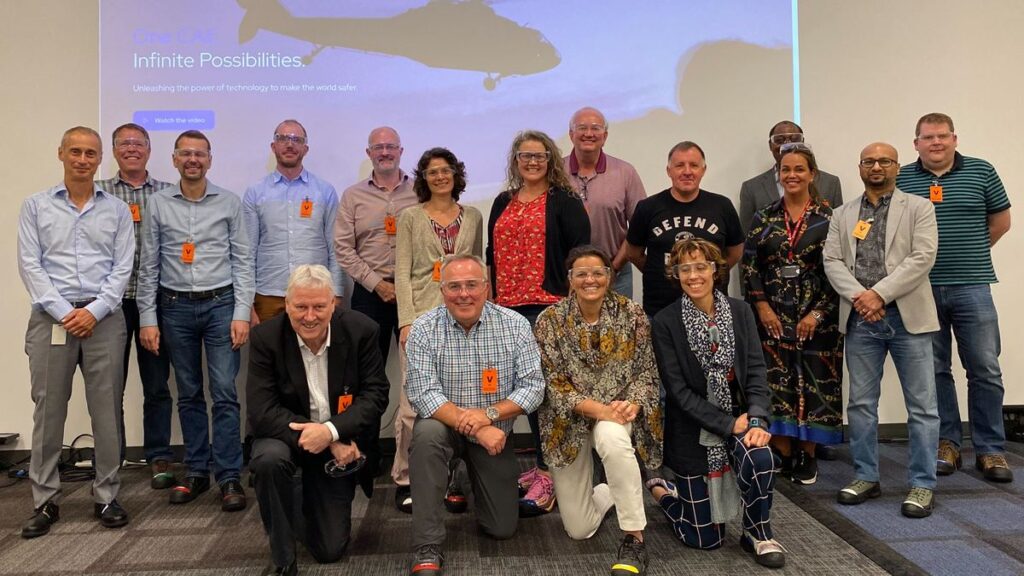 The OGC Executive Planning Committee during their visit to the CAE Factory.
Closing Plenary
The OGC Executive Planning Committee during their visit to the CAE Factory.
Closing Plenary
Wrapping up the week, I opened Thursday’s Important Things session with a rapid, 7-minute summary of the entire meeting week. This presentation was followed by some introductory remarks from Ryan Ahola of Natural Resources Canada to identify issues with Spatial Data Infrastructures (SDIs) and domains requiring geospatial standardization. Member discussion focused primarily on ensuring that SDI planning and management be aware of the larger data ecosystems in which the SDI must exist. This topic then led into a more detailed discussion on the mechanics of communicating how users should look to transition from the legacy OGC Web Services to OGC API Standards, where appropriate. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording, including of the 7-minute overview, on this page in the OGC Portal. Additionally, OGC Members can access as session notes on the “Important-Things-2024-06” Etherpad.
The Closing Plenary then saw a keynote from Jong Tae Ahn of the Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport that briefed the long-term roadmap for spatial information standardization in Korea. The remainder of the session was dedicated to advancing Standardization activities in OGC. Slides and content from a large number of Working Group sessions were included. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
Thank you to our communityAs always, it was such a pleasure seeing our community come together to talk about their recent achievements, learn from each other, and drive innovation and Standards development forward. I sincerely thank our members for investing their time and energy, as well as their dedication to making OGC the world’s leading and most comprehensive community of location experts.
The next OGC Member Meeting is scheduled for November 4-8 in Goyang in the Seoul Capital Area of the Republic of Korea. Join members of the OGC Community to learn about the latest happenings at OGC, advance geospatial standards, network with the leaders of geospatial, and see what’s coming next. Registration will open soon on ogcmeet.org. To hear about it when it opens, feel free to subscribe to the OGC Newsletter – a digest of all things OGC, sent every two weeks.

The post A recap of the 129th OGC Member Meeting, Montreal, Canada appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 Andreas Matheus receives OGC’s 2024 Gardels Award
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)Last night at the 129th Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Member Meeting, held in Montreal, Canada, Andreas Matheus was presented the OGC’s prestigious Kenneth D. Gardels Award. The Gardels Award is presented each year to an individual who has made exemplary contributions to OGC’s consensus standards process. The Gardels Award was conceived to memorialize the spirit of a man who dreamt passionately of making the world a better place through open communication and the use of information technology to improve the quality of human life.
Andreas Matheus, Managing Director at Secure Dimensions GmbH, was selected by previous Gardels Award winners as the 2024 recipient because of his persistent efforts to ensure best practices in security and API design in OGC.
A member of the nominating committee commented that Andreas has “been the go-to security expert for almost as long as OGC has existed.” Another committee member noted that Andreas’ “dedication on security and citizen science has been constant” and that he is “fully focused on promoting OGC solutions and other Standards for security.”
“The OGC Board of Directors thanks Andreas for his work as a chair and active member of many OGC Working Groups and for providing his insight and expertise to several OGC Standards and Collaborative Solutions and Innovation (COSI) initiatives,” commented Prashant J. Shukle, Chair of the OGC Board of Directors. “Your tireless voice of expertise on security matters continues to be critical to OGC activities and exemplifies the values associated with the Gardels Award.”
Andreas Chairs the OGC Security, Citizen Science, and Blockchain & Distributed Ledgers Domain Working Groups as well as the GeoXACML and OWS Common – Security Standards Working Groups. Andreas is also the principal editor for several OGC Testbed Engineering Reports and both the GeoXACML and OWS Web Services Security Standards.
In all this work, Andreas exemplifies the highest values of OGC, and has demonstrated the principles, humility, and dedication in designing, supporting, and promoting spatial technologies to address the needs of humanity that characterized Kenn Gardels’ career and life.
About the OGC Gardels Award
The Kenneth D. Gardels Award is a gold medallion presented each year by the Board of Directors of the Open Geospatial Consortium, Inc. (OGC) to an individual who has made exemplary contributions to OGC’s consensus standards process. Award nominations are made by members – the prior Gardels Award winners – and approved by the Board of Directors. The Gardels Award was conceived to memorialize the spirit of a man who dreamt passionately of making the world a better place through open communication and the use of information technology to improve the quality of human life.
Kenneth Gardels, a founding member and a director of OGC, coined the phrase “Open GIS.” Kenn died of cancer in 1999 at the age of 44. He was active in popularizing the open source Geographic Information System (GIS) ‘GRASS’, and was a key figure in the Internet community of people who used and developed that software. Kenn was well known in the field of GIS and was involved over the years in many programs related to GIS and the environment. He was a respected GIS consultant to the State of California and to local and federal agencies, and frequently attended GIS conferences around the world.
Kenn is remembered for his principles, courage, and humility, and for his accomplishments in promoting spatial technologies as tools for preserving the environment and serving human needs.
More information on the OGC Gardels Award, including previous winners, can be found at: ogc.org/about-ogc/ogc-awards/gardels-awards/The post Andreas Matheus receives OGC’s 2024 Gardels Award appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 Standards Enabling Collaboration For Global Challenges
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is a membership organization dedicated to solving problems faced by people and planet through our shared belief in the power of geography. OGC is one of the world’s largest data and technology consortia and—at 30 years old—one of its longest standing. OGC works with new and established partners and stakeholders to develop and apply accelerated, practical, and implementable solutions to today’s biggest issues, from climate resilience, emergency management, and risk management & insurance, to supply chain logistics, transportation, and health care and beyond.
OGC holds regular member meetings across the globe where geospatial professionals convene to develop standards and advance innovation initiatives led by OGC Members. Most sessions are open to the public and offer valuable opportunities to network with leaders from industry, academia, and government, define future technology trends, and contribute to the open geospatial community.
OGC’s 129th Member Meeting will be held in Montreal, Canada, from June 17–22, 2024. The event kicks off OGC’s 30th anniversary celebrations and carries the theme ‘Standards Enabling Collaboration for Global Challenges.’ Support for the meeting comes from OGC Strategic Member Natural Resources Canada, with additional support from Esri Canada, CAE, Safe Software, and dinner sponsor Bentley Systems.
Eric Loubier, Director General of the Canada Centre for Mapping and Earth Observation at Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) will open the week with a keynote, followed by a 30-year Canadian retrospective by OGC Board Chair Prashant J. Shukle.
“The 129th Member Meeting provides a great opportunity to hear from our incredible Canadian partners and community,” said OGC CEO Peter Rabley. “Some of OGC’s earliest—if not our first—and longest-running supporters have been Canadians and Canadian firms. Our keynote from Eric Loubier and the exciting 30-year Canadian retrospective by Prashant Shukle will serve well to kick off the week’s exciting sessions and discussions.”
“Throughout the 30 years of OGC’s history, Canadians have played a foundational role,” said OGC Board Chair Prashant J. Shukle. “My friend and mentor Dr. Bob Moses, who founded PCI Geomatics, was one of OGC’s first funders and a long-time supporter of OGC. As an emergency room doctor, Bob saw the power of new technologies and data. Critically, he understood that technologies had to work together seamlessly and effectively to really address complex problems.
“Like Bob, many other Canadians instantly saw the powerful role and impact that OGC could have, and I am constantly amazed at their leadership and vision. It is my privilege to honor those Canadians who have gone almost unnoticed here in Canada, but who have fundamentally changed how the world uses technology across so many industries.”
Other highlights of the week will include a Methane Summit, a meeting of the OGC Canada Forum, the popular Future Directions session (this meeting’s topic is AI), as well an abundance of working group sessions on diverse topics such as marine, climate & disaster resilience, and beyond.
The Methane Summit is organized by Steve Liang, Professor and Rogers IoT Research Chair at the University of Calgary and Founder and CTO of OGC Member SensorUp. Steve is spearheading this summit to tackle the critical global challenge of monitoring and tracking methane emissions. The event will feature speakers from McGill University and Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC), who will discuss the challenges and opportunities of data management in methane emissions management. Attendees will also be introduced to the Methane Emissions Modeling Language (MethaneML)—a new tool designed to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of methane emissions tracking & reduction. This summit promises to be a significant step forward in our collective efforts to address climate change through innovative data solutions.
The meeting of the OGC Canada Forum is scheduled for June 17 & 18. The Canada Forum is open to all Canadian organizations, regardless of OGC membership status. The sessions have the aim of facilitating collaboration to address Canada’s geospatial needs through capacity building, innovation, standards, and economic growth. Cameron Wilson, Project Manager at Natural Resources Canada (NRCan), will delve into the history, progress, and future priorities of the forum, highlighting key issues crucial for the Canadian community.
Another highlight of the Forum will be a debate addressing the topic: In an era of ever-increasing data availability, there is a pressing need for digital interoperability to solve today’s biggest problems through rapid innovation. Standards only slow this down and are therefore no longer necessary. Debaters include Ed Parsons, Geospatial Technologist at Google, the aforementioned Steve Liang, Will Cadell, CEO of Sparkgeo, and Bilyana Anicic, President of Aurora Consulting. This session promises to offer diverse perspectives on the role that standards can, should, or won’t play in today’s rapidly evolving geospatial landscape.
This meeting’s Future Directions session, held Tuesday morning, is all about AI, with presentations and a panel from Bentley Systems, GeoRoundtable/IEEE GRSS, makepath, and TerraFrame.
Participation in the 129th OGC Member Meeting is welcomed both in-person and remotely. This event is an exciting opportunity to engage in sessions that celebrate three decades of geospatial collaboration and innovation. Attendees will have the chance to learn from, and network with, leading experts from around the world.
Register now for the 129th OGC Member Meeting to be part of OGC’s continued efforts to advance location data and technology and collaboratively address critical global challenges.
The post Standards Enabling Collaboration For Global Challenges appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 Registrations Open for OGC’s July 2024 Open Standards Code Sprint
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) invites developers and other contributors to the July 2024 Open Standards Code Sprint, to be held from July 10-12 in London and online. Participation is free and open to the public, with travel support funding available to select participants. Sponsorship opportunities are also available.
The Code Sprint is sponsored by OGC Principal Member Google at the Silver Level, with additional Strategic Member support from Natural Resources Canada (NRCan).
This will be a collaborative and inclusive event to support the development of open Standards and applications that implement those Standards. All OGC Standards are in scope for this Code Sprint, including OGC API Standards. The Sprint will feature three special tracks on Data Quality & Artificial Intelligence, Validators, and the Map Markup Language (MapML).
OGC Code Sprints experiment with emerging ideas in the context of geospatial Standards and help improve interoperability of existing Standards by experimenting with new extensions or profiles. They are also used for building proofs-of-concept to support standards development activities and the enhancement of software products.
Non-coding activities such as testing, working on documentation, or reporting issues are welcome during the Code Sprint. OGC Sprints also provide an opportunity to onboard developers that are new to OGC Standards, through the sprints’ mentor streams.
Organizations are invited to sponsor the Code Sprint. A range of packages are available offering different opportunities for organizations to support the geospatial development community while promoting their products or services. Visit the Event Sponsorship page for more information.
A one-hour pre-event webinar will take place at 14:00 BST (UTC+1) on June 13. The webinar will outline the scope of work for the Code Sprint and provide an overview of the specifications that will be its focus. The pre-event webinar will take place on OGC’s Discord server.
Travel Support Funding is available for selected participants. Participants interested in receiving travel support funding should indicate their interest on the registration form. Any participant applying for funding will need to submit their registration form by June 30. Applicants will be notified within 2 weeks of their application whether travel support will be available to them or not.
The code sprint will begin with an onboarding session at 09:00 (UTC+1) on July 10, and ends at 17:00 (UTC+1) on July 12. Registration for in-person participation closes at 17:00 (UTC+1) on July 3. Registration for remote participation will remain open throughout the Code Sprint.
Registration is available on the July 2024 Code Sprint website. To learn more about future and previous OGC code sprints, visit the OGC Developer Events Wiki, the OGC Code Sprints Website, or join OGC’s Discord server.
The post Registrations Open for OGC’s July 2024 Open Standards Code Sprint appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 12:45
12:45 OGC announces Peter Rabley as new CEO
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce the appointment of Peter Rabley as OGC’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO). The announcement was made last night at the Geospatial World Forum 2024 in Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
Peter brings to OGC a wealth of experience from the private, governmental, and not-for-profit sectors, including in venture financing, and in developing and implementing scale-up strategies for international not-for-profits.
“I am excited and honored to be appointed as OGC’s CEO,” said Peter Rabley. “OGC is well positioned to build on its incredible 30 year legacy by responding to the ever-increasing rate of change seen in technology and society alike. Opportunities and challenges have never been more apparent and I see tremendous potential for growth in new markets around the globe. This is the time of geospatial.”
“I am particularly excited to have Peter leading OGC,” commented Prashant Shukle, Chair of the OGC Board of Directors. “Peter has a proven track record in the public, private, and not-for-profit areas of the geospatial industry, and closely aligns with what our key stakeholders and partners were telling us they wanted in a CEO. The OGC Board took the time to get this selection right, and we are very excited about how Peter fits with our plans for a reinvigorated and repositioned OGC.”
Peter’s appointment to CEO is timely, with it coming during OGC’s 30th anniversary year—a time when OGC is taking stock of its successes while modernizing to respond to a global economy that increasingly uses geospatial technologies across so many domains and applications.
The OGC is one of the world’s largest data and technology consortia and one of its longest standing. Under Peter’s leadership, OGC will work with new and existing partners and stakeholders to bring accelerated, practical, and implementable solutions to our community.
About Peter Rabley
Peter Rabley is a technology executive, investor and geographer. He has spent the last thirty years creating and operating geospatial businesses that map the earth to improve lives and protect the resources of our planet. Prior to OGC, Peter Rabley co-founded PLACE, a non-profit data trust that makes mapping more accessible and affordable so that decision makers have the data they need to improve the places around them. At PLACE, Peter was responsible for strategy and managing the organization’s investment portfolio. Before PLACE, Peter was a venture partner at leading impact investing firm Omidyar Network, where he led the Property Rights initiative.
Peter has built various businesses including ILS, an enterprise software firm that provided property taxation, registration and mapping solutions to governments globally. After its acquisition by Thomson Reuters, he became Vice President for Global Business Development and Strategy at Thomson Reuters.
Peter remains on the board of PLACE. He also serves on the board of the Radiant Earth Foundation, Meridia, and Microbuild. He is a Fellow of the Royal Geographical Society and the Royal Society of Arts. Peter graduated from the University of Miami with a B.A. in Geography and Economics and an M.A. in Geography. Peter Rabley (L) on stage at Geospatial World Forum 2024 with OGC Board Members (L-R) Zaffar Sadiq Mohamed-Ghouse, Rob van de Velde, Chair Prashant J. Shukle, Frank Suykens, and Deborah Davis.
Peter Rabley (L) on stage at Geospatial World Forum 2024 with OGC Board Members (L-R) Zaffar Sadiq Mohamed-Ghouse, Rob van de Velde, Chair Prashant J. Shukle, Frank Suykens, and Deborah Davis.The post OGC announces Peter Rabley as new CEO appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 1:32
1:32 A recap of the 128th OGC Member Meeting, Delft, The Netherlands
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)Two records were broken in Delft this March: not only was OGC’s 128th Member Meeting our biggest ever – with over 300 representatives from industry, government, and academia attending in-person (and over 100 virtual) – but the meeting also saw a record number of motions for votes on new Standards, highlighting the very productive activities undertaken by the OGC community in recent months.
Held in Delft, Netherlands from 25-28 March, 2024, OGC’s 128th Member Meeting brought together global standards leaders and geospatial experts looking to learn about the latest happenings at OGC, advance geospatial standards, and see what’s coming next. Hosted by TU Delft and sponsored by Geonovum with support from GeoCat and digiGO, the overarching theme for the meeting was GeoBIM for the Built Environment.
As well as the many Standards and Domain Working Group meetings, the 128th Member Meeting also included a Land Administration Special Session, a Geospatial Reporting Indicators ad hoc, a Data Requirements ad hoc, the OGC Europe Forum, an Observational Data Special Session, two Built Environment sessions subtitled The Future of LandInfra and What Urban Digital Twins Mean to OGC, a public GeoBIM Summit, a Quantum Computing ad hoc, and the usual Monday evening reception & networking session and Wednesday night dinner.
The dinner was held at the historic Museum Prinsenhof Delft, former residence of William of Orange, and – grimly – where he was assassinated. On a lighter note, during the dinner Ecere Corporation, represented by Jérôme Jacovella-St-Louis, received an OGC Community Impact Award for their tireless work in driving OGC Standards forward. Congratulations Ecere and Jérôme!
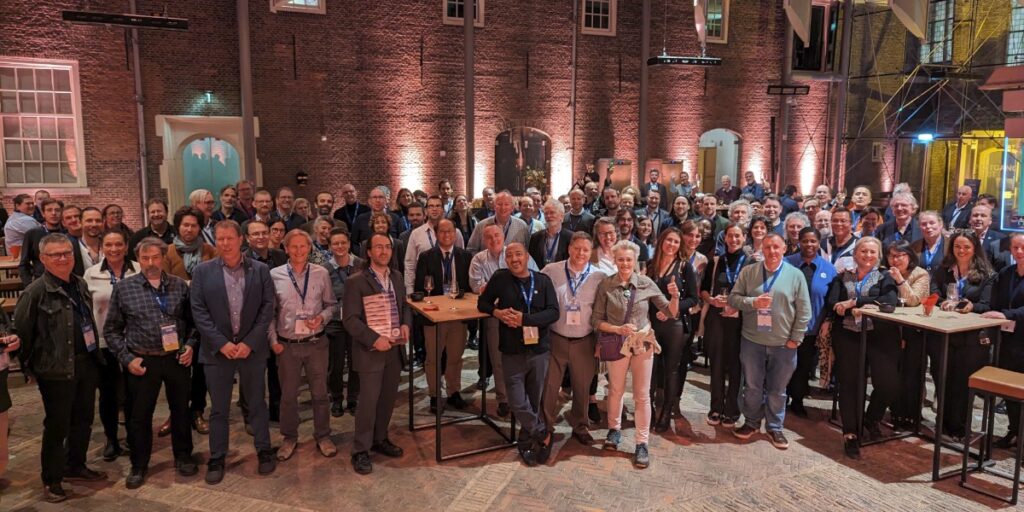 Attendees of the Wednesday night dinner at OGC’s 128th Member Meeting.
Attendees of the Wednesday night dinner at OGC’s 128th Member Meeting.
Also during the meeting members of the OGC GeoPose and POI SWGs in collaboration with the Open AR Cloud team and XR Masters, and support from Geonovum demonstrated interoperable AR browsers. The two AR browsers (one native app, MyGeoVerse by XR Masters, and spARcl, a WebXR-based browser) were able to share/see the same POIs while being geolocalized using the Augmented City Visual Positioning Service (VPS). The VPS receives requests from (and returns) ‘GeoPoses’ to any OGC-compliant app that has implemented the GeoPose standard. The project details are described on this page and captured in this two minute video on YouTube.
In tandem with the theme of GeoBIM, two other technology areas stood out during the meetings: Data Spaces, and the transition from OGC Web Services to OGC APIs.
Data SpacesThere has lately been a dramatic increase in the number of discussions on Data Spaces, both in and outside of OGC, as the concept becomes more commonplace in European projects and policy. As per the European Union Data Spaces Support Centre, a Data Space is defined as “an infrastructure that enables data transactions between different data ecosystem parties based on the governance framework of that data space.” In other words, the “space” in a Data Space defines a context for which the data are useful: a container, governance, and access. Given the ubiquitous use of geospatial data, directly and indirectly, an understanding of the Data Space ecosystem may be key to participate in emerging data infrastructures.
OGC Web Services to OGC API transitionThe full set of capabilities offered by the OGC Web Services Standards (e.g., Web Map Service (WMS), Web Feature Service (WFS), etc.) is now reflected in OGC API Standards that have either been published, are approaching final approval vote, or are being actively developed. Over the coming months, OGC will establish a process and resources to aid in the transition to the more modern Standards, while ensuring that the user community recognizes that the legacy web services are still functional and valuable.
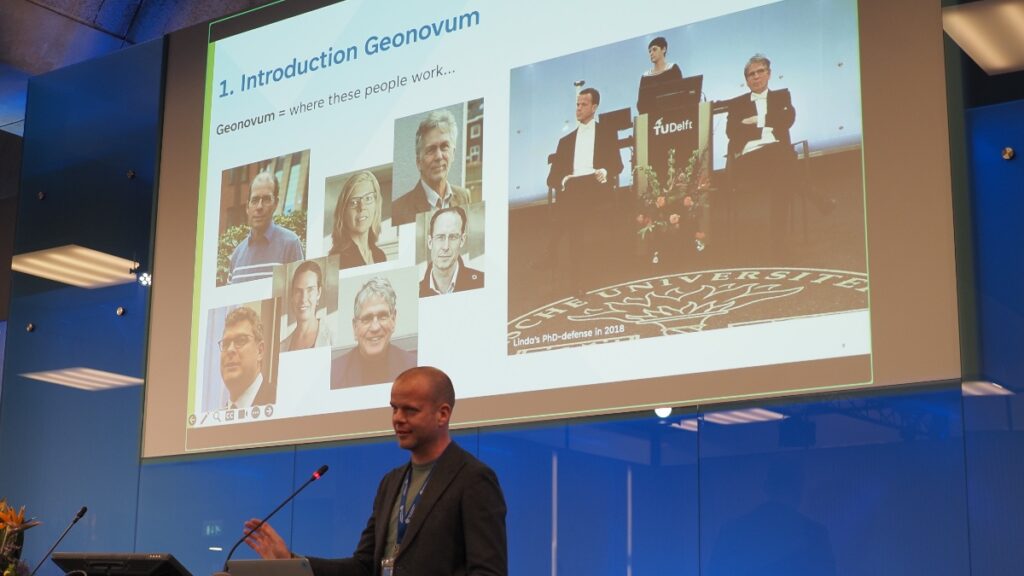 Friso Penninga, CEO of Geonovum, opens the week with an introduction to Geonoum and Delft.
Opening Session
Friso Penninga, CEO of Geonovum, opens the week with an introduction to Geonoum and Delft.
Opening Session
The week opened with a welcome from Friso Penninga, CEO of Geonovum, who outlined not only the work of Geonovum, but also the culture of Delft. Following this, Prof. Jantien Stoter of 3Dgeoinfo, TU Delft highlighted activities at TU Delft in the meeting theme area and previewed Wednesday’s GeoBIM Summit. Pieter van Teeffelen of digiGO then presented a Dutch platform for digital collaboration in the built environment. Finally, Jeroen Ticheler of GeoCat explained challenges in social welfare and the work of the GeoNetwork to address these challenges.
Next, it was time to settle a long-running dispute in OGC: who has the better chocolate, Switzerland or Belgium? After a blind taste-test, the audience voted Belgium as the winner. Is the debate now settled? Only time – and perhaps our taste buds – shall tell.
The chocolate contest was followed by a demonstration of the Netherlands Publieke Dienstverlening Op de Kaart (PDOK) geodata platform, which integrates a number of published and draft OGC API Standards.
Special tribute was then paid to two instrumental figures in OGC’s history who passed away in November 2023: Jeff de la Beaujardiere (OGC Gardels and Lifetime Achievement Awards recipient) and Jeff Burnett (former OGC Chief Financial Officer).
 Prof. Jantien Stoter of 3Dgeoinfo, TU Delft, offered a preview of Wednesday’s GeoBim Summit during the Opening Session.
Today’s Innovation, Tomorrow’s Technology, and Future Directions
Prof. Jantien Stoter of 3Dgeoinfo, TU Delft, offered a preview of Wednesday’s GeoBim Summit during the Opening Session.
Today’s Innovation, Tomorrow’s Technology, and Future Directions
As always, the popular Today’s Innovation, Tomorrow’s Technology, and Future Directions session runs unopposed on the schedule so that all meeting participants can attend. At this Member Meeting, the session was presented by Marie-Françoise Voidrot and Piotr Zaborowski of OGC’s Collaborative Solutions and Innovation Program (COSI). The session focused on several projects that OGC is participating in and are developing capabilities that will be of use to all members. Many of these projects are sponsored by the European Union to advance interoperable science and data management and are supporting OGC resources such as the OGC RAINBOW registry, GeoBIM integration, and learning and developer resources, such as the Location Innovation Academy.
OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording from the session on this page in the OGC Portal. An overview of some of the European projects highlighted during the session, entitled European Innovation, Global Impact, was published on the OGC Blog last year.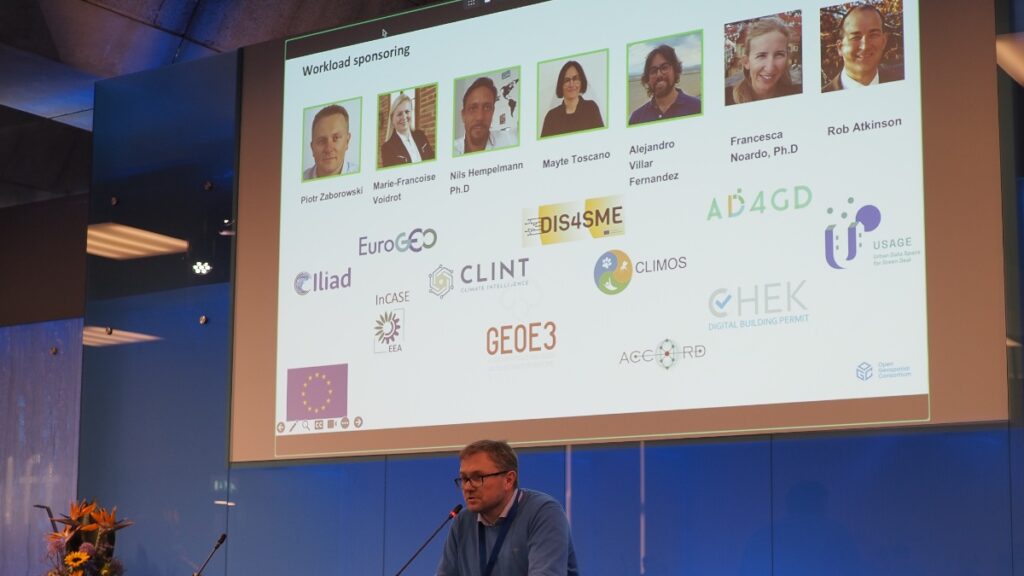 Piotr Zaborowski, Senior Director, of OGC’s Collaborative Solutions and Innovation Program, presents some of the European Union funded projects in which OGC is involved.
Meeting Special Sessions
Piotr Zaborowski, Senior Director, of OGC’s Collaborative Solutions and Innovation Program, presents some of the European Union funded projects in which OGC is involved.
Meeting Special Sessions
The Land Administration Special Session was dedicated to updating OGC membership on the progress of Land Administration activities amongst members and in ISO/TC 211, where the Land Administration Domain Model (LADM) is managed. A new Land Administration Domain Model Standards Working Group (SWG) is being considered to create Part 6 of LADM: the encoding of Parts 1-5 in one or more formats. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording here (Session 1) and here (Session 2) in the OGC Portal.
Geospatial Reporting Indicators have been discussed in the OGC Climate Resilience Domain Working Group (DWG) in the context of Land Degradation. However, the means to exchange indicator information reporting the degree of land degradation (or influencing factors) is not standardized in the community. OGC members are therefore proposing a new SWG to develop such standardized reporting indicators, possibly as extended functionality of work in Analysis Ready Data (ARD). OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
An ad hoc session on Geospatial Data Requirements was held to assess the chartering of a new SWG. The purpose of this proposed SWG is to develop a Standard for describing what geospatial data a project or task needs to collect, store, analyze, and present to achieve the project objectives. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The OGC Europe Forum met on Tuesday with presentations focused on Data Spaces: understanding the European Commission principles of data spaces and how OGC members can engage in the topic. The Forum featured speakers from the International Data Spaces Association (IDSA), ISO/TC211, and the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre (JRC) as well as an open panel discussion. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
 Peter van Oosterom, from TU Delft and the co-chair of the OGC Land Administration DWG, presents during the Land Administration Special Session.
Peter van Oosterom, from TU Delft and the co-chair of the OGC Land Administration DWG, presents during the Land Administration Special Session.
The Observational Data Special Session was organized to identify the various OGC Working Groups that are building Standards or assessing the collection & use of observational data. The session clarified the commonalities between these WGs so they can be considered in future development of observational data Standards. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
Two sessions were held to discuss and prioritize the next steps for OGC activities concerning standardization in the Built Environment. The first of these sessions focused on the future development of the LandInfra suite of Standards: whether priority should be made on new encodings, new Parts, or other tasks. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The second Built Environment session considered the topic of what Urban Digital Twins mean to OGC. Presentations on human engagement as sensors and the place for digital twins in data spaces were followed by a preview of the OGC Urban Digital Twins Discussion Paper and a panel of OGC specialists to discuss where Urban Digital Twins are most important in OGC. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The public GeoBIM Summit emphasized the theme of this meeting: there is a great amount of continuity between the geospatial and Building Information Modeling (BIM) communities and their respective technologies and practices. Numerous rapid presentations highlighted activities using OGC and BIM Standards and use-cases for interoperability. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal. Presentations and recordings will soon be made available to the public on the GeoBIM Summit event page.
The Quantum Computing ad hoc session included open discussion from OGC Members working with or researching the application of quantum computing technology on geospatial issues. Future ad hoc meetings are planned to move towards the development of an OGC Quantum Computing Working Group.
Closing PlenaryThe Closing Plenary normally includes two sessions: an open discussion of Important Things suggested by members, followed by motions, votes, and presentations from members to advance the work of the Consortium. However, with the Member Meeting being compressed down to four days (as Friday was a regional holiday) the Important Things discussion was not held. As such, I opened the Closing Plenary with a rapid, 7-minute summary of the entire meeting week, which included Slides and content from a large number of the week’s Working Group sessions, available to OGC Members on this page in the OGC Portal. The Closing Plenary included a record number of motions for votes on new Standards, highlighting the very productive activities of OGC members in recent months.
Thank youOur 128th Member Meeting was our biggest yet. As always, it’s a pleasure to see hundreds of OGC Members get together to discuss, collaborate, and drive technology and standards development forward. Once again, a sincere thank you to our members for investing their time and energy, as well as their dedication to making OGC the world’s leading and most comprehensive community of location experts.
Be sure to join us at Centre Mont-Royal in Montreal, Canada, June 17-21, 2024, for our 129th Member Meeting. Registration is open now on ogcmeet.org. Sponsorship opportunities remain available – contact OGC for more info.
To receive a digest of the latest OGC news in your inbox every two weeks, be sure to subscribe to the OGC Newsletter.
The post A recap of the 128th OGC Member Meeting, Delft, The Netherlands appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 12:43
12:43 Ecere Corporation receives OGC Community Impact Award
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) has announced Ecere Corporation, represented by Jérôme Jacovella-St-Louis, as the latest recipient of the OGC Community Impact Award. The award was presented last night at the Executive and VIP Dinner of the 128th OGC Member Meeting in Delft, The Netherlands.
The Community Impact Award is given by OGC to highlight and recognize those members of the OGC Community who, through their exceptional leadership, volunteerism, collaboration, and investment, have had a positive impact on the wider geospatial community.
Gobe Hobona, OGC Director of Product Management, Standards, commented: “Jérôme and colleagues from Ecere have been active participants of most OGC Code Sprints over the past five years, as well as contributors to several activities of Standards Working Groups. Their willingness to assist other participants during Code Sprints has helped to get many participants up to speed and to boost the work of the Code Sprints’ community of experts.
“Jérôme has also been a steadfast advocate of OGC Standards for symbology and portrayal, as demonstrated by his engagement of the cartographic community on the next generation of OGC web mapping and portrayal Standards. This engagement has facilitated the collaboration between the OGC and its partner communities in the cartographic domain.”
“Jérôme has been a key enabler for the implementation of OGC Standards,” added Joana Simoes, OGC Developer Relations. “Besides providing extremely complete implementations in GNOSIS, which can be used by others as a reference, he has always been available to help other projects – both online through Github and in-person during Code Sprints. Many OSGeo projects have improved their standards support thanks to GitHub issues filed or answered by Jérôme.”
Notably, Jérôme is also the Co-Chair of five OGC Standards Working Groups: OGC API – Common SWG, Coverages SWG, Styles & Symbology Encoding SWG, Discrete Global Grid Systems SWG, and OGC API – Tiles SWG. In addition to this, Jérôme is also Co-Editor of the OGC API – Maps, OGC API – Processes – Part 3: Workflows, OGC CDB 2.0 – Part 2: GeoPackage Data Store, and OGC API – 3D GeoVolumes Standards.
Ecere Corporation has, and continues to, make an impact within the OGC Community through their active leadership, collaboration, and engagement across numerous OGC Code Sprints, Collaborative Solutions and Innovation Program (COSI) Initiatives, Working Groups, and Member Meetings.
The OGC Community Impact award highlights the importance of collaboration, volunteering time and energy, advancing technologies and Standards, raising awareness, and helping solve critical issues across the geospatial community. Jérôme and Ecere Corporation exemplify all of these qualities in their tireless work during Code Sprints and across so many Standards Working Groups.
The post Ecere Corporation receives OGC Community Impact Award appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 15:00
15:00 Registration opens for OGC Innovation Days Europe 2024
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that registration is open for OGC Innovation Days Europe. Held in conjunction with FOSS4G Europe 2024, on July 1-2, in Tartu, Estonia, the event will focus on themes of Climate and Disaster Resilience, One Health, and the corresponding Data Spaces. Registration is available here.
OGC Innovation Days Europe seeks to address stakeholders’ and policymakers’ need for digital solutions that can meet their requirements efficiently and in a user-friendly way. To this end, the event will bring internationally leading software development and data management experts together with non-technical experts – such as urban planners, policy makers, economists, and other beneficiaries of geospatial information – to exchange information and learn from each other. The stakeholders’ needs will be discussed and understood in depth while newly developed prototypes will be presented.
OGC is co-organizing Innovation Days Europe with the General Authority for Survey and Geospatial Information (GEOSA, Saudi Arabia) and FOSS4G-Europe.
The European IT landscape is changing rapidly. Several initiatives are underway, such as developing Data Spaces and Digital Twins, supporting the Green Deal, or otherwise trying to integrate the largely heterogeneous IT landscape. What do these mean for the leading challenges of our century? How can these predominantly technologically oriented efforts help with climate change and disaster resilience? Do they support Land Degradation Neutrality?
OGC Innovation Days Europe provides a platform to discuss how current technical efforts can be combined effectively with the necessary governance and policy aspects. What decision processes do we need? What agreements are required for efficient decision processes or homogeneous reporting models for, for example, Climate Change or Land Degradation Neutrality?
Thematic focus: Climate and Disaster Resilience, One Health, and Data Spaces.Achieving climate and disaster resilience and sustainability requires reliable location information on the environment, land, and climate. Generating this information dedicated to the users’ needs is challenging. It needs highly optimized spatial data infrastructures and climate resilience information systems operated within a targeted policy framework and driven by an efficient policy model. Interoperable data pipelines and well-organized data spaces with their data assessment applications, combined with analysis, visualization, and reporting tools, are required to gain the knowledge to enroll climate strategies and actions.
OGC Innovation Days Europe will foster a dialogue between technical experts, decision-makers, and policy experts, with a focus on climate & disaster resilience, one health, the role of data spaces, and the need for modernized knowledge exchange and analysis environments.
OGC Innovation Days Europe supports the shift in IT solutions from being purely technology-oriented to a more holistic approach that better accounts for the various needs of the stakeholders. The event will identify these needs and thus make an essential contribution to improving the direction of future technological developments, supporting operational setups that are driven by efficient governance models and that operate within a solution-oriented policy framework.
OGC Innovation Days Europe 2024 is sponsored by OGC, the General Authority for Survey and Geospatial Information, Saudi Arabia, and the European Commission through the Horizon projects CLINT (GA-101003876), AD4GD (GA-101061001), USAGE (GA-101059950), Iliad (GA-101037643), EuroGEOSec (GA-101134335), CLIMOS (GA-101057690) and other projects of the Climate-Health Cluster.
OGC Innovation Days Europe will run in conjunction with FOSS4G Europe 2024 from July 1-2, in Tartu, Estonia. Learn more and register on the FOSS4G Europe 2024 website.

The post Registration opens for OGC Innovation Days Europe 2024 appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 12:13
12:13 Geo-BIM for the Built Environment
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)OGC holds three Member Meetings each year – one each in Europe, the Americas, and Asia Pacific – where OGC’s Standards Working Groups (SWGs), Domain Working Groups (DWGs), Members, and other geospatial experts meet to progress Standards, provide feedback on initiatives being run by the OGC Collaborative Solutions and Innovation (COSI) Program, hear about the latest happenings at OGC, network with the leaders of the geospatial community, and see what’s coming next. The meetings are open to the public, though there are some closed sessions, and provide a great way to start to get to know – and get involved with – the OGC Community.
The next OGC Member Meeting, OGC’s 128th, will be held at TU Delft on March 25-28, 2024. Fitting for TU Delft and the Netherlands, the theme of the meeting will be ‘Geo-BIM For the Built Environment.’ Meeting sponsorship is generously provided by TU Delft and Geonovum, with support from GeoCAT and digiGO. In the lead up to the event, Geonovum produced a short video highlighting what to expect in Delft.
“In many respects, the Netherlands is the world leader in the use of advanced integration of building data and detailed urban mapping, as well as the use of Open Standards and Open APIs to interface with those data to provide citizen services,” commented Scott Simmons, OGC’s Chief Standards Officer.
“More specifically, TU Delft is a world-leading research institute in Geo-BIM integration, while Geonovum, another meeting sponsor, has done so much to promote the effective use of Open Standards in government & e-government, including documenting proof that Open Standards make things work better, faster, and cheaper.”
Under the theme, the OGC Member Meeting will include several sessions related to the built environment and the integration of Geospatial and Building Information Models (BIM). Such sessions will include: a Geo-BIM Summit that non-members are encouraged to attend; a Built Environment Joint Session; and a Land Administration Special Session.
On top of these, there will be a meeting of the OGC Europe Forum, sessions on Geospatial Reporting Indicators, Observational Data, the ‘Today’s Innovations, Tomorrow’s Technologies’ Future Directions Session, networking opportunities, and the usual host of OGC Working Group meetings on topics ranging from APIs to agriculture, and the sea-floor to space. Most sessions are open to the public, with special encouragement for non-OGC-members to attend the Geo-BIM Summit and any of the Domain Working Group meetings. As always, the opening session will consist of presentations from local organizations that showcase the world-leading geospatial technologies seen in The Netherlands.
 Dr. Rune Floberghagen, Head of the Science, Applications and Climate Department in the Directorate for Earth Observation Programmes, ESA, was one of the local experts that presented at the opening session of the 125th Member Meeting in Frascati, Italy.
Geo-BIM Summit
Dr. Rune Floberghagen, Head of the Science, Applications and Climate Department in the Directorate for Earth Observation Programmes, ESA, was one of the local experts that presented at the opening session of the 125th Member Meeting in Frascati, Italy.
Geo-BIM Summit
The Geo-BIM Summit will run on Wednesday afternoon and will focus on the integration of geographic data and Building Information Models (BIM).
“In the Building Information Modeling (BIM) world, geographical data about the environment of the construction is becoming increasingly important,” said Prof. Dr. Jantien Stoter, Chair of the OGC 3D Information Management DWG, and part of the organizing committee for the Geo-BIM session. “Similarly, in the Geospatial domain, the need for detailed information about buildings is also growing. There are many initiatives to develop solutions that better facilitate this integration, including projects that realize this integration for a specific use case; automated conversion of data between the two domains; methods to georeference BIM files in a standardized and straightforward way; and profiles for standards that establish the integration for specific use-cases. The Geo-BIM session will present such initiatives in order to address the question of “what more is needed to improve the integration?” This will further shape the OGC & buildingSMART Road Map on integration of both domains, and contribute to the best practices currently under development.”
Built Environment Joint SessionTwo sessions on the Built Environment will run on Wednesday morning. The first is entitled “The Future of Land Infra” and will discuss what more we need to do in the standardization of built infrastructure data, in terms of updating, improving or adding to the OGC Standards Portfolio, and will include input from several OGC activities: the Integrated Digital Built Environment (IDBE) subcommittee, LandAdmin DWG, Model for Underground Data Definition and Integration (MUDDI) SWG; and the Geotech Interoperability Experiment, as well as the wider OGC Collaborative Solutions and Innovation (COSI) Program.
The next session is entitled “What Urban Digital Twins mean to OGC” and will focus on the wider work that OGC is doing in the space and how the Digital Twins DWG can help harmonize it. The session will also include a cross-working-group discussion on the in-progress OGC Urban Digital Twins Position Paper, as well as a presentation by Binyu Lei, researcher at the Urban Analytics Lab at the National University of Singapore, entitled “Humans as Sensors in Urban Digital Twins.”
 Attendees at the 123rd Member Meeting in Madrid, Spain.
Land Admin Special Session
Attendees at the 123rd Member Meeting in Madrid, Spain.
Land Admin Special Session
Following the opening session and keynotes on Monday is a Land Admin special session run by the OGC Land Administration (Land Admin) DWG.
“Worldwide, effective, and efficient land administration is an ongoing concern, inhibiting economic growth and property tenure,” commented Eva-Maria Unger, co-chair of the OGC Land Admin DWG. “Only a limited number of countries globally have a mature land information system.”
The Land Admin Special Session will also be the first meeting of the soon-to-be-formed OGC Land Administration Domain Model (LADM) SWG.
“This is a fairly significant session as we’re going to use it to kick off an effort to create an encoding Standard for Land Administration data that’s globally relevant,” said Scott Simmons. “It’s great to be holding it in Delft because Kadaster, the Netherlands’ Cadaster, Land Registry and Mapping Agency, is one of the world leaders in providing expertise on use of Land Administration and Land Administration modernization across not just Europe but for developing nations around the world. So it’s an opportunity to bring together their expertise along with representatives from all levels of sophistication of land management around the world.”
Peter van Oosterom continued: “The new SWG will work on the Land Administration Domain Model (LADM) Implementation Standard in OGC, which will be included as part 6 of the existing ISO 19152 series of Standards. This sounds modest, but is actually a big step forward. The LADM Standards today are only Conceptual Models, which means that countries implementing them have to find their own solutions for developing their country file, technical encodings, code list values, processes/workflows, etc.
“An open LADM Implementation Standard will not only reduce implementation costs by providing free, proven technical encodings, but would also enable solution vendors to provide commercial off-the-shelf software that works across multiple countries/jurisdictions, rather than having to adapt it to each unique approach.”
Networking, social, and other sessionsIn addition to these sessions, the 128th OGC Member Meeting will also see meetings of over 50 different working groups or committees covering almost the full breadth of geospatial applications and domains, as well as several social and networking events.
Registration remains open, as do sponsorship opportunities. Non-members are encouraged to attend. To see the full agenda, visit ogcmeet.org.
 As well as the host of technical content and informative presentations, OGC Member Meetings also include networking events, such as the Wednesday night dinner.
As well as the host of technical content and informative presentations, OGC Member Meetings also include networking events, such as the Wednesday night dinner.The post Geo-BIM for the Built Environment appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 13:58
13:58 Enterprise Products: A Collaborative Journey with OGC
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)In the ever-evolving realm of energy infrastructure, the success of an organization is often determined by its ability to adapt, innovate, and collaborate effectively. Enterprise Products Partners, L.P. has exemplified these qualities through their ongoing relationship with the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC).
Under the leadership of Gary Hoover, Enterprise Products’ team of geospatial technology experts has helped develop an open, international geospatial Standard for the pipeline industry, PipelineML, and deployed disruptive open-source geospatial technology.
Doing so helped Enterprise Products optimize the management of their extensive 50,000-mile pipeline network, and supports the larger goal of safe and sustainable energy infrastructure within the oil and gas sector.
Pioneering the PipelineML StandardEnterprise Products became a voting member of OGC in 2013. Shortly after, Data Architect John Tisdale rolled up his sleeves and got to work, learning OGC’s consensus-based Standards process and serving as a charter member and co-chair of the PipelineML Standards Working Group (SWG). In 2019, the PipelineML Conceptual and Encoding Model Standard was approved by the OGC Membership, making it an official OGC Standard.
The PipelineML Standard – collaboratively developed by Enterprise Products and contributors from across the US, Canada, Belgium, Norway, Netherlands, UK, Germany, Australia, Brazil, and Korea – defines concepts that support the interoperable interchange of data related to oil and gas pipeline systems. PipelineML addresses two critical business use cases specific to the pipeline industry: new construction surveys and pipeline rehabilitation.
The Standard defines individual pipeline components, provides support for lightweight data aggregation, and provides a mechanism for extensions focused on safety and sustainability through effective data management practices. By working with OGC’s Land and Infrastructure Domain Working Group, PipelineML was aligned with related Standards that ensure compatibility with future land management requirements.
 Three use-cases addressed by the OGC PipelineML Standard.
A Step Towards Modernization
Three use-cases addressed by the OGC PipelineML Standard.
A Step Towards Modernization
June 26, 2023, marked a significant milestone in Enterprise Products’ technical history: in partnership with select technology vendors, the company implemented open-source technology to revamp their existing Asset Information Management (AIM) Program.
To move off the legacy PODS data model and a dependence on proprietary software, the Enterprise Products team spent years developing, prototyping, and refining the Pipeline Component Data Model (PCDM). Instead of utilizing an ageing linear referencing methodology, PCDM leverages modern geospatial technologies to gather GPS coordinates in the field that accurately mark the real-world location of pipeline components. This “Digital Twin” approach makes PCDM more adaptable to evolving business requirements.
Emerging from this initiative, the AIM Data Architecture Platform and Development Framework now provides data and services that serve as the lifeblood of the organisation.
The Pillars of Value-addingEnterprise Products’s Asset Data Management group has played a vital role in elevating the company’s performance with contributions that have rippled across the organization to deliver tangible value in several areas:
Standards & GovernanceTo facilitate seamless information exchange across business units and external service providers, Enterprise Products has established stringent data standards and governance protocols that ensure consistent and accurate data for decision-making. By aligning their asset data with OGC Standards, Enterprise Products has established a universal language for geospatial data that simplifies communication and interoperability.
Data IntegrationIncorporating integrated inline inspection data has been pivotal in maintaining the integrity of Enterprise Products’ extensive pipeline network. The AIM Data Architecture Platform functions as a nexus for data integration that enables a seamless flow of information across departments that promotes collaboration and efficiency.
Spatio-temporal AnalyticsThe integration of spatio-temporal analytics has introduced a new dimension to Enterprise Products’ pipeline management. Real-time geospatial insights have not only improved operational efficiency but have also fostered proactive problem solving. By incorporating database-native geoprocessing, Enterprise Products has streamlined analytical workflows and enhanced the speed and accuracy of decision-making.
Data DeliverabilityEnterprise Products has democratized data access within the organization by creating a map-based interface that provides intuitive visualisations and reports that empower stakeholders to make informed decisions. This map-based interface supports over 1200 individual users across various departments, including Asset Integrity, Business Development, Field Operations, and Public Awareness.
Safety and SustainabilitySpanning the pipeline asset life-cycle from new construction to divestitures, the AIM Data Architecture supports several Safety and Sustainability programs that ensure safe, reliable operations. Programs such as Public Awareness, OneCall (aka 811 “Call Before You Dig”), Inline Inspections, Pipeline Rehabilitation, Regulatory Compliance, Integrity Assessments, and Field Operations all depend on highly available asset information.
 Rather than linear referencing, Enterprise Products uses GPS coordinates to accurately mark the real-world location of pipeline components.
Scaling for the Future
Rather than linear referencing, Enterprise Products uses GPS coordinates to accurately mark the real-world location of pipeline components.
Scaling for the Future
The volume, variety, and velocity of data required to manage and optimize large pipeline networks presents substantial challenges. However, Enterprise Products’ open architecture effortlessly manages the scale of their installation and provides ample room for growth. To put this into perspective, consider the following statistics:
- 50,000 Miles of Pipeline
- 2,500 Facilities
- 5.6 million Pipe Components
- 45 million rows of inline inspection data – 30 years’ worth
- 80 million Rows of geospatially referenced data, with 10x better lossless compression over the legacy proprietary system
One of the most striking aspects of Enterprise Products’ journey is their embrace of Open Standards and Open Source technology. The AIM Data Architecture Platform represents a complete departure from proprietary systems. Key standards and technologies used by Enterprise Products include PipelineML, GeoServer, QGIS, PostgreSQL, PostGIS Spatial Extender, Python & other open libraries, and XML, GML, JSON, & GeoJSON encoded schemas.
This strategic shift not only reduced dependence on commercial vendors and licensing costs, but also established Enterprise Products as an industry pioneer that set a new standard for innovation and interoperability.
OGC Membership: A Driving ForceEnterprise Products’ journey is a compelling story of innovation and progress, with the OGC Community playing a pivotal role. Through collaborative efforts and a steadfast commitment to OGC’s consensus-based process, Enterprise Products led the development of the PipelineML Standard that has proven vital to optimizing the management of Enterprise Products’ extensive pipeline network.
Working with OGC has provided Enterprise Products with a significant competitive advantage, allowing them to leverage the collective knowledge and resources of the international geospatial community. Their journey underscores the transformative potential when industry leaders partner with organizations like OGC to drive positive change. As the world continues to seek sustainable and efficient energy infrastructure, Enterprise Products serves as a prime example of what is achievable when technology, data, and partnerships come together.
The post Enterprise Products: A Collaborative Journey with OGC appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:34
16:34 Enhancing capabilities by adopting Standards for emerging technologies
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The pace of technological change is increasing as new products are made available, with ground-breaking innovation often resulting in disruptive change. Coupled with this technological change is the explosion of data from new sources relevant to the geospatial domain, including imagery, sensor feeds, and real-time tracking data. Organisations in the public, private, and third sectors must remain agile and resilient to thrive in this emerging landscape.
Adoption of new technological innovations into large, controlled IT enterprises can be challenging, because of associated costs, integration challenges, and processes. The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is a standards body that, for the last 30 years, has been working to innovate and create community driven Standards in the geospatial domain. These Standards are designed to ensure data and services are Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR), whilst ensuring that the developed Standards are suited to the target domain and straightforward to adopt. FAIR principles can also be applied to the integration of new technologies into large enterprises, to ensure that interaction patterns with new technologies are known, and the components offering the technology are interchangeable.
Standardising AI/ML Training DataAn OGC Standard supporting a decidedly recent phenomenon is the OGC Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence. Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and associated applications have been the subject of research since the 1990s and earlier. However, it is only recently that the necessary computational power and, importantly, the data to train AI models, have been available. Training data is the lifeblood of AI. As the old axiom goes, “garbage in, garbage out” and AI models are no different. Additionally, AI models and their inner workings can be opaque with the ‘black box’ effect on the inputs and outputs. Therefore, standardising the management of training data is important for scientific endeavours, not least for repeatability but also the FAIR principles.
In addition to utilising AI to do typical geospatial and imagery work, we are also seeing AI used to create simulated data for training – or even nefarious purposes. Recording information about the input data to ML models in a standardised manner assists with the management and authenticity of outputs. By way of example, the image below is a completely fictional landscape created using some training data of a UK city and a Generational Adversarial Network (GAN). Standardising the training dataset metadata enables others to create their own simulated data with the same feel, whilst understanding the input parameters and likely outcomes.
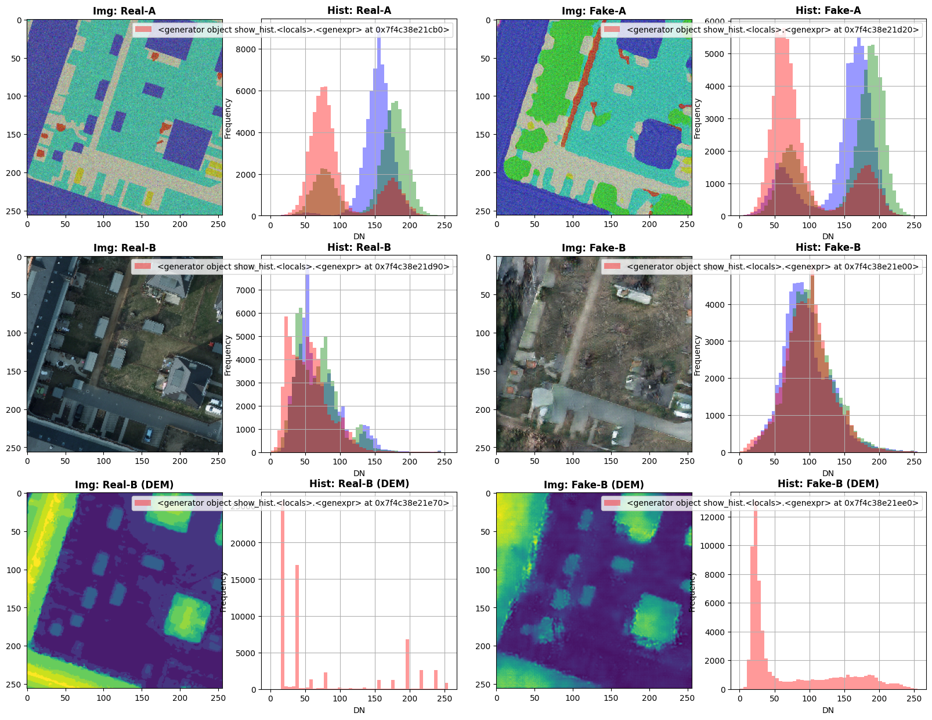 Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing
While AI/ML is one current technology trend that offers a great example of how the technological landscape can change overnight, like with the 2022 release of ChatGPT, another disruptive technology set that has been on the horizon for the past few decades is Quantum Computing.
Although not likely to be a complete replacement for classical computing, quantum computing potentially offers an exponential speed-up to solving problems that are difficult for classical computing to manage. This is not necessarily because quantum computers are faster in the super computing sense, it is that their approach to solving problems is fundamentally different to classical computing. Classical computing operates by manipulating bits that are either in a 1 or a 0 position, chaining enough of these operations together enables computing machines to do useful work. Quantum computers are different in that their fundamental building block is the qubit that can exist in a superposition of both 1 and 0. There are also different types of quantum computing, circuit-based quantum computers are those that can do the headline-grabbing factoring of large numbers and therefore will be able to crack RSA encryption (which is built on the principle that factoring large numbers is hard). The second type of quantum computing is quantum annealing or adiabatic quantum computing that lends itself to solving optimisation problems.
The geospatial domain is full of optimisation problems, a typical example is the Travelling Salesperson Problem where a salesperson is required to visit several geographically dispersed locations with the constraint that they must visit each location once and only once while completing the route with the lowest cost (shortest distance, fastest drivetime). Another optimisation style problem is the Structural Imbalance Problem where an algorithm attempts to split a social network (often with a geospatial element) into friendly groups where, in a balanced graph, all relationships within the groups are friendly, while all the relationships between the groups are hostile. In the real world it is not usually possible to get a perfect result. This highlights relationships that do not fit the model (strained), which can be a predictor of conflict.
Practical quantum computing is now possible, there are several providers such as Rigetti, D-Wave, and the likes of Amazon, Google, and Microsoft who are starting to make their quantum computing resources available via the cloud. Although none of the quantum computers are sizable enough to provide a quantum advantage in the optimisation space, new quantum computers are planned that will be able to. As a stop gap, there are classical/quantum hybrid approaches that offer advantages of quantum computing but can solve practical problems.
As with many emerging technologies, the interaction patterns for these new quantum computers and hybrid solvers have not yet been standardised and are bespoke down to the hardware. The D-Wave system with the Ocean SDK for quantum computing has patterns and calls that cover many of the optimisation style calls that one could use a quantum solver for. Perhaps the next move for the OGC is to understand the impact of quantum computing through a Domain Working Group to support geospatial optimisation-style problems through a group dedicated to quantum computing and the opportunities it affords.
Where next?Keeping a close eye on emerging technologies and getting ahead of the curve, in terms of adoption, enables Standards to be created that assist with integration and can provide meaningful change to organisations. The technology is the exciting piece and can offer untold opportunities, and the quicker and smoother these technologies can be adopted into the organisations that make use of them, the better the return for businesses, users, and citizens. Good, domain-driven Standards-definition is key to a FAIRer technology landscape.
A quantum computing ad-hoc session will be held at 15:30 CET on March 27 , 2024, as part of the 128th OGC Member Meeting in Delft, Netherlands, to discuss the possibility of Standardisation in the Quantum Computing domain.
The overall theme of the meeting is “Geo-BIM for the Built Environment” and will additionally include a Geo-BIM Summit, a Land Admin Special Session, an Observational Data Special Session, a Built Environment Joint Session, a meeting of the Europe Forum, as well as the usual SWG & DWG meetings and social & networking events. Learn more and register here.Sam Meek is the Chief Technology Officer at Helyx Secure Information Systems Ltd.
The post Enhancing capabilities by adopting Standards for emerging technologies appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:00
16:00 Developers invited to the February 2024 OGC API – Coverages Virtual Code Sprint
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) invites developers to the 2024 OGC API – Coverages Virtual Code Sprint, to be held February 13-15, 2024. Registration is free and open to the public.
The Sprint will focus on refining the OGC API – Coverages – Part 1: Core candidate Standard. OGC API – Coverages enables clients to efficiently retrieve a subset of spatiotemporal data for a given time, area, and resolution of interest through a simple Web API.
Typically, this data is returned in a gridded format such as netCDF, GeoTIFF, CoverageJSON, or CIS JSON, although this also extends to other coverage data types, such as point clouds in e.g. LAS/LASZip format, or tiled coverage data. The candidate Standard also supports the listing and retrieving of data and metadata for individual scenes making up a coverage.
Example types of coverages, sometimes called GeoDataCubes, include weather and climate datasets, Earth Observation time series, static environmental data such as digital elevation models, land cover classification, and point clouds obtained from LiDAR capture or photogrammetry. Furthermore, in recent OGC activities, the development of a proposed GeoDataCube API Standard has leveraged OGC API – Coverages as a Core foundation for data access.
An OGC Sprint is a collaborative and inclusive event driven by innovative and rapid programming with minimal process and organization constraints to support the development of candidate standards and applications that implement those standards.
During the virtual code sprint, there will be an opportunity for joint discussion with all participants on the goals and objectives of the event, as well as the final briefing of findings and opinions of the participants. However, the majority of the time will be spent in collaboration between participants in active coding.
To learn more about how the family of OGC API Standards work together to provide modular “building blocks for location” that address both simple and the most complex use-cases, visit ogcapi.org. For more technical information about OGC Standards, including how to get started, links to each Standards’ GitHub page, official Standards documents, compliance, and more, visit developer.ogc.org
The Sprint will take place on GoToMeeting and Discord platforms from 8:00am to 6:30pm (US Eastern) each day from February 13-15, 2024.
For more information on the Sprint, including objectives, agenda, and registration, visit the February 2024 OGC API ? Coverages Virtual Code Sprint wiki page on GitHub. Information on other OGC Sprints or events for developers can be found on the OGC Developer Events wiki on GitHub.
The post Developers invited to the February 2024 OGC API – Coverages Virtual Code Sprint appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:00
16:00 OGC forms new GeoZarr Standards Working Group to establish a Zarr encoding for geospatial data
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce the formation of the OGC GeoZarr Standards Working Group (SWG). The new SWG will develop a Zarr encoding for geospatial gridded data in the form of Zarr conventions.
Zarr is a cloud-native data format for n-dimensional arrays that enables access to data in compressed chunks of the original array. Zarr facilitates portability and interoperability on both object stores and hard disks.
As a generic data format, Zarr has increasingly become popular to use for geospatial purposes. As such, in June 2022, OGC endorsed Zarr V2.0 as an OGC Community Standard. The purpose of the GeoZarr SWG is to have an explicitly geospatial Zarr Standard (GeoZarr) adopted by OGC that establishes flexible and inclusive conventions for the Zarr cloud-native format that meet the diverse requirements of the geospatial domain. These conventions aim to provide a clear and standardized framework for organizing and describing data that ensures unambiguous representation.
The objectives of GeoZarr conventions include:
- Compatibility: Ensuring easy compatibility with popular mapping and data analysis tools such as GDAL, Xarray, ArcGIS, QGIS, and other visualization tools, enabling seamless integration into existing workflows.
- Dimensions: Supporting multi-dimensional data, such as hyperspectral and altitude information, to address diverse geospatial data requirements.
- Data Discovery: Providing metadata for discovering, accessing, and retrieving the data, including composite products made of multiple data arrays.
- Mixing Data: Facilitating the combination of different types of geospatial data, including satellite images, elevation maps, and weather models, to create comprehensive and informative datasets.
- Flexibility: Allowing scientists and researchers to work with diverse data types and projections in their preferred software and programming languages, promoting flexibility and adaptability in geospatial data processing and analysis.
In addition to the encoding of geospatial data and metadata, the GeoZarr Standard will provide a multi-dimensional alternative to the two-dimensional Cloud-Optimized GeoTiff format (COG – adopted by OGC in May 2023), which has lately gained popularity due to its serverless capabilities. These capabilities will allow for inherent support of traditionally server-based functions, such as visualization (similar to OGC API – Maps), data subset access (analogous to OGC API – Coverages), and symbology (equivalent to OGC API – Styles). These aspects are planned to be incorporated as optional profiles (e.g. conformance classes).
OGC Members interested in staying up to date on the progress of this standard, or contributing to its development, are encouraged to join the GeoZarr Standards Working Group via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about participating in this SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
The post OGC forms new GeoZarr Standards Working Group to establish a Zarr encoding for geospatial data appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 12:44
12:44 Insights from Innovation Days 2023
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)At the end of another year of prototyping software, experimenting with data access, and debating how to overcome geospatial technology’s many challenges, teams from OGC member organizations gathered in Washington DC to share 2023’s work and help OGC decide what challenges we should address in 2024.
Representatives of government agencies and industry – from FEMA and Natural Resources Canada, to Intact, Canada’s largest insurer – highlighted their successes, current needs, and aspirations. Through panel discussions, demos, and conversations over coffee, teams from startups, like FloodMapp and Navteca, to established industry players, like Bentley Systems and GDIT, shared what they could do to meet today’s needs and shape the tools and systems we’ll be using next.
Here are three key takeaways learned from listening in:
- While looking at maps is the obvious way to interact with spatial data, advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI) mean that a conversation with a map may become normal. Though what this change implies is less clear.
- Sensors, surveys, and citizens continue to produce data at scale. Different approaches – from indexing and cataloging to tagging and the semantic web – help us navigate this endless sea of data, yet too often unable to find the right data when we need it.
- If we were to add another ‘A’ to the FAIR Principles, it might stand for ‘Actionable.’ Even when you can find the data you need, access it, and combine it with other data, robust methods for transforming all that data into actionable intelligence remain limited. The push for organizations to report on how their data supports their decisions may, in 2024, drive collaboration on Standards for describing chains of modeling, inference, and reasoning.
 Moderator Eldrich L. Frazier (FGDC and panelists Ryan Ahola (NRCan), Matt Webster (Barbaricum) Tom Landry (Intact Financial Corporation) and Jim Antonisse (WiSC) discuss the transformative power of Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI).
AI is changing how we interact with maps and spatial data
Moderator Eldrich L. Frazier (FGDC and panelists Ryan Ahola (NRCan), Matt Webster (Barbaricum) Tom Landry (Intact Financial Corporation) and Jim Antonisse (WiSC) discuss the transformative power of Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI).
AI is changing how we interact with maps and spatial data
Following the late 2022 public launch of ChatGPT, “AI” became mainstream in 2023 – and its applications in geospatial broadened. This was clear at Innovation Days 2023.
In the early 2020s, excitement around AI in the geospatial tech community centered around automating the laborious process of identifying the important objects in satellite images and pulling out key data points from large datasets. This transformed the work of many geospatial analysts and developers, as noted by AI Panel chair Rich Frazier (USGS), but had limited impact on how most people interact with maps and spatial data. The panel’s conversation on AI centered on the potential consequences of our newfound ability to speak to an AI tool and ask it to create a map or run a spatial analysis.
Many of us are already doing this in specific contexts, such as asking your phone for driving directions, but advanced spatial analysis still requires mice and menus. This is why Natural Language Processing (NLP) felt like such a breakthrough in 2023. First, it has the potential to bypass specialized software and technical language and almost remove the barrier to entry for harnessing geospatial data. It’s therefore no surprise that NLP featured in several presentations, including those by Navteca co-founder Shayna Solis and Voyager Search’s founder Brian Goldin. Additionally, it might let developers and analysts operate more efficiently and create better products. As highlighted by Matt Webster of Barbaricum, who paraphrased economist Richard Baldwin from his presentation at the May 2023 World Economic Forum’s Growth Summit, “AI won’t take your job, but someone using AI will.” The specialist using NLP AI technology has another tool to deploy and they’re likely to use it to their advantage.
 Shayna Solis, CEO & Co-founder of Navteca demonstrated using Conversational AI to interact with geospatial data for disaster response.
Shayna Solis, CEO & Co-founder of Navteca demonstrated using Conversational AI to interact with geospatial data for disaster response.
The takeaway is that the current stage of AI not only democratizes access to geospatial information but also enhances user experience and engagement – if we can learn to ask the right questions with the right words. This is the sticky part of the problem. If geospatial really is in everything, there’s a diverse set of questions (aka prompt engineering) for us to teach the NLP AIs to understand. The organizations who gathered at Innovation Days 2023 might start building lots of one-task NLP tools, proliferating the “driving directions” application, or aim for more general ways of describing our mapmaking aims when we speak with an AI tool. Either way, this area looks set for a busy 2024.
Finding the right data when we need it is still too hard“When it comes to asset-scale climate resilience planning, most people don’t want data, they want data-based answers to key questions. Our challenge is helping them extract actionable intelligence from our data in the form of plain-language answers to their questions.”
David Herring, Communication, Education and Engagement Division Chief – NOAA Climate Program Office.A common refrain at Innovation Days 2023 was the ongoing difficulty surfacing the ‘right data’ when it’s needed. Scott Kaplan (USGS, Civil Air Patrol) spoke about the critical need for the ‘right data’ to support crews fighting wildfires. Kasie Richards (American Red Cross) called out the need for the ‘right data’ for planning for future patterns of extreme weather events that will look different from the past. Tom Landry (Intact) pointed to the need to enable public-private partnerships that could make the ‘right data’ held by private entities discoverable and usable for applications that benefit the public.
Catalogs, indexes, semantic knowledge organization systems, and machine-readable metadata systems have proliferated as organizations attempt to keep pace with the growth in data, but the conversations among panelists suggest that these approaches haven’t solved the problem – and it’s worsening as more data is generated.
Alan Lediner (NYC GISMO) characterized the inability to ask for and find what we need in all this data as a “communication problem.” This framing links what we’re stuck on (finding the right data) to where we’re moving toward (using natural language prompts) but requires (again) that we figure out how to describe what we mean when we say ‘the right data.’
 Discussions about how to find the right data were threaded throughout the panels at Innovation Days 2023, highlighted by Alan Leidner speaking about data for emergency response.
Discussions about how to find the right data were threaded throughout the panels at Innovation Days 2023, highlighted by Alan Leidner speaking about data for emergency response.
There’s another factor that makes addressing the findability problem particularly urgent for 2024: spiraling costs due to duplication. People often make local copies of data they think they’ll need so that they can later access it quickly and reprocess it on their own infrastructure. Dave Borges (CEOS, NASA) pointed to the unintended consequences of this widespread practice: spiraling financial (and environmental) costs, and, perversely, greater difficulty finding the ‘right’ version of a dataset, as multiple organizations make their own versions of datasets cloud-accessible. It’s hard to see us breaking this habit without creating confidence that other organization’s datasets will be findable (and generally FAIR) when they’re needed. Designs that account for people’s behavior and attitudes toward their data sources may push forward Findability as the organizations gathered at Innovation Days 2023 build the next cloud-native geospatial systems.
Data is actionable when it is accountableResponding to emergencies, preparing for future extreme events, and redesigning infrastructures for resilience in a changing climate are all high-stakes uses of geospatial data and technologies that impact lives and communities. Craig Fugate (FEMA), in his keynote at Innovation Days 2023, emphasized these impacts.
 Craig Fugate, Former Administrator, Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), during his keynote address.
Craig Fugate, Former Administrator, Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), during his keynote address.
Craig encouraged us to think differently about our challenges, suggesting specific changes like taking a “maximum of maximums approach” when formulating an emergency response plan that can quickly scale up the response as an emergency is unfolding. Equally important, in his judgment, were proposed changes to longer term planning and response, such as explicitly considering equity and equality when planning how to deploy resources to prevent disasters or rebuild after they occur. This push for innovation, many years in the making and challenging in its own right, is facing new complications as it intersects with a growing drive for accountability.
Accountability, and the ability to demonstrate that decisions were backed by sound data and reasoning, is emerging as an essential part of decision-making processes – particularly for government and public sector organizations. It’s also supporting new, effective practices because it can allow people and organizations to confidently back the changes made. Synthesizing comments from Shanna McClain (NASA), Norman Speicher (DHS), and Ryan Ahola (NRCan), this in practice means the geospatial community needs to develop methods and systems that allow audits of the complex chains of data, models, tools, and people that inform decisions.
Building these methods and systems will require organizations to grapple with how we express uncertainty, which is only compounded by the growing use of AI tools. One example of how this challenge may play out came from the AI Panel’s discussion on visually representing results in ways that won’t impart false confidence. Juliette Murphy’s (FloodMapp) presentation provided another, highlighting the challenges of getting people to think in terms of probabilities when buying a home in a flood-prone area. Looking to 2024, expect to see considerations of uncertainty and accountability continue to intersect as new geospatial approaches to climate & disaster resilience are developed.
 Juliette Murphy (FloodMapp) discusses the challenges of conveying uncertainty, probability and risk.
What comes next?
Juliette Murphy (FloodMapp) discusses the challenges of conveying uncertainty, probability and risk.
What comes next?
The tendency for geospatial organizations to operate as “Silos of Excellence” was a common theme brought up by several speakers at Innovation Days 2023. The collaborative, consensus-driven approach that underpins all activities at OGC is a proven method for overcoming this challenge. Progress in 2024 will require more collaboration across the community, including between those who use geospatial tools and those affected by the decisions they’re informing. Indeed, how we interact with location data, how we find the geospatial information we need, and how we make data-driven decisions accountable are all issues being tackled by our community through OGC COSI Initiatives, Working Groups, and events. A few to look out for in 2024:
- The OGC Artificial Intelligence in Geoinformatics Domain Working Group (GeoAI DWG) is exploring the implications of natural language processing (NLP) integration with GIS. This public group is broadly focused on fostering collaboration among diverse stakeholders to address gaps and impacts of AI on OGC standards, and is launching a monthly speaker series in early 2024.
- SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC) is a proposed OGC Community Standard that conforms to OGC APIs and provides an interoperable metadata framework that simplifies the process of finding and using geospatial assets from different providers. In 2024, multiple OGC Code Sprints will continue to give our community a platform to collaborate on emerging OGC and Community Standards and implementations.
- Trust is an essential component of producing actionable geospatial intelligence. As the push continues towards interoperable tool chains for modeling, inference, and reasoning, Standards such as OGC Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence (TrainingDML-AI) can improve trustworthiness by formalizing how modeling training data is prepared, including data provenance and quality. The Training Data Markup Language for AI Standards Working Group will continue this important work in 2024.
- The Climate and Disaster Resilience Pilot will kick off in Spring 2024, continuing to prototype new Standards-based tools, models, and methods for critical applications – from building warning systems that support natural disaster response to integrating Climate models into emergency management planning. There’s still time to apply to participate and receive funding to address these critical challenges.
By necessity, this blog is only able to cover a small snapshot of the many discussions, insights, and conversations resulting from OGC Innovation Days 2023. A big thank you goes out to all the presenters, panelists, attendees, and other OGC community members that helped make it such a success.
We look forward to seeing many of our community members at the 128th OGC Member Meeting in Delft, Netherlands, March 25-29, and later at OGC Innovation Days 2024.
Want to join the conversation around collaboration and innovation across geospatial data and technologies? Contact OGC or sign up to the OGC Newsletter to hear about upcoming events, funding opportunities, and the latest geospatial Standards.
The post Insights from Innovation Days 2023 appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:00
16:00 Announcing the 2024 Joint OGC ASF OSGeo Code Sprint
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), Apache Software Foundation (ASF), and Open Source Geospatial Foundation (OSGeo) are pleased to announce the date of the 4th annual Joint OGC ASF OSGeo Code Sprint as February 26-28, 2024.
As a hybrid event, the face-to-face component will be held in Casa Cordovil-Universidade de Évora (Évora, Portugal), while the virtual component will be held via the OGC Events Discord server. Registration for the code sprint is free and open to the general public here.
The code sprint will be hosted by Universidade de Évora, NaturalGIS and Geobeyond. Catering will be sponsored by NaturalGIS, Geobeyond and the European Union-funded GEOE3 project. Further sponsorship opportunities remain available: see below for more information.
The code sprint will engage with multiple ASF and OSGeo projects, supported by OGC Standards – including OGC API Standards, the building blocks for location on the web. All OGC, Apache, and OSGeo projects, working groups, and members, as well as the wider public, are encouraged to participate. In addition to developers, technical writers are also encouraged to participate to help the various projects and working groups with their documentation.
A code sprint is a collaborative and inclusive event driven by innovative and rapid programming with minimal process and organization constraints to support the development of new applications and candidate Standards.
The goal of the 2024 Joint OGC ASF OSGeo Code Sprint is to advance support of open geospatial Standards within the developer community, while also advancing the Standards themselves. The code sprint will provide software developers a period of three days in which to focus on projects that implement open geospatial Standards.
There will be an opportunity for joint discussion with other participants, as well as daily briefings from each project and working group. However, the majority of the time will be spent in collaboration between participants in active coding and related activities such as testing, reporting issues, and working on documentation.
The sprint will also provide a mentor stream that’s aimed at developers who are not yet familiar with the software projects and Standards. Through tutorials and 1:1 mentoring, the mentor stream aims to support developers in taking the first steps in their journey toward mastery of open geospatial Standards and projects.
For more information on the code sprint, including registration, the projects and Standards involved, and FAQ, visit the 2024 Joint OGC-ASF-OSGeo Code Sprint website. Registration for in-person participation closes at 9:00am WET on the 19th of February, 2024. Registration for remote participation will remain open throughout the code sprint.
To set the context of the code sprint, and to help participants prepare, there will be a one-hour pre-event webinar on Discord at 14:00 WET/UTC/GMT, on February 20.
The agenda and other logistical information about the code sprint can be found on the 2024 Joint OGC – OSGeo – ASF Code Sprint GitHub Wiki. Information on other OGC Sprints or events for developers can be found on the OGC Developer Events wiki on GitHub.
Event SponsorshipOpportunities to sponsor the code sprint remain available. A range of packages are available that offer different opportunities for organizations to support the geospatial development community while promoting their products or services. Visit the OGC Code Sprint sponsorship page for more information. Organizations interested in sponsoring the Code Sprint should contact the OGC Standards Program and OSGeo point of contact.
About OSGeo
OSGeo is a not-for-profit organization whose mission is to foster global adoption of open geospatial technology by being an inclusive software foundation devoted to an open philosophy and participatory community driven development.About the Apache Software Foundation
Since 1999, The Apache Software Foundation has been shepherding, developing, and incubating Open Source innovations “The Apache Way”. The ASF’s all-volunteer community comprising 816 individual Members and 8,500 Committers on six continents steward 227M+ lines of code, oversee 350+ Apache projects and their communities, and provide $22B+ worth of software to the public at 100% no cost.The post Announcing the 2024 Joint OGC ASF OSGeo Code Sprint appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 15:27
15:27 In Memory of Jeff Burnett
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)With great sadness, OGC announces the passing of our cherished colleague, Mr. Jeffrey Burnett of Littleton, Mass, on 28 November 2023, from cancer.
Jeff joined OGC as Vice President for Operations and Finance in April, 2000, serving as OGC’s Chief Financial Officer and member of the Board of Directors until his retirement in 2020. In the 20 years prior to joining OGC, Jeff held product management positions in the emerging imaging and high-performance computing market with Digital Equipment Corporation and the Massachusetts Computer Corporation (MASSCOMP). It was during this time that he first met and worked with the founders of OGC, who would later call upon Jeff to lead the Consortium’s senior staff to support OGC’s continued expansion.
Jeff was deeply committed to OGC and proved to be incredibly talented as the Consortium’s finance lead. Jeff constantly sought ways to improve the Consortium’s approach to the fiscal and operational intricacies of OGC‘s global mission. He approached his work with professionalism, tremendously sharp wit, and a delightfully wry sense of humor – qualities appreciated by OGC Directors, Staff, and the many Member representatives he worked with.
Jeff Burnett was a talented student and manager from the beginning of his career. Having grown up a sailor on the shores of Massachusetts Bay, Jeff was also an avid reader. He earned a bachelor’s degree in English Literature from Dartmouth College where he graduated also as a commissioned Naval officer. Upon graduation, Jeff served with honor in the U.S. Navy. A student at heart, upon returning as a reserve officer Jeff then attended Harvard University Business School where he earned his MBA. He was a patriot, a storyteller, and an avid amateur genealogist – discovering and creating lasting relationships with extended family and relatives around the world. Most importantly, Jeff was a deeply caring family man to his wife Janine, son Evan, and daughter Sarah.
This remarkable colleague and friend of OGC will be deeply missed.
A formal obituary for Jeff Burnett is online here.
The post In Memory of Jeff Burnett appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 19:39
19:39 How OGC Contributes to FAIR Geospatial Data
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)Standards are a key element of the FAIR Principles of Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reusability. As such, the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) has been supporting the FAIR Principles for geospatial information since its formation 30 years ago.
Following the more recent codification of the FAIR principles, the growing recognition of their potential to improve data production, storage, exchange, and processing is seeing them being used to support and enhance recent technological developments such as artificial intelligence, crowdsourcing, data spaces, digital twins, cloud computing, and beyond. This blog post, therefore, offers an overview of select OGC standards and components that support FAIRness in geospatial data.
Within the whole OGC Standards suite, we can broadly distinguish two types of Standards: data format and transfer standards that facilitate data exchange between systems; and semantic interoperability standards that support a common understanding of the meaning of data. For example, OGC Standards that define interoperable geometrical information formats, such as 3D Tiles, GML, GeoPackage, GeoTiff, or KML, support FAIRness by facilitating data Access and Reuse.
Communication Standards
Starting with OGC Web Map Service (WMS) 1.0 in 2000, the suite of OGC Web Services Standards grew to become OGC’s most popular and successful suite of Standards. Services that implement OGC Web Services Standards give access to different kinds of data through the web. Most OGC Web Services provide instructions on how to post a message or build a query URL that gives access to the data behind the service. The URL contains an action to perform and parameters to modify the action and specify the form of the result.
While perfectly functional, the OGC Web Services Standards do not completely follow modern practices on the Web. In particular they do not focus on resources but on operations. To correct that issue, the OGC is evolving the OGC Web Services into the OGC APIs – open web APIs that define resources and use HTTP methods to retrieve them. OGC APIs have diverse functionalities, as explained below.
Communication Standards for Finding DataThe Catalog Service for the Web (CSW) is an OGC Web Service that provides the capacity to query a collection of metadata and find the data or the services that the user requires. Deploying a CSW (e.g. a GeoNetwork instance) is a way to comply with the FAIR sub-principle “F4. (Meta)data are registered or indexed in a searchable resource.” CSW is compatible with Dublin Core and ISO 19115 metadata documents. An interesting characteristic of the GeoNetwork is its capability to store attachments to the metadata. This provides a way to store the actual data as an attachment and link it to the distribution section of an ISO 19115. This ensures not only Findability of the metadata but also Findability of the data. In the Open Earth Monitor (OEMC) project, CSW can be effectively used to store metadata about the in-situ data and some of the results of the pilots, making them Findable on the web. The original Remote Sensing data is offered through a SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC).
The OGC API – Records Standard is an alternative to CSW that uses the aforementioned resource-oriented architecture. It gives a URL to each and every metadata/data record stored in the catalog, making it compliant with the FAIR sub-principle “F1. (Meta)data are assigned a globally unique and persistent identifier.” The OGC API – Records Standard is still in its draft phase and the authors are making efforts to exploit STAC good practices and make the two compatible.
For flexibility, in the CSW and OGC API – Records Standards, a metadata record is not obligatory, though it is desirable in many cases. This is useful for improved findability, but also for preservation purposes when the dataset may no longer be available. This ensures compatibility with the FAIR sub-principle “A2. Metadata are accessible, even when the data are no longer available.”
Communication Standards for Accessing DataThe OGC Web Feature Service (WFS) and the Web Coverage Service (WCS) give access to feature or coverage data independently of the data’s data model or schema. Implementations of these services are based on Open Standards that can be implemented for free. This complies with the FAIR sub-principle “A1.1 The protocol is open, free, and universally implementable.” It is possible to get the whole resource or a subset of it based on spatial or thematic queries. However, these services are based on a service-oriented architecture and do not necessarily provide a URI for each resource.
The newer OGC API – Features and OGC API – Coverages Standards, though, provide similar functionality with a resource-oriented architecture. They provide a URI for each resource they expose. This makes the OGC API Standards, as well as the SensorThings API, compliant to the FAIR sub-principle “A1. (Meta)data are retrievable by their identifier using a standardized communications protocol.” OGC Web Services and OGC APIs both use the HTTP protocol over the Internet and can make use of the current standards and practices for authentication and authorization, such as OpenID Connect.
However, the resource-oriented architecture of the OGC API Standards means they are better positioned to adopt best practices for authentication and authorization. In this paradigm, authorization on geospatial resources can be fine-tuned for each resource URI in the same way as any other resource on the Web. As such, OGC API – Features, OGC API – Coverages, and The Sensor Things API comply with the FAIR sub-principle “A1.2 The protocol allows for an authentication and authorization procedure, where necessary.”
Semantic Interoperability Standards The OGC RAINBOW
The OGC RAINBOW
To better support the “Interoperable” FAIR principle as it applies semantic interoperability, OGC is implementing the OGC RAINBOW (formerly the OGC Definitions Server) as a Web accessible source of information about concepts and vocabularies that OGC defines or that communities ask the OGC to host on their behalf. It applies FAIR principles to the key concepts that underpin interoperability in systems using OGC specifications.
The OGC Registry for Accessible Identifiers of Names and Basic Ontologies for the Web (RAINBOW) is a linked-data server, published and maintained by OGC, used to manage and publish reference vocabularies, standard definitions with profiles, ontologies, and resources. It is intended to be a node in an interoperable ecosystem of resources published by different communities. It supports a wide spectrum of resources and allows more value to be realized from data. It can be accessed at opengis.net/def.
OGC RAINBOW is implemented using Linked Data principles that provide enhanced findability, making it compliant with the FAIR sub-principles “F1. (Meta)data are assigned a globally unique and persistent identifier” and “F4: (Meta)data are registered or indexed in a searchable resource.” It is accessed using the HTTP protocols over the Internet, so is also compliant with “A1. (Meta)data are retrievable by their identifier using a standardised communication protocol” and “A1.1 The protocol is open, free, and universally implementable.”
The set of concepts stored in the RAINBOW or in other vocabularies can be used by data and metadata to comply with the FAIR sub-principles “I1. (Meta)data use a formal, accessible, shared, and broadly applicable language for knowledge representation” and “I2. (Meta)data use vocabularies that follow FAIR principles.”
The OGC SensorThings APIThe OGC SensorThings API is an open and free standard that complies to the FAIR sub-principle “A1.1 The protocol is open, free, and universally implementable.” It incorporates a data model that includes two properties that allow for linking to URLs for “units of measurement” and “observed properties” (e.g. references to variable definitions) that makes it compliant with the FAIR sub-principle “I2. (Meta)data use vocabularies that follow FAIR principles.” However, other services and APIs, such as OGC API – Features and OGC API – Coverages, do not specify how this could be done in practice, so more work needs to be done in that respect.
On the other hand, the new OGC APIs use link mechanisms to connect datasets, resources, and resource collections to other resources for different purposes, making them compliant with the FAIR sub-principle “I3 (Meta)data include qualified references to other (meta)data.”
Similarly, the new OGC SensorThings API plus (STAplus) Standard includes an additional element called “Relation” that allows for relating an observation to other internal or external observations. It also adds an element called “License” associated with the datastream or observation group that complies with the FAIR sub-principle “R1.1. (Meta)data are released with a clear and accessible data usage license.” Further, the STA data model can be extended to domain-specific areas by subclassing some of the entities, such as “Thing” and “Observation,” allowing it to meet the FAIR sub-principle “R1.3. (Meta)data meet domain-relevant community standards.”
STAplus includes many considerations for secure operations and can support authentication and authorization through the implementation of business logic, making it compliant with the FAIR sub-principle “A1.2. The protocol allows for an authentication and authorization procedure where necessary.”
Other Standard Thematic Data ModelsOGC also offers Standards that define thematic data models and knowledge representations. For example, WaterML is an information model for the representation of water observations data. In addition, PipelineML defines concepts supporting the interoperable interchange of data pertaining to oil and gas pipeline systems. The PipelineML Core addresses two critical business use-cases that are specific to the pipeline industry: new construction surveys and pipeline rehabilitation.
Another example is the Land and Infrastructure Conceptual Model (LandInfra) for land and civil engineering infrastructure facilities. Subject areas include facilities, projects, alignment, road, railway, survey, land features, land division, and “wet” infrastructure (storm drainage, wastewater, and water distribution systems). CityGML is intended to represent city objects in 3D city models. The (upcoming) Model for Underground Data Definition and Integration (MUDDI) represents information about underground utilities. IndoorGML offers a data model to represent indoor building features. Finally, GeoSciML is a model of geological features commonly described and portrayed in geological maps, cross sections, geological reports and databases. This standard describes a logical model for the exchange of geological map data, geological time scales, boreholes, and metadata for laboratory analyses.
The existence of these Standards can help each thematic sector to comply with the FAIR Interoperability sub-principle “I1. (Meta)data use a formal, accessible, shared, and broadly applicable language for knowledge representation.” As well as these standards, connecting their vocabularies to information systems or databases would significantly increase their usefulness and encourage the principle of Reusability “R1.(Meta)data are richly described with a plurality of accurate and relevant attributes” and sub-principle “R1.3 (Meta)data meet domain-relevant community standards.”
FAIR in Everything We DoOGC’s Mission, to “Make location information Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR),” places the FAIR Principles at the heart of everything we do. This post has shown how OGC Standards explicitly address the FAIR Principles to contribute to FAIR geospatial data.
The Standards shown here were chosen due to their popularity and utility, but represent only a small portion of what’s available from OGC. You can see the full suite of OGC Standards at ogc.org/standards.
For more detailed information on OGC API Standards, including developer resources, news of upcoming code sprints, or to learn how the family of OGC API Standards work together to provide modular “building blocks for location” that address both simple and the most complex use-cases, visit ogcapi.org.
The post How OGC Contributes to FAIR Geospatial Data appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:00
16:00 OGC Compliance Certification now available for the GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the Executable Test Suite (ETS) for version 1.0 of the OGC GeoPose Data Exchange Standard has been approved by the OGC Membership. Products that implement OGC GeoPose 1.0 and pass the tests in the ETS can now be certified as OGC Compliant.
The OGC Compliance Program offers a certification process that ensures organizations’ solutions are compliant with OGC Standards. It is a universal credential that allows agencies, industry, and academia to better integrate their solutions. OGC Compliance provides confidence that a product will seamlessly integrate with other compliant solutions regardless of the vendor that created them.
Implementers of the GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard are invited to validate their products using the new test suite in the OGC validator tool. Testing involves submitting an OGC GeoPose 1.0 document produced by the product being assessed. These tests typically take only 5-10 minutes to complete. Once a product has passed the test, the implementer can apply to use the ‘OGC Compliant’ trademark on their product.
OGC GeoPose is a free and open Implementation Standard for exchanging the location and orientation of real or virtual geometric objects (“Poses”) within reference frames anchored to Earth’s surface (“Geo”) or within other astronomical coordinate systems. The Standard specifies a JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) encoding for representing conformant poses.
The GeoPose Standard specifies a number of conformance classes, most being optional. One conformance class is defined for each corresponding set of Structural Data Units (SDUs), where each SDU is linked to the Logical Model as an alias for a class or attribute. The following conformance classes from the OGC GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard (OGC 21-056r11) are supported by the ETS:
- Basic-YPR (Yaw-Pitch-Roll) SDU JSON
- Basic-Quaternion SDU JSON – Permissive
- Advanced SDU JSON
- Graph SDU JSON
- Chain SDU JSON
- Regular Series SDU JSON
- Stream SDU JSON
Some of the products implementing the GeoPose Standard that have already been certified as OGC Compliant include Away Team Software’s 3D Compass 1, OpenSitePlan’s SolarPose 1.0, and Ethar Inc.’s GeoPose C# Library 1.0. These products apply GeoPose in a wide variety of applications, such as Augmented Reality (AR), mobile Location Based Services (LBS), web APIs, and more. To implement GeoPose in your product, please refer to the OGC GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard document, freely available from OGC. Additional documentation is also available on the GeoPose website.
More information about the OGC compliance process, and how it can benefit your organization, is available at ogc.org/compliance. Implementers of the OGC GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard – or other OGC Standards – can validate their products now using the OGC Validator Tool.
The post OGC Compliance Certification now available for the GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:09
16:09 OGC India Forum 2023: Key Highlights from Hyderabad
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)A meeting of the OGC India Forum was held on October 18, 2023, in Hyderabad, where over 40 experts from government, industry, and academia met to discuss the future of geospatial technologies in India. With its booming tech industry, Hyderabad provided an apt backdrop for discussions on innovation and standards in the geospatial realm.
The event was supported by the following organizations: The Association of Geospatial Industries (AGI India), which represents India’s geospatial private sector capabilities; the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the national standards body that underpins technical excellence; and Geospatial World, a media company and the host for GeoSmart India 2023, where the forum was organized.
A pivotal moment at the event was the unveiling of the OGC India Forum’s new Charter, heralding a renewed commitment to advancing geospatial standards and innovation within the Indian context. Also at the Forum, OGC and AGI India renewed their partnership in line with the policy priorities of India.
 Harsha Madiraju, OGC, and Sreeramam GV, AGI India, exchanging the partnership agreement.
Harsha Madiraju, OGC, and Sreeramam GV, AGI India, exchanging the partnership agreement.
The forum facilitated a series of expert-led panels, dissecting the latest trends, challenges, and opportunities in the geospatial and Earth Observation sectors. It provided a platform for participants to contribute insights and actively shape the Forum’s committees and future directives.
Emphasizing the Economic Value of Geospatial StandardsHarsha Madiraju, Lead – OGC India Forum, set the stage with a presentation on the economic impact of standards in geospatial technologies. Citing the 2012 ISO publication on Standards and Economic Growth, he highlighted the positive correlation between the proliferation of standards and national economic development. This underscores the importance of investment in geospatial interoperability and its tangible benefits to industries and economies.
 Harsha Madiraju, Lead – OGC India Forum, delivering his opening address.
Harsha Madiraju, Lead – OGC India Forum, delivering his opening address.
From the Indian Context, Harsha said that we need proven methodologies and best practices for implementing Standards in India’s diverse and complex landscape. From this perspective, he said, the “Guide to the Role of Standards in Geospatial Information Management” prepared by ISO/TC 211, OGC, and IHO, and endorsed by UN-GGIM, provides a reliable framework around geospatial standards implementation. Quoting the guide, he said the Indian community can refer to the Goal-based Approach to geospatial standards implementation, where different maturity levels from Tier 1 to Tier 4 are prescribed.
 Goal-based Approach to geospatial standards implementation
Goal-based Approach to geospatial standards implementation
Harsha said about the interoperability scenario in India: “Our data and systems are not yet fully interoperable, and our community is at varying stages of maturity compared to more developed geospatial ecosystems. The opportunity here is immense. It’s not just about sharing maps: it’s about evolving towards a spatially enabled nation where we can take advantage of the authoritative datasets coming up for India.”
He further called for collaboration by saying “In a country like India, with its unique challenges and opportunities, the role of standards in accelerating the maturity of our technology ecosystems is crucial. At OGC India Forum, we aim to work on standards, compliance, and innovation. It’s not just the responsibility of a few: it’s a collective endeavor. Your expertise and contributions can shape the future of geospatial technology in India.”
Concluding his talk, he said, “We have the framework, the global endorsement, and, most importantly, a community willing to drive change. Let’s invest wisely in standards to shape a future that benefits us all.”
Panels and Discussions for India – Tech Trends, Adoption of Standards, and Academic Perspectives.The event then proceeded with three panels on the following topics:
Panel on Geospatial and Earth Observation Technology Innovation in IndiaThe panel discussed India’s contributions to geospatial and Earth Observation technologies and the possible advancements that may come from the Indian government, private sector, and especially start-ups. The session also discussed the untapped sectors and applications that these technologies could significantly impact. Finally, the discussions identified key challenges in technology adoption and scalability and discussed how the community can help overcome these challenges.
 Panelists on Geospatial and Earth Observation Technology Innovation in India, along with along with AGI and OGC Staff (on the right side)
Panelists on Geospatial and Earth Observation Technology Innovation in India, along with along with AGI and OGC Staff (on the right side)
Rajesh Mathur, Esri India, said that federated GIS architecture is a new paradigm enabling collaboration and data sharing. According to him, India’s National Geospatial Policy 2022 is a progressive and transformational initiative that will accelerate the adoption of geospatial technologies by encouraging collaboration and data sharing among all the stakeholders. This opens up exciting opportunities for GIS deployment – both on the Cloud and in a federated architecture. Data partnerships enabled by Standards and interoperability will allow users from multiple organizations to collaborate and share content through trusted and secure workflows.
Shubham Sharma, GalaxEye Space, said that the OGC India Forum provided a great platform to interact with the panel members and the audience with diverse experiences. With discussions ranging from the evolution of technology in the geospatial sector to standardization, the discussions centred around the implementation of OGC standards in India. With the continued expansion of the geospatial sector, Open Standards will pave a smoother road for building scalable and sustainable products.
S S Raja Shekar, National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), said OGC standards have changed how geospatial data and applications are handled, providing simple solutions to complex exchanges of data and services. A growing focus on standards in the space domain and in sectors of priority to the country where geospatial applications are critical is needed. This session also brought perspectives and ideas from entrepreneurs and proved to be highly constructive.
Akshay Loya, Founder & CEO of GISKernel Technologies, said “I was asked how I envision the evolution of the geospatial industry in India. My response was straightforward: we, as young founders, can share our insights alongside esteemed figures on a platform like OGC India Forum, which is a significant evolution in our industry.”
Panel on Geospatial and Earth Observation Standards in IndiaThe second panel examined the current adoption of BIS/ISO and OGC standards in India, focusing on areas where they are most – and least – implemented. The panel also discussed the avenues available for contributing to geospatial and Earth Observation Standards, both at a national and international level. The session then also delved into the compliance and procurement aspects.
 Speakers at the Panel on Geospatial and Earth Observation Standards
Speakers at the Panel on Geospatial and Earth Observation Standards
Abhiroop Bhatnagar, Lead, Platform at Aereo, said “I would like to share the message regarding the importance of cloud-native geospatial formats. The essential property of cloud-native formats is that they allow data delivery directly from cloud-based storage to clients without involving any compute in between – for example consider direct requests to S3 from web browsers. The world is quickly transitioning towards a cloud-based data-delivery paradigm. Under this new paradigm, if we have to ensure scalability along with preserving efficiency, it is critical to utilize cloud-native geospatial formats. In that respect, Cloud-optimized GeoTIFF has already been accepted as an OGC standard and is well-supported by the ecosystem. We at Aereo have already integrated support for COGs in our WebGIS platform, Aereo Cloud. We actively promote it as the preferred format for raster data within the industry and the government.”
Ashish Tiwari, Joint Director of the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), said that ISO/TC211 and OGC have a strong history of collaboration on geospatial standards. BIS, through the Geospatial Information Sectional Committee, has adopted over twelve Standards and is working on adopting fourteen more. BIS looks forward to collaborating with the OGC community, as this will be valuable in many areas where BIS can understand recent trends and best practices.
Participating in this session, Vishnu Chandra, Former Deputy Director General & HOG -NIC, Geospatial Technology Services Division, said that open geospatial Standards are the core foundation of geospatial information interoperability and play a crucial role through open geospatial APIs for the exchange of data and Service Delivery. OGC India Forum can play a critical role in bringing the global OGC standards to India in collaboration with various government, industry, and academic stakeholders.
OGC standards have a significant role given the context of the Indian National Geospatial Policy 2022, which calls for the creation of the National Geospatial Foundation around 14 Thematic Areas to support UN-GGIM objectives associated with the UN Sustainable Development Goals. These themes also have relevance in digital public infrastructures and platforms for specific governance, planning, and service delivery in the Indian context. Therefore, each data theme needs Standards implemented across the entire geospatial information value chain.
Panel providing Perspectives from Academia & Research on Innovation and Standards in IndiaThe final panel discussed the current awareness and usage of geospatial and Earth Observation Standards in academic programs and research projects. The discussions explored the extent to which Standards are integrated into educational curricula. The panel also delved into how academic and research institutions can contribute to standards development, implementation testing, and even lead the creation of new standards.
 Speakers at the Panel Providing Perspectives from Academia & Research
Speakers at the Panel Providing Perspectives from Academia & Research
Dr. Sanjay Chaudhary, Professor and Associate Dean, Ahmedabad University, School of Engineering and Applied Science, said “There is a lack of interest in geospatial technologies in India from the students in the broader computer science and IT community. Helping them understand the value and opportunities available in this sector will be important. With the evolution of OGC Standards into APIs and the availability of developer resources, we can make these students learn and invest in this direction, which will be valuable to their professions and bring skilled resources to India.”
Professor Dr. Karbhari Vishwanath Kale, Vice-Chancellor of Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, Raigad, Maharashtra, said “Through our engagement with the Bureau of Indian Standards, I have been making personal efforts to bring awareness in our professional circles on the value and importance of Standards. As an OGC Member, our university closely follows the development of international Standards by OGC. Some of our core interests lie in the intersection of multi- and hyper-spectral sensor data for agriculture, material detection, disaster management, and health care. We must invest in developing sensors and data dissemination platforms and make applications and data more broadly available, specifically in agriculture. In line with the Indian National Education Policy 2020, our university has set goals to establish and design the course curriculum with a research lab where IoT, sensors, and Standards can be brought together for the overall benefit of end users. We look forward to collaborating with the international network of OGC and taking this on.”
Dr. Sumit Sen, GISE Hub, IIT Bombay, said “Our Hub is established as an interdisciplinary project funded by the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, to enable the research and development of geospatial technology solutions. In turn, our hub works with many academic and research organizations to further fundamental research in GIScience. Standards and Interoperability is one of the focus areas, and we continue to work closely with OGC and other stakeholders like IIT Kanpur, IIT Tirupati, and IIIT Hyderabad in enabling the geospatial community with the right skills on OGC Standards and APIs. The Winter School is one of India’s unique learning programs on geospatial standards. It is a fifteen-day on-campus training program supported by OGC Staff and Members. It provides hands-on and practical training on OGC Standards to India’s government, private, and research organizations. The 2023 program will be on the OGC API Stack. We will continue our international engagement and work closely with the OGC India Forum community.”
Next StepsThe OGC India Forum 2023 event was a success. The event concluded with a broader agreement around the need to identify areas of engagement in the coming days. It was agreed that there is a need for partnerships and to organize events, training programs, and policy roundtables on geospatial standards, in collaboration with OGC Members and Partners in India and the broader community.
The post OGC India Forum 2023: Key Highlights from Hyderabad appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:00
16:00 OGC and Joint Research Centre renew Collaboration Agreement to enhance Geospatial Standards
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) and the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission (JRC) have renewed their collaboration agreement to enhance the development and use of geospatial standards.
The ongoing collaboration enables JRC to more effectively contribute to the OGC Standards process and facilitate the consideration of European objectives, requirements, and policies during the development of international open geospatial standards.
The agreement formalizes the partners’ collaboration in the field of development, application, maintenance, and promotion of international open geospatial standards and best practices that support the implementation of EU policies, for example, INSPIRE, European Data Spaces, Open Data, and Earth Observation, including Copernicus and Galileo.
Further, the agreement will enable OGC and JRC to jointly organize workshops for exchanging scientific and technological information on topics of mutual interest, for example, spatial law and policy, Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) Best Practices, and emerging technologies (e.g. metaverse, digital twins, cloud/edge computing, platforms, and Artificial Intelligence (AI)).
“We at OGC are pleased to continue our collaboration with the JRC,” commented Ingo Simonis, Ph.D, OGC Chief Technology Innovation Officer. “With the modernization of national and international spatial data infrastructures, the semantic enhancement of existing data offerings, and the development of cross-domain yet flexible solutions for heterogeneous communities, we have many core activities in common. Bringing the JRC and OGC communities together allows us to address these important topics far more efficiently.”
About JRC
The European Commission’s Joint Research Centre provides independent, evidence-based knowledge and science, supporting EU policies to positively impact society.?It plays a key role at multiple stages of the EU policy cycle.
It works closely with research and policy organisations in the Member States, with the European institutions and agencies, and with scientific partners in Europe and internationally, including within the United Nations system. In addition, the JRC offers scientific expertise and competences from a very wide range of disciplines in support of almost all EU policy areas.The post OGC and Joint Research Centre renew Collaboration Agreement to enhance Geospatial Standards appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 15:00
15:00 Climate, Disaster, and Emergency Communities invited to Innovation Days 2023
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) invites anyone involved in climate resilience, disaster response, and emergency management to attend OGC Innovation Days 2023. The event will be held December 5-7 at the American Red Cross Headquarters in Washington, D.C. Attendance is free for OGC Members using this link.
OGC Innovation Days 2023 brings together diverse members of the climate, disaster, and emergency resilience and response communities to explore what OGC-enabled geospatial technologies have made possible and to ask: what do we need to do next?
This multi-day event will benefit anyone interested or involved in climate resilience, disaster response, or emergency management by providing an opportunity to learn about the latest geospatial data and technology developments from the OGC community, contribute to shaping future work, and interact with stakeholders from industry, government, research, and the private sector.
OGC has for many years been developing solutions that support climate and disaster resilience and response, from supporting the development of FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) climate resilience information systems, to empowering first responders with the information they need, when they need it.
But to most effectively address the multi-faceted challenges of the changing climate and associated disasters, we want to hear about the problems being faced by city-managers, community members, first responders, climate scientists, insurers, government bodies, and others, as they respond to the changing climate and associated disasters – so that we can use OGC’s collective expertise to address them.
By bringing the climate, disaster, and emergency communities together, OGC Innovation Days 2023 provides a unique opportunity for attendees to meet people facing similar challenges to their own and learn about the solutions that worked for them, while guiding OGC towards creating impactful free and open solutions where none currently exist.
The event runs across three days: a day of panels and discussions, a day of demonstrations, and a day exclusively for the OGC Strategic Member Advisory Committee, OGC Executive Planning Committee, and special guests.
Gain insights from experts from leading organizations, including: event hosts American Red Cross, OGC Strategic Members Department of Homeland Security (DHS) / Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Natural Resources Canada (NRCan), and United States Geological Survey (USGS), as well as others from across government and industry. See the full agenda here.
Day 1 consists of panels and discussions centered around 4 topics: Disaster Response & Emergency Management; Wildfires; Climate Change & Disaster Risk Reduction; and the role that Artificial Intelligence and related technologies can play in building disaster and climate resilience. Throughout each panel, expect information on the FAIR solutions and workflows developed through OGC initiatives – such as the Disasters Pilot 2023 and the Climate Resilience Pilot – the gaps that remain between the data & tools we have and the ones we need, panelists’ successes & challenges, and audience feedback.
Day 2 provides attendees the opportunity to see working demonstrations of cutting-edge solutions for climate, disaster, and emergency resilience and response developed in OGC COSI Program Initiatives or using OGC innovations in geospatial technologies such as Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning, Earth Observation, Analysis Ready Data (ARD), Decision Ready Indicators (DRI) for emergency response, FAIR systems & data, cloud-native geospatial, and more.
Day 2 will also include a demonstration of General Dynamics Information Technology (GDIT)’s standards-based Raven mobile command-center, which collects and distributes mission-critical information at the edge. Powered by AI systems, the Raven can filter information so data-driven decisions can be made and disseminated to first responders, analysts, and decision makers in real-time.
Join us at the American Red Cross Headquarters in Washington, DC, USA, to tackle climate, disasters, and emergencies together using FAIR geospatial data and systems. A video overview of the 2022 OGC Innovation Days event is available on OGC’s YouTube channel.
For more information, including registration, agenda, venue & accommodation info, and more, visit the OGC 2023 Innovation Days webpage. The event is free for OGC Members – see this page on the OGC Portal for your discounted registration link. Sponsorship opportunities remain available, contact OGC to find out more.
The post Climate, Disaster, and Emergency Communities invited to Innovation Days 2023 appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 15:00
15:00 OGC Compliance Certification Available for v2.0 of the Web Processing Service (WPS) Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the Executable Test Suite (ETS) for version 2.0 of the Web Processing Service (WPS) Standard has been approved by the OGC Membership. Products that implement the Standard and pass the tests in the ETS can now be certified as OGC Compliant.
The OGC Compliance Program offers a certification process that ensures organizations’ solutions are compliant with OGC Standards. It is a universal credential that allows agencies, industry, and academia to better integrate their solutions. OGC Compliance provides confidence that a product will seamlessly integrate with other compliant solutions regardless of the vendor that created them.
The WPS Standard supports the wrapping of computational tasks into executable processes that can be offered by a server through a web service interface and be invoked by a client application. The processes typically combine coverage, raster, vector, and/or point cloud data with well-defined algorithms to produce new information. Some of those algorithms may apply Machine Learning and other Artificial Intelligence (AI) approaches, as demonstrated by the OGC Testbed-16 initiative.
Implementers of the WPS 2.0 Standard are invited to validate their products using the new test suite, which is available now on the OGC Validator Tool. Testing involves submitting the endpoint of a WPS implementation to be assessed. The validator tool sends the appropriate requests to the endpoint of the implementation and then evaluates the responses. These tests typically take only 5-10 minutes to complete. Once a product has passed the tests, the implementer can submit an application to OGC for use of the OGC Compliant trademark on their product.
To support developers with implementation of the standard, GeoLabs ZOO-Project 2.0 and the 52°North 52N Web Processing Service 4.0.0-beta.10 product have been designated as reference implementations of the standard after the software products successfully passed the compliance tests.
More information about the OGC compliance process, and how it can benefit your organization, is available at ogc.org/compliance. Implementers of version 2.0 of the WPS Standard – or other OGC Standards – can validate their products using the OGC Validator Tool.
The post OGC Compliance Certification Available for v2.0 of the Web Processing Service (WPS) Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 19:00
19:00 CLIMOS and a FAIR data-to-information value chain
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The visible effects of climate change continue to grow over time, in both frequency and severity. Extreme meteorological events, such as heavy rains, severe storms, strong winds, and high temperatures, are causing extreme floods, landslides, droughts, heatwaves, wildfires, biodiversity loss, desertification and more, and severely impacting infrastructure, crops, livestock, and lives.
As such, the last three decades have seen policy initiatives put in place to try and limit the impacts of global warming, reverse land degradation/desertification, stop the loss of biodiversity, protect finite natural resources, and reduce the risks associated with environmental disasters. These initiatives are summarised under the umbrella of the United Nations Agenda 2030 and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which together aim at increasing the resilience of people and systems to the changing environmental and socioeconomic conditions. Within this framework, Climate Action (SDG 13) and particularly Health (SDG 3) are defined goals to be tackled by the international community through collaborative solutions.
Extreme weather-induced hazards and disasters certainly provide a very visible example of the impact of climate change. However, most of the mortality caused by climate change comes in less cataclysmic forms. One obvious example is the increased mortality rate during heatwaves. A less obvious example is the changing risk of exposure to disease for humans, other animals, and plants.
Changes in temperature and precipitation, combined with changes in land use and cover, are creating spatial shifts in the life-cycle dynamics of disease-transmitting vectors, such as bats, small mammals, or mosquitoes, which has resulted in changing risks of exposure to disease.
The EU project CLIMOS, which OGC is a partner, is examining one such change by focussing on diseases transmitted by sandflies. CLIMOS works towards enhancing the scientific knowledge of the parameters that affect the spread of sandflies – and thus their ability to transmit disease – in the context of a changing climate. The project calls for technical systems that can combine and process: raw data output by climate models; earth observations of ongoing meteorological events and changes to land cover; and ecological data describing the life cycles of the sandflies.
Technical systems that are able to find, access, integrate, and process data for use in building climate resilience are coming to be known as Climate Resilience Information Systems (CRIS). CRIS are already being used to develop and provide interoperable Analysis Ready Data (ARD), usually in the form of data cubes, to scientists for further processing using scientific algorithms, and/or for developing Decision Ready Indicators (DRI) that allow for clear interpretation of current events by decision makers.
The “raw data to information” value chain underpinning CRIS is made possible when the FAIR data principle is respected, that is that data and systems are developed in a manner that ensures they are Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable. CLIMOS is therefore focussing on the use of FAIR-aligned Climate Services for data assessment, scientific knowledge generation, early warning, and to better understand how meteorological conditions are increasing the risk of sand fly-borne diseases in particular areas.
As part of the CLIMOS project, the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is supporting the move toward FAIR systems for use in the emergency alert systems and data pipelines. Specifically, OGC is addressing the interoperability challenges faced when combining health, environmental, Earth observation, and climate model data. These challenges are being examined and addressed through various technical testbeds and data pilot studies that emphasise the FAIR principles, as well as within OGC Domain Working Groups. For the objectives of CLIMOS, OGC’s Climate Change Resilience, Emergency Management, and Health Domain Working Groups are each providing excellent sources of experience and knowledge related to these three aspects of the CLIMOS project.
The work of CLIMOS is an essential contribution to realise the SDG 3 goal to “Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.”
This post originally appeared on the CLIMOS Project blog.
The post CLIMOS and a FAIR data-to-information value chain appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Calls for Participation in its Open Science Persistent Demonstrator Pilot
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) invites organizations and individuals to join the OGC Open Science Persistent Demonstrator (OSPD) Pilot. The multi-year project will support collaborative open science for the scientific community, decision-makers, and the general public. Responses are due by December 1, 2023. Funding is available for Participants.
Collaborative Open Science is essential to addressing complex challenges whose solutions lie in cross-sector integrations that leverage expertise and data from diverse domains while prioritizing integrity. By making it simple to connect data and platforms together in transparent, reusable and reproducible workflows, the OGC OSPD Pilot aims to enable innovation through collaborative open science.
OGC’s OSPD Pilot focuses on connecting geospatial and Earth Observation (EO) data and platforms to enable and demonstrate solutions that create capacity for novel research and accelerate its practical implementation.
The Pilot will produce a web portal to demonstrate how platforms operated by different organizations can be used for collaborative research and data representation, facilitate testing the compatibility of in-development data or platforms with other elements in a multi-platform workflow, and promote training in methods for collaborative, open innovation by providing learning and outreach materials.
The OSPD Pilot will produce three main elements:
- The development of a web portal that demonstrates how platforms operated by different organizations can be used for collaborative research and data representation;
- A test environment for web platforms to explore mutual use and which provides a collaboration space for existing and in-development platforms to use each other and test aspects such as reproducibility of workflows; and
- The provision of learning and outreach materials that make the Open Science platforms known and accessible to a wide range of users and enable efficient use.
The OSDP is sponsored by OGC Strategic Members the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Agency (NASA), who will provide vision and leadership throughout the initiative.
The OGC Open Science Persistent Demonstrator Pilot will be conducted under OGC’s Collaborative Solutions and Innovation (COSI) Program, a collaborative, agile, and hands-on prototyping and engineering environment where sponsors and OGC members come together to address location interoperability challenges while validating international open standards. To learn about the benefits of sponsoring an OGC COSI Program Initiative such as this, visit the OGC COSI Program webpage.
More information on OGC’s OPSD Pilot, including the CFP document and how to respond, is available on the OGC Open Science Persistent Demonstrator Pilot webpage. Responses to the CFP are due by December 1, 2023.
The post OGC Calls for Participation in its Open Science Persistent Demonstrator Pilot appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:34
17:34 Webinar: Location Innovation Academy for NMCA
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The online Location Innovation Academy recently launched to provide online training material for geospatial data management. It currently offers 12 e-learning modules in three clusters. These materials are designed to help government agencies, particularly national mapping organizations, make the most of their data and digital infrastructure.
On Thursday, 26th October, 2023 at 11:00 – 12:30 CET, OGC and GEOE3 will host a webinar that aims to serve as an introduction to the Academy for National Mapping and Cadastral Agencies (NMCA), and will focus on the integration of climate and meteorological data into data portals used and provided by NMCA.
Additionally, anyone who wishes to use materials from the online academy in their own training courses will learn the information needed to navigate the academy platform and its core content. Teachers, professors, coaches, consultants, and other professionals providing training in geoinformatics, spatial planning processes, and related fields are therefore also encouraged to attend.
During these demonstrations, training materials for the use of OGC climate resilience application packages and for integration of meteorological data into portals managed by NMCA will be presented as examples out of the GEOE3 project.
For more information about the Academy, or to enroll in a free course, visit the Location Innovation Academy website.
Topics: Integration of Meteorological Data; Climate Application Packages
Time: Thursday, 26th October. 11:00 – 12:30 CET
Registration: Click here for registration
Virtual Room: Dial-in info will be provided after registration.
Language: English

The post Webinar: Location Innovation Academy for NMCA appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) published as official OGC Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) Standard v1.0 has been approved by the OGC Membership for adoption as an official OGC Standard. COG, as an OGC Standard, formalizes existing practices already implemented by the community, such as the GDAL library or the COG explorer and other implementations.
COG allows for the efficient streaming and partial downloading of imagery and grid coverage data on the web, and enables fast data visualization and geospatial processing workflows. COG-aware applications can efficiently stream/download only the parts of the information they need to visualize or process web-based data. With so much remote sensing imagery available in cloud storage facilities, the benefits of optimizing their visualization and processing will be widespread. COG is one of the preferred formats used in catalogs conforming to the SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC) specification, and sits alongside other emerging cloud-optimized formats of relevance to OGC, such as Zarr, COPC, and GeoParquet.
The COG Standard specifies how TIFF files can be organized in a way that favors the extraction of convenient parts of the data at the needed resolution while remaining compatible with traditional TIFF readers. It also specifies how to use HTTP (or [HTTPS)] to transmit only the part of information needed without downloading the complete file.
The OGC COG Standard depends on the TIFF specification and the OGC GeoTIFF Standard. For large files, it depends on the BigTIFF specification. The standard takes advantage of some existing characteristics of the TIFF specification and the existing HTTP Range Request specification (IETF RFC 7233) and does not modify them in any way.
The early work for crafting this OGC Standard was undertaken in the Open-Earth-Monitor Cyberinfrastructure (OEMC) project, which received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation program under grant agreement number 101059548 and in the All Data 4 Green Deal – An Integrated, FAIR Approach for the Common European Data Space (AD4GD) project, which received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation program under grant agreement number 101061001.
This work was followed by an activity within OGC’s Testbed-17 that formally specified COG requirements in the OGC Testbed-17: Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF specification Engineering Report. The lessons from the initiatives were then used to inform the standardization of COG by the OGC Membership.
OGC Members interested in staying up to date on the progress of this standard, or contributing to its development, are encouraged to join the GeoTIFF Standards Working Group (SWG) via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about participating in this SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
As with any OGC standard, the open Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) Standard v1.0 is free to download and implement.
The post Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) published as official OGC Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 16:52
16:52 A recap of the 127th OGC Member Meeting, Singapore
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)From September 25-29, 2023, more than 100 geospatial experts from around the world converged in Singapore to attend OGC’s 127th Member Meeting, with another 100+ attending online. As always, big thanks go out to our dedicated members that either attended in-person, or juggled lives across multiple timezones to attend virtually.
Sponsored by OGC Principal Member, the Singapore Land Authority (SLA), the meeting was themed “Building future standards for the next generation of geospatial experts.” Once again, the Member Meeting was held in conjunction with the Singapore Geospatial Festival 2023 operated by SLA’s GeoWorks.
Alongside the usual assortment of Standards Working Group (SWG) and Domain Working Group (DWG) meetings, the Member Meeting also saw several special sessions, including: a two-part Data Quality Workshop; a session on Modeling of Humanities’ Spatio-Temporal Data; a Digital Twins special session; a session on the OGC Academy; a Connecting Land and Sea special session; an Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) ad hoc; and a meeting of the OGC Asia Forum.
Monday evening’s welcome reception celebrated Simple Features’ 25th birthday with a suitably delicious cake and an enthusiastic rendition of “Happy Birthday.” Simple Features, which is jointly published with ISO, is OGC’s earliest standard and describes how to model the location of “features” (a geometric representation of anything of interest) on a 2-dimensional space representing the surface of a planet. And of course there was the usual Wednesday night “VIP Dinner” (held at the delicious Red House Seafood), where Wuhan University received an OGC Community Impact Award, and a Diversity Luncheon held on Thursday.
 OGC Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons, leads the celebrations for Simple Features’ 25th birthday.
Themes from the week
OGC Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons, leads the celebrations for Simple Features’ 25th birthday.
Themes from the week
As is befitting of the location in Singapore, with its advanced modeling of the whole nation, across the entirety of the Member Meeting were presentations related to Digital Twins – twins not only of the built environment, but for vegetation, the ocean, and the subsurface. Several Working Groups regularly include discussion on Digital Twins related to their scope, especially the Urban Digital Twins DWG. Related topics regarding the Metaverse and Interoperable Simulation and Gaming also continue regular appearances at OGC meetings.
Marine and coastlines play an important role in economies and climate resilience strategies alike. OGC has a long-running pilot project on marine geospatial infrastructure, and we continue to refine models for describing and managing the coastal land-sea interface. We expect this work to be extended to the topics of ITS and logistics in the coming years, too.
A Kick-off and a Joint OpeningThe OGC Member Meeting started on Monday, but as it was held jointly with the Singapore Geospatial Festival, the joint opening wasn’t until Tuesday. Monday, then, kicked off with a brief welcome session before the ever-popular Today’s Innovations, Tomorrow’s Technologies and Future Directions session.
The topic of this meeting’s Future Directions session was Geospatial Artificial Intelligence. Dr. Gobe Hobona, OGC’s Director of Product Management, opened with an overview of where this topic fits in the context of previous sessions. He was then followed by three presentations:
- Kyoung-Sook Kim from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science & Technology (AIST) presented a Design Standardization Roadmap for GeoAI.
- Peter Baumann, Dimitar Misev, and Otoniel Campos of Constructor University (formerly Jacobs University) presented on Scalable Datacube-Enabled AI Infrastructure Based on Open Standards.
- Amey Godse and Sunil Shah of Duality Robotics presented on Building Digital Site Twins Using Geospatial Data and Artificial Intelligence.
The speakers then participated in a panel fielding audience questions, including their views on the fundamental scope of the AI domain in a geospatial context, and what types of machine learning need OGC’s attention and which may be less relevant. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The joint Opening session on Tuesday featured keynote remarks from Colin Low, Chief Executive, SLA, and myself. The Guest of Honor was Dr. Mohamad Maliki Bin Osman, Minister in the Prime Minister’s Office, Second Minister for Education & Foreign Affairs. The session also featured presentations from local students who had performed impressive geospatial projects in their primary schools. It finished with a panel on “Geospatial: Enriching Minds, Empowering Lives,” which was also the key theme for the Singapore Geospatial Festival.
 The theme of the Member Meeting was “Building future standards for the next generation of geospatial experts.”
Meeting Special Sessions
The theme of the Member Meeting was “Building future standards for the next generation of geospatial experts.”
Meeting Special Sessions
The week continued with its usual array of SWG and DWG meetings, interspersed with several special sessions, outlined below.
The OGC Data Quality DWG held two sessions to comprise a workshop covering a breadth of data quality topics. The first session focused on the work of ISO/TC 211 on data quality measures and a registry to be hosted by OGC. The second session included presentations on the data quality requirements and considerations for a variety of types of geospatial data, including 3D and imagery. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The session on Modeling of Humanities’ Spatio-Temporal Data was organized by participants in the HumSpatial Consortium, in which OGC participates, to address the complexities of representing “named places” in geospatial technologies. Presentations were given by scholars and practitioners from the humanities research and government sectors heavily involved with place-names and other types of geospatial data. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
Several sessions over the course of the week included presentations related to Digital Twins, often in the context of other domains, such as Artificial Intelligence or Data Quality. A dedicated special session for Digital Twins was organized to demonstrate different information types and practices and facilitate discussion on the relative meaning/relationship between digital twins, the metaverse, and the industrial metaverse. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The OGC Academy is an information portal for distributing OGC knowledge related to the work of the Consortium and general geospatial interoperability. The web-based resources are under development with an estimated completion in 2026. Content is continuously refreshed. This session discussed capacity building and the academy more broadly. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The OGC Marine DWG organized a follow-up session to the one hosted last year in Singapore on “Connecting Land and Sea” to highlight activities in the OGC Federated Marine Spatial Data Infrastructure Pilot as well as work from OGC members around the world. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) ad hoc session highlighted work in ISO/TC 204, with whom OGC maintains a liaison, and explored the next steps for related work in OGC. Attendees generally accepted that ITS work intersected several OGC Working Groups and that a new effort to refine the road network model developed in TC 204 would be suitable for OGC activities. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
At each OGC Member Meeting, one or more local forums meet to present and discuss topics of regional interest. On Friday of the Member Meeting, the OGC Asia forum offered a short history on the forum and five presentations from across the region. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
 Winston Yap from the National University of Singapore’s Urban Analytics Lab presents during the Digital Twins Special Session.
Closing and Important Things
Winston Yap from the National University of Singapore’s Urban Analytics Lab presents during the Digital Twins Special Session.
Closing and Important Things
The Member Meeting’s Closing session began with the Important Things session and my rapid, 15-minute summary of the entire meeting week that included slides and content from a large number of Working Group sessions. OGC Members can access the presentation and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The Important Things session then proceeded with two discussion topics:
- “Is the ‘fundamental model’ of geospatial 2D, 3D, 4D, or more D?” with consideration to whether the minimum number of dimensions is necessary, or whether all dimensions should just be assumed.
- “The need to establish a policy for the governance of building blocks” where the TC concluded that more discrete definitions are needed for “building blocks” and other registered items that act as useful components in geospatial architecture.
Notes from the session were recorded in the Etherpad “Important-Things-2023-09”, which is available to OGC Members via the Portal.
The formal Closing Plenary then followed, which focuses on Working Group presentations and voting. The session advanced a number of Standards, SWGs, and documents toward vote or publication, so keep your eye on our news page, or subscribe to the “Standards updates” topic on the OGC Mailing List to get notifications sent straight to your inbox.
Thank youOur 127th Member Meeting was yet another memorable meeting. It’s so great to see OGC Members discuss, collaborate, and drive technology and standards development forward in support of some of the biggest issues facing humanity. Once again, a sincere thank you to our members for investing their time and energy, as well as their dedication to making OGC the world’s leading and most comprehensive community of location experts.
Be sure to join us at TU Delft, Netherlands, on March 25-29, 2024, for our 128th Member Meeting. Registration and further info will be available soon on ogcmeet.org. Sponsorship opportunities are also available – contact us for more info. You can subscribe to the “Events” and other topics on the OGC Mailing List to stay up to date on all aspects of OGC, including when registration goes live for our Member Meetings.
In the meantime, don’t miss our 2023 Innovation Days event, December 5-7 in Washington, DC, USA. The multi-day event brings together policy makers, program decision-makers, and other experts in geospatial to showcase climate, emergency, and disaster management & resilience solutions that scale from local to global impacts.
 Attendees of the 127th OGC Member Meeting in Singapore, 2023.
Attendees of the 127th OGC Member Meeting in Singapore, 2023.The post A recap of the 127th OGC Member Meeting, Singapore appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 11:00
11:00 OGC and the International Data Spaces Association sign Memorandum of Understanding
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) and the International Data Spaces Association (IDSA) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that outlines how they will together contribute to a flourishing data economy through the creation and development of standards for data spaces that ensure sovereign, interoperable, and trusted data sharing.
“As the number of available data sources continues to grow, the challenge of integrating them into high-value products becomes ever greater,” commented OGC Chief Technology Innovation Officer, Ingo Simonis, Ph.D. “In order to develop effective solutions for cross-border data integration, international collaboration is critical. As such, OGC is eager to work with IDSA to tackle this task together.”
“Committed to driving digital transformation, IDSA champions economic growth, innovation, and a cohesive data-sharing approach,” said Silvia Castellvi, Director of Research & Standardization at IDSA. “Partnering with OGC ensures our standards align and resonate. Enhancing features, like the geolocation of IDS Connectors, not only advances our standard but boosts its appeal for future developers and users.”
OGC is an international non-profit consortium aiming to make geospatial (location) information and data services FAIR – Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable. IDSA is an international non-profit association that follows a user-driven approach to create a global standard for international data spaces and interfaces based on sovereign data sharing.
The MoU seeks to align activities between the two organizations so that OGC and IDSA Standards can work in tandem. This will be achieved in part through joint participation in potential future projects and initiatives, particularly in the areas of global supply chains, intelligent transport, and smart city data spaces.
Projects in global supply chains and intelligent transport may include developing solutions that support the monitoring of shipping routes, tracking freight, sharing ocean currents and weather data, and more. Projects in smart city data spaces could focus on improving data sharing from business and technical perspectives, and could include data ranging from traffic to population migration.
The two organizations have already identified several ongoing or completed projects relevant to their work together, including: Divine, Flexigrobots, DEMETER, ATLAS & AgriDataValue, Iliad, AD4GD, OGC Rainbow, and others.
About IDSA
The International Data Spaces Association (IDSA) is on a mission to create the future of the global, digital economy. Its 140+ member companies and institutions have created the International Data Spaces (IDS) standard: a secure system of sovereign and trusted data sharing in which all participants can realize the full value of their data. IDS enables new smart services and innovative business processes to work across companies and industries, while ensuring that the control of data remains in the hands of data providers. We call this data sovereignty.
Visit internationaldataspaces.org for more informationPress contact:
Nora Grass
+49 162 2104263
nora.gras@internationaldataspaces.orgThe post OGC and the International Data Spaces Association sign Memorandum of Understanding appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 CoverageJSON v1.0 Adopted as OGC Community Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that version 1.0 of CoverageJSON has been approved by the OGC Membership for adoption as an official OGC Community Standard. CoverageJSON enables the development of interactive visualizations that display and manipulate spatio-temporal data within a web browser.
The key design goals for CoverageJSON are simplicity, machine and human readability, and efficiency in the storage and use of complex data.
Coverages and collections of coverages can be encoded using CoverageJSON. Coverage data may be gridded or non-gridded, and data values may represent continuous values (such as temperature) or discrete categories (such as classes of land cover).
This OGC Community Standard was an outcome of the European Union project “Maximizing the Exploitation of Linked Open Data in Enterprise and Science” (MELODIES), which ran from 2013 to 2016, and was released under a Creative Commons 4.0 License by the University of Reading. There are several widely-used open source implementations and libraries available. Furthermore, CoverageJSON is one of the encodings supported by the OGC API – Environmental Data Retrieval Standard.
CoverageJSON is based on the popular JavaScript Object Notation (JSON), and provides an effective, efficient format that’s friendly to web and application developers and consistent with the OGC API family of Standards.
CoverageJSON supports the efficient transfer of usable quantities of data from big data stores to lightweight clients, such as browsers and mobile applications. This enables straightforward local manipulation of the data by scientists and other users.
The simplest and most common use-case is to embed all the data values of all variables in a Coverage object within the CoverageJSON document to create a self-contained, standalone, document that supports the use of very simple clients.
Another simple use case is to put data values for each variable (parameter) in separate array objects in separate CoverageJSON documents that are linked from a parent CoverageJSON object. This is useful for a multi-variable dataset, such as one with temperature, humidity, wind speed, etc., to be recorded in separate files. This allows the client to load only the variables of interest.
A sophisticated use case is to use tiling objects, where the data values are partitioned spatially and temporally, so that a single variable’s data values would be split among several documents. A simple example of this use case is encoding each time step of a dataset into a separate file, but the tiles could also be divided spatially, like a tiled map server implementation.
As with any OGC Standard, the OGC CoverageJSON Community Standard is free to download and implement. Interested parties can learn more about, view, and download the Standard from OGC’s CoverageJSON Community Standard Page.
The post CoverageJSON v1.0 Adopted as OGC Community Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 Wuhan University receives OGC Community Impact Award
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) has announced Wuhan University, represented by Professor Peng Yue, as the latest recipient of the OGC Community Impact Award. The award was presented at the VIP Dinner of the 127th OGC Member Meeting in Singapore.
The Community Impact Award is given by OGC to highlight and recognize those members of the OGC Community who, through their exceptional leadership, volunteerism, collaboration, and investment, have had a positive impact on the wider geospatial community.
“Wuhan University and Professor Peng Yue exemplify the mission of OGC through their combined efforts in technical leadership and international consensus building,” commented OGC Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons. “Their recent contributions toward standardization in AI were inclusive of the breadth of OGC membership and will prove truly useful for the geospatial community.”
Wuhan University has, and continues to, make an impact within the OGC Community through their active leadership, international collaboration, and engagement across numerous OGC Collaborative Solutions and Innovation Program (COSI) Initiatives, Working Groups, Member Meetings, and the OGC China Forum. Professor Peng Yue was also the primary lead on the newly published Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence (Part 1) Standard.
The OGC Community Impact award highlights the importance of collaboration, volunteering time and energy, advancing technologies and standards, raising awareness, and helping solve critical issues across the geospatial community. Wuhan University exemplifies all of these qualities in their work to drive innovation and standards for AI/ML and associated training data, and their efforts in leading the OGC Community in China.
The post Wuhan University receives OGC Community Impact Award appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Adopts Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence Conceptual Model as Official Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the OGC Membership has approved the OGC Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence (TrainingDML-AI) Part 1: Conceptual Model for adoption as an official OGC Standard. The Standard defines the conceptual model for standardized geospatial training data for Machine Learning.
Training data plays a fundamental role in Earth Observation (EO) Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning (AI/ML) applications, especially Deep Learning (DL). It is used to train, validate, and test AI/ML models. Understanding the source and applicability of training data allows for better understanding of the results of AI/ML operations.
To maximize the interoperability and re-usability of geospatial training data, the TrainingDML-AI Standard defines a model and encodings consistent with the OGC Standards baseline to exchange and retrieve the training data via the Web. Part 1 of the Standard contains the Conceptual Model, as well as example JSON encodings. Future Parts of the Standard will cover other encodings.
Additionally, the Standard provides detailed metadata for formalizing the information model of training data. This includes but is not limited to the following aspects:
- How the training data is prepared, such as provenance and quality;
- How to specify different metadata used for different ML tasks;
- How to differentiate the high-level training data information model and extended information models specific to various ML applications;
- How to describe the version, license, and training data size;
- How to introduce external classification schemes and flexible means for representing ground-truth labeling.
OGC Members interested in staying up to date on future progress of this standard, or contributing to its development, are encouraged to join the Training Data Markup Language for AI Standards Working Group via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about participating in this SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
As with any OGC standard, the open OGC Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence (TrainingDML-AI) Part 1: Conceptual Model Standard is free to download and implement.
The post OGC Adopts Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence Conceptual Model as Official Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 18:05
18:05 Making The Data Count, Not Just Counting The Data
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)After three years of collaborative development, the release of the first iteration of the IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap is a milestone moment in exploiting geospatial data for the inclusive socio-economic development of nations. This Maturity Roadmap – involving the UK Hydrographic Office (UKHO) as lead sponsor, as well as the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), the World Bank Group, and the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) – complements existing resources by providing a quantitative toolkit for nations, ministries, departments, agencies, regions, municipalities, and even individual cities or ports, to benchmark their geospatial development against the United Nations’ Integrated Geospatial Information Framework (IGIF) principles. This independent initiative aligns with, and supports, the mission, vision, and goals of the UN-GGIM initiative (Global Geospatial Information Management), who developed the IGIF core principles for all geospatial data considerations.
(Marine) Spatial Data InfrastructureIGIF provides a vision for developing and strengthening geospatial information management, to assist countries in bridging the geospatial digital divide, secure socio-economic prosperity, and leave no community behind. Marine Spatial Data Infrastructure ((M)SDI) is the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO)’s concept for a future ecosystem of marine data services that can enable the IGIF vision to become a reality. Empowered by OGC standards, the interoperable (M)SDI data services can “make it real through technology.” Bringing these elements together in a straightforward and accessible document, the intent of the Maturity Roadmap is to provide a quantitative “quick start” or “stepping stone” for nations beginning an IGIF-aligned (M)SDI implementation.
With its terrestrial heritage, the World Bank SDI Diagnostic Toolkit is augmented with IHO and OGC contributions to maximise its benefits to the marine community, while remaining aligned with the IGIF principles and, therefore, the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As a guiding simplification, the involvement of the World Bank is crucial in providing answers for questions around financing (including business cases), alongside the ‘why’ (UN), ‘what’ (IHO), and ‘how’ (OGC). This aspect of measuring socio-economic return is commonly a key hurdle that prevents real-world progress beyond concepts and ideas. The modular IHO and OGC additions ensure interoperability with the World Bank IGIF methodology, which can lead to the financing of approved (M)SDI development projects. Even as an independent tool, undertaking an (M)SDI assessment provides a clear reference point aligned with international best practice. Without such a starting point, progress towards any (M)SDI end-state will be difficult to govern and manage.
Fully interoperable across all geospatial domainsAs part of the OGC’s Federated Marine SDI (FMSDI) initiative, the Maturity Roadmap seeks to promote the inclusive development of an IGIF-Aligned (M)SDI as the marine and maritime community’s contribution to an all-domain National Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI) across air, land, sea, space, and cyberspace. Although initially adapted for marine considerations, the Maturity Roadmap is fully interoperable across all geospatial domains and scalable from the national level to regions, municipalities, cities, ports, and government departments or agencies.
Within the Maturity Roadmap, the concept of an IGIF-(M)SDI Balanced Pathway of Development seeks to promote inclusive geospatial development via two key messages: ‘driving technology, not being driven by technology’ and ‘making the data count, not just counting the data.’
These twin ideas promote the effective governance of technology & standards to meet sovereign national requirements, however expansive or constrained, over the acquisition and possession of the latest technological solutions independent of cost-benefit considerations. OGC contributes to this by providing best practice around the implementation of standards, alongside an active cross-sector global forum to share applied knowledge, cooperate on emerging technologies, and collaborate on standards development. The engagement of the OGC membership at all levels of socio-economic development is vital for realising the cost benefits stemming from the common implementation of technologies across different countries, regions, sectors, and communities, regardless of economic spend.
The benefits of benchmarking IGIF-MSDI maturityWhen objectively and independently applied, the benchmarking provided by the IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap offers a useful planning and comparison baseline for countries undertaking a public geospatial development programme. The example here is a radar chart output across nine assessment categories corresponding to the IGIF Nine Pathways, for an initial baseline – and a subsequent baseline two years later. The underlying data is from real-world assessments taken under World Bank and partner oversight, which was openly published by the Agency for Land Relations and Cadastre of the Republic of Moldova. Such benchmarking exercises can be executed across different scales (from whole nations to cities or ports) and across different domains (from space to cyberspace), sometimes yielding deep insights into potential opportunities around discovered disparities.
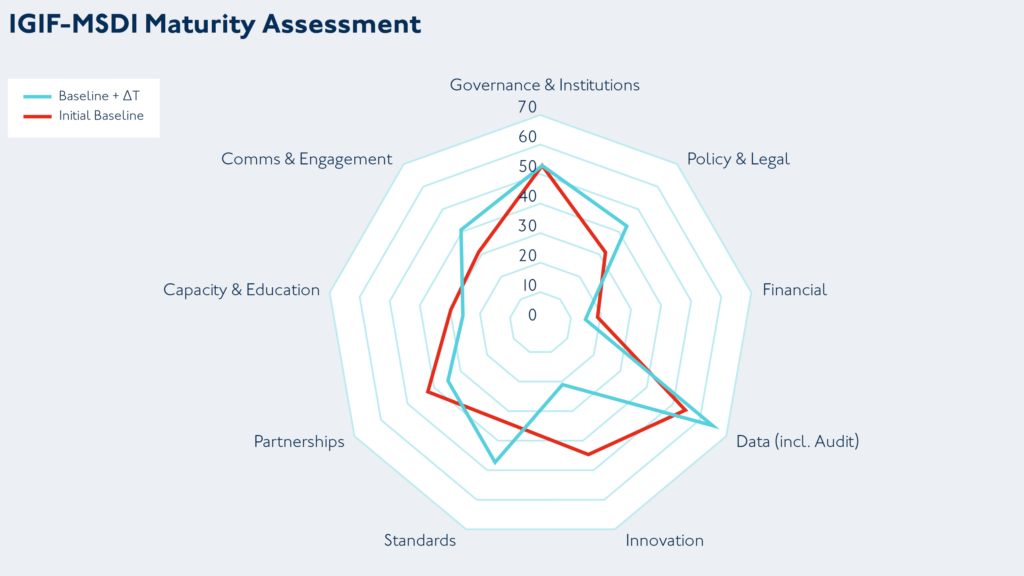
Also included with the Maturity Roadmap is a practically orientated appendix that covers best practice for multi-agency governance, where, during a national geospatial development programme, multiple agencies or departments may have to work closely to operationally deliver joint geospatial outcomes. This may be useful in situations where long-standing traditions and conventions could have created a culture that is not conducive to the tight-knit cooperation needed to develop complex IGIF-(M)SDI solutions. Such solutions require the pooling of expertise, resources, and capabilities that one or even two agencies can not provide alone.
Positive approach to improve ineffective practices is essential to joint IGIF-(M)SDI successOne crucial characteristic for joint IGIF-(M)SDI success is a healthy scepticism and a drive to improve ineffective practices, especially when they have become entrenched as tradition, convention, or “how things have always been done.” I like to counter such perceptions, particularly amongst those that genuinely want to evolve, with the view that “if you always do what you’ve always done, you’ll always get what you’ve always gotten.” Long-term existing practices may have been fine because they met some requirement in a particular environment and once satisfied a need effectively. However, maintaining those same practices now, when society’s expectations and technology have moved forward, can lead to stagnation.
Departments and agencies should foster a keen interest in human behaviour around the use (and misuse) of data or information. Traditional or conventional “hard governance” centres around the assumption that people only make the wrong decisions because they have the wrong information or not enough of it. This traditional view of data governance then coalesces into hard compliance measures and management surveillance, which includes formal audits, regular in-depth reporting, restrictive checklists, and a focus on top-down, non-negotiable command & control. This approach was suited to traditional mass manufacturing of standardised products, but is insufficient by itself for modern data services that are digital-first by design and characterised by near real-time changes.
Soft governance works with the grain of human behaviour to achieve better results by enablement and empowerment, rather than by command and control alone. Principles take precedent over prescription, thus allowing an organisation to leverage the deep insights and frontline experiences of their entire workforce. Shortcut thinking, lack of active engagement and wrong assumptions are some of the key targets for a soft governance approach, which still requires the ultimate backstop of hard governance – but meaningfully targeted and monitored using a risk-based approach. Combining the two approaches can yield outsized and transformative results, which is essential for joint IGIF-(M)SDI success that leaves no community behind.
The IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap and related resources are available for free on OGC’s IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap webpage.
To best inform future revisions, iterations, and the optimization of the Roadmap, feedback and applied experiences from the geospatial community are sought via OGC Member Meetings, Forums, or directly.
The IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap is an independent initiative not endorsed by or officially connected to, but in alignment and support of, the mission, vision, and goals of the United Nations Initiative on Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM).

Dr. Gerald J Wong is the Data Governance Lead at the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office (UKHO), which is a world-leading centre for hydrography and an executive agency of the Ministry of Defence (MoD). Dr Wong is the Lead Author of the IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap, being a specialist in synergising traditional rules-based hard governance with modern and empowering soft governance, which works with the grain of human behaviour to achieve better outcomes.
As an OGC Strategic Member and a sponsor of OGC’s FMSDI initiative, the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office (UKHO) is the UK’s agency for providing hydrographic and marine geospatial data to mariners and maritime organisations across the world. The UKHO is responsible for operational support to the Royal Navy and other defence customers. Supplying defence and the commercial shipping industry, the organisation helps ensure Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), protect the marine environment, and support the efficiency of global trade.
Together with other national hydrographic offices and the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), the UKHO works to develop and raise global standards of hydrography, cartography, and navigation. The UKHO also produces a commercial portfolio of ADMIRALTY Maritime Data Solutions, providing SOLAS-compliant charts, publications, and digital services for ships trading internationally.
The post Making The Data Count, Not Just Counting The Data appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 Registrations Open for OGC’s October 2023 Open Standards Code Sprint
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) invites software developers to the October 2023 Open Standards Code Sprint. The hybrid event will be held on Oct. 30 to Nov. 1, with the face-to-face element held at the Geovation Hub in London. A pre-event webinar will be held on October 12th. Participation is free and open to the public. Registration is available on the OGC Open Standards Code Sprint website. Travel support funding is available.
The Code Sprint is sponsored at the Gold Level by OGC Strategic Member Ordnance Survey (OS), and at the Silver Level by OGC Member the European Union Satellite Centre (SatCen). Additional support comes from OGC Strategic Member the US National Geospatial Intelligence Agency (NGA) and OGC Principal Member the UK Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (Dstl). Additional sponsorship opportunities remain available for organizations to support the geospatial development community while promoting their products or services. Visit the Event Sponsorship page for more information.
The code sprint will be a collaborative and inclusive event to support the development of Open Standards and supporting applications. All OGC Standards are in scope for this code sprint.
OGC code sprints experiment with emerging ideas in the context of geospatial standards, help improve interoperability of existing standards by experimenting with new extensions or profiles, and are used for building proofs-of-concept to support standards development activities and enhancement of software products.
Non-coding activities such as testing, working on documentation, or reporting issues are also welcome during the code sprint. The Code Sprint also provides the opportunity, via its mentor stream, to onboard developers new to OGC Standards.
A one-hour pre-event webinar will take place on October 12 at 14:00 BST (UTC+1). The webinar will outline the scope of work for the code sprint and provide other useful information for participants. Any participants interested in Imagery formats will be invited to stay on after the webinar for a technical overview of the formats in focus for the code sprint. As with the virtual portion of the sprint, the pre-event webinar will take place on OGC’s Discord server.
The Code Sprint will prototype and advance implementations of multiple approved and candidate OGC Standards, for example:
…and more.
In the context of OGC Standards, the Code Sprint will also experiment with the ability to access or provide imagery conforming to NGA’s emerging GEOINT Imagery Media for ISR (GIMI) Profile through implementations of OGC API Standards. The GIMI Profile is based on the ISO/IEC 23008-12 High Efficiently Image File Format (HEIF) and the ISO/IEC 14496-12 ISO Base Media File Format (ISOBMFF) standards. This part of the Code Sprint will also prototype creation of GIMI files from still imagery encoded in JPEG 2000 (with GMLJP2), and motion imagery encoded in H.264 and H.265 formats.
Some Travel Support Funding is available for selected participants. Anyone interested in receiving travel support funding should indicate their interest on the registration form. Requests for funding will need to be received before October 2. They will be notified within 2 weeks of their application whether their application for travel support is approved or not.
The code sprint begins at 09:00 UTC on October 30 with an onboarding session, and ends at 17:00 UTC on November 1. To learn more about future and previous OGC code sprints, visit the OGC Developer Events Wiki or join OGC’s Discord server.
Registration for in-person participation closes at 17:00 UTC on October 25. Registration for remote participation will remain open throughout the code sprint. Registration and further information is available on The Code Sprint website.
The post Registrations Open for OGC’s October 2023 Open Standards Code Sprint appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC forms new GeoParquet Standards Working Group
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce the formation of the OGC GeoParquet Standards Working Group (SWG). The new SWG will work to advance the GeoParquet encoding format for adoption as an OGC Encoding Standard for cloud-native vector data.
GeoParquet adds geospatial types to Apache Parquet, described by Apache as “an open source, column-oriented data file format designed for efficient data storage and retrieval. It provides efficient data compression and encoding schemes with enhanced performance to handle complex data in bulk.” For an introduction to the GeoParquet format, see this blog post.
GeoParquet started over 3 years ago as a community effort by different Open Source Projects and organizations that have committed to its implementation and support.
OGC is advancing a number of Standards to enable cloud-native geospatial ecosystems. GeoParquet fits in the group of data encoding Standards that are highly performant for large, cloud-based data stores, such as Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF for tiled rasters and Zarr for datacubes. GeoParquet will, in time, enable vector datasets to be as readily accessible from the cloud as the other formats already well-used in the community.
The GeoParquet SWG will take the initial efforts incubated in OGC’s GeoParquet GitHub repository as a draft specification from which a candidate Standard will be developed. As with many other recent OGC Standards, the repository will remain open to contributions from outside OGC and documentation will evolve in concert with prototype implementations.
GeoParquet will be another encoding of the OGC Simple Features Standard, and as such will handle all Simple Feature geometries. While other OGC Standards also encode Simple Features, GeoParquet is intended to be optimized for native use in cloud environments. It is expected that GeoParquet will be tested as an encoding to be accessed by the OGC API family of Standards. The new SWG expects to have a candidate Standard ready for review and approval within one year.
The OGC GeoParquet Standards Working Group Charter is publicly available via the OGC Portal.
OGC Members can join the GeoParquet Standards Working Group via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members are welcomed to contribute via OGC’s GeoParquet GitHub repository or by joining the OGC GeoParquet SWG Mailing List. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about full participation in the SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
The post OGC forms new GeoParquet Standards Working Group appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC, UKHO, and partners release the IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is pleased to host and release the first iteration of the IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap and supporting materials for community consideration and engagement across not only the marine domain, but any geospatial domain connected to the oceans.
Developed as part of OGC’s ongoing Federated Marine Spatial Data Infrastructure (FMSDI) Initiative, the Integrated Geospatial Information Framework – (Marine) Spatial Data Infrastructure (IGIF-(M)SDI) Maturity Roadmap is a quick-start guide for nations and marine organizations that seeks to advance and simplify efforts in Marine SDI and ensure their alignment with the UN-IGIF principles.
“The IGIF-MSDI maturity roadmap is an important step that supports a holistic understanding of data-exchange and -processing environments,” commented OGC Chief Technology Innovation Officer, Ingo Simonis, Ph.D. “The Roadmap enhances and complements the usual technological focus of SDIs with the equally important criteria outlined in the IGIF Principles. With the Roadmap, OGC continues its engagement and research in support of powerful, sustainable, interoperable geospatial ecosystems at all levels, including technology & standards, policies, communities, education, and capacity building efforts.”
One of the key messages of the document is that an (M)SDI is a continual journey and not an “end state” of expensive technological solutions. The document asserts that nations are sovereign in what manner of (M)SDI they genuinely need for their national requirements, and not governed by an externally imposed or presumed level of technological sophistication.
“Working collaboratively with partners at the World Bank, NOAA, OGC, IHO, and private industry, The UK Hydrographic Office (UKHO) believes that the IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap will help many Governments begin their IGIF-aligned digital transformation journeys – whether that be within the Marine or Terrestrial domains,” commented Dr. Gerald J Wong, Data Governance Lead, UKHO.
“As an accessible “Quick Start” or “Stepping Stone” toolkit, the core of the IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap is formed by the World Bank SDI Diagnostic Toolkit where, with contributions from IHO and OGC, its Terrestrial heritage was augmented to maximize its benefits to the Marine community. The IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap is aligned with the UN-IGIF principles and is fully interoperable with Terrestrial interests.”
When properly executed, the resulting MSDI Diagnostic Toolkit provides a quantitative assessment for nations or marine agencies to baseline their MSDI maturity, as aligned to the UN-IGIF principles. The modular IHO and OGC additions ensure interoperability with the World Bank IGIF methodology, which can lead to the financing of approved MSDI development projects. Even as an independent tool, undertaking an MSDI assessment provides a clear reference point that’s aligned with international Best Practice. Without such a starting point, progress towards any MSDI end state will be difficult to govern and manage.
“As the provider of ADMIRALTY navigation products and services worldwide, the UKHO supports nations in unlocking the many and varied benefits of their marine space,” commented James Carey, Deputy Chief Data Officer at the UKHO “We are a strategic member of the Open Geospatial Consortium and proudly lend our expertise to the development of Marine Spatial Data Infrastructure (MSDI), as an enabler of security, prosperity, and environmental stewardship. By fusing marine data with spatial insights it is possible to forge a path to a more interconnected world where oceans inspire growth and communities prosper.”
The IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap and related resources are available for free on OGC’s IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap webpage.
To best inform future revisions, iterations, and the optimization of the Roadmap, feedback and applied experiences from the geospatial community are sought via OGC Member Meetings, Forums, or directly.
The IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap is an independent initiative not endorsed by or officially connected to, but in alignment and support of, the mission, vision, and goals of the United Nations Initiative on Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM).
The post OGC, UKHO, and partners release the IGIF-(M)SDI Maturity Roadmap appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 12:49
12:49 European Innovation, Global Impact
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)From Europe to the World, OGC’s Collaborative Solutions and Innovation (COSI) Program is proud of its ongoing contributions to European research topics related to geospatial data. The research topics are driven by projects co-funded by the European Commission (EC) and cover many different domains and fields of application, including data spaces, climate, digital building permits, agriculture, digital twins for the oceans, knowledge generation, and beyond. While these topics are high on the European research agenda, the challenges – as well as their solutions – have global application.
These EC-funded projects are organised as small or large consortiums where different organisations cover different aspects of the projects’ objectives. As one such organisation, OGC is proud to play its part in the European Digital Strategy that is helping to ensure a secure and sustainable life for citizens of Europe and beyond.
OGC’s COSI Program conducts and organises its research around a central theme of “Full Spectrum Interoperability and Agile Reference Architecture.” Full Spectrum Interoperability refers to capturing the many different facets of interoperability that exist between systems. Agile Reference Architecture explores how software architectures can be developed and operated in a cost-efficient, agile, and sustainable manner that also maximises interoperability between systems. This research theme is therefore complementary to the European Digital Strategy.
Much of OGC’s current European work was showcased at the OGC European Innovation Days at Data Week Leipzig 2023. This blog post serves to provide an overview of that work and more for those who couldn’t attend – and who don’t want to have to wait for the next OGC European Innovation Days showcase, to be held July 2024 at FOSS4G Europe in Tartu, Estonia.
Data Spaces
Strong progress is being made towards Common European Data Spaces with the projects All Data for Green Deal (AD4GD) and Urban Data Space for Green Deal (USAGE). In both of these projects, OGC is contributing to the development of interoperable, federated systems that support information dissemination and knowledge generation. Such systems will use OGC Standards to enable interoperability at several technical and administrative levels and optimise the value chain that transforms raw data into decision-ready information.
AD4GD’s mission is to co-create and shape the European Green Deal Data Space as an open hub for FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) data and standards-based services that support the key priorities of pollution, biodiversity, and climate change. The focus is on interoperability concepts that will bridge the semantic and technology gaps that are currently preventing stakeholders and application domains from accessing multi-disciplinary and multi-scale data. These gaps are also impeding the full exploitation of processing services and processing platforms at different levels, including Cloud, HPC and edge computing. AD4GD recently published this blog post summarising its second plenary meeting, which was co-located with Data Week Leipzig 2023.
The Horizon Europe USAGE project aims to provide solutions and mechanisms for making city-level environmental and climate data FAIR – and thus available to everyone. Leveraging standards for data and service interoperability, such solutions combine innovative governance mechanisms, consolidated arrangements, AI-based tools, and data analytics to streamline the sharing, access, and use of authoritative and crowdsourced city-level Earth Observation (EO) and Internet of Things (IoT) data.
In both of these projects, OGC Standards will play a fundamental part in enabling the resulting FAIR solutions. The main research challenge is developing Building Blocks for common data problems. These Building Blocks bring together data models, examples, code snippets, and schemas, and undergo continuous testing to make them easily accessible and usable by developers, modellers, and users. The goal is to identify and describe common patterns that exist across communities. This will lead to enhanced interoperability within and between data spaces.
Interested in learning more about Data Spaces? OGC will host a session on European common data spaces at the 2023 INSPIRE Conference this November.
Climate
OGC’s current crop of climate-related projects seek to support FAIR climate services and streamline the value chain that transforms raw data into decision-ready information.
Specifically, as part of the Climate Intelligence (CLINT) project, OGC is developing blueprints for transforming scientific algorithms into climate application packages that can be deployed, regardless of their backend, in the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). More widely, the CLINT project seeks to develop Machine Learning (ML) techniques and algorithms that climate scientists can use to process the large climate datasets required for predicting and identifying the causes of extreme events such as heatwaves, warm nights, droughts, and tropical cyclones.
Focusing on the health impacts of climate change, the CLIMOS (Climate Monitoring and Decision Support Framework for Sand Fly-borne Diseases Detection and Mitigation with COst-benefit and Climate-policy MeasureS) project aims to mitigate the emergence, transmission, and spread of pathogens by sand flies. The project is establishing an Early Warning System and decision support tools for more accurate climate and health models. It will also provide predictions of infection risk and spread, as well as adaptation options. OGC is addressing the interoperability challenges faced when combining health, environmental, Earth observation, and climate model data.
Digital Building Permits
OGC is bringing its geospatial expertise to the digitalisation of building permits across two projects: ACCORD and CHEK. Albeit with a different focus, both projects aim to transform what is currently a largely manual process into a semi-automated one that allows building applications to be submitted in digital form.
In support of sustainability and resource conservation, the ACCORD (Automated Compliance Checks for Construction, Renovation, or Demolition works) has a strong focus on regulations analysis and the use of ontologies and linked data to automate the compliance checks. ACCORD will develop a semantic framework for European digital building permit processes, regulations, data, and tools. This framework will drive the formalisation of rules and the integration of existing compliance tools as Standards-based microservices, for example using OGC APIs. The solutions and tools being developed by ACCORD will provide consistency, interoperability, and reliability with national regulatory frameworks, processes, and standards.
The CHEK (Change toolkit for digital building permit) project is looking at the entire workflow for the digitalisation of building permits and is facilitating the introduction of digital building permit procedures for municipalities by developing flexible, adaptable solutions that take into account all the rules and conditions of the procedure. As with ACCORD, CHEK is using a Standards-based microservices approach to its architecture. CHEK will also develop training for municipalities, which will be made available through the Location Innovation Academy (see below).
As part of CHEK, OGC is investigating how needs-based data models can be derived dynamically as profiles of common conceptual models. The goal is to leave behind the basic problems of standardised data models. Due to their ambition to comprehensively represent a domain, they tend to be over-specified. On the other hand, to adapt to the needs of different use cases, they allow too much flexibility in implementation and modelling details. OGC is currently focused mostly on the transformation of administrative data using ontologies generated from CityGML and CityJSON.
Agriculture
The DEMETER project, which is now coming to an end, has helped to digitally transform Europe’s agri-food sector. DEMTER adopted advanced IoT technologies, data science, and smart farming to ensure the long-term viability and sustainability of the agriculture sector. One of the key results is the production of an Agriculture Information Model (AIM). The AIM is a data model and ontology for agriculture applications that ensures semantic interoperability between data and components involved in agri-food applications. To further enhance the AIM, OGC has now formed the Agriculture Information Model Standards Working Group (AIM SWG). The OGC AIM will provide a common language for agriculture applications to harmonise and improve data and metadata exchange by defining the required data elements, including concepts, properties, and relationships relevant to agriculture applications, as well as their associated semantics/meaning for information exchange.
Oceans and the Blue Economy
The Iliad Digital Twins of the Ocean project is developing a federated, multidimensional representation of the maritime and oceanic ecosystem. As with many of these projects, OGC Standards will be used to enhance the value chain as data sourced from smart IoT, satellite Earth Observations, and Citizen Science is transformed into decision-ready information and knowledge. As such, it fits perfectly into the OGC focus theme of “marine spaces.”
Iliad is developing several Digital Twin pilots in a number of key areas, including: wind energy; renewable energy from the ocean (currents, waves & floating solar); fisheries & aquaculture; marine traffic & harbour safety; pollution; met ocean data (hind, now & forecasts); biodiversity assessments & monitoring; and insurance for marine & maritime activities.
OGC is involved in defining the standards-based Data Transfer Object (DTO) data management APIs built on the OGC APIs framework, as well as ensuring semantic interoperability between the APIs, Citizen Science, and thematic domains. Finally, we are leading standardisation and best practice tasks to enable the solution to fit within the ecosystem of the Digital Twin of the Earth.
Location Innovation Academy
The recently launched Location Innovation Academy is a free online training program based on the knowledge and ideas generated by the GeoE3 project. The free online academy empowers users to improve the accessibility, interoperability, and integration of their geospatial data and services. The academy is currently targeted towards national mapping agencies, meteorological institutions, and other organisations producing or using geospatial data from different countries. The Academy aims to help overcome the interoperability gaps that still exist between European countries.
The growing online training package currently includes three different courses for developing skills in: Data Management; Service Management; and Data and Service Integration.
The Location Innovation Academy also serves as the experimentation platform for a future OGC Academy that will help learners access and exploit the enormous amounts of knowledge generated by OGC. The Location Innovation Academy is hosted by OGC at academy.ogc.org. In support of the academy, OGC is also a Pact For Skills Member.
The Academy continues to be the main component of the DIS4SME project. DIS4SME aims to provide SMEs with high quality specialised training courses on data interoperability across different areas, including location data.
By Europe, for the WorldAs a participant in projects funded by the European Commission, OGC’s COSI Program – with its complementary research theme of “Full Spectrum Interoperability and Agile Reference Architecture” – is proud to develop valuable solutions that support the European Digital Strategy and help ensure a secure and sustainable life for not only the citizens of Europe, but the entire world.
The next OGC European Innovation Days showcase will be held July 2024 at FOSS4G Europe in Tartu, Estonia.
OGC is also hosting a session on European common data spaces at the 2023 INSPIRE Conference this November.
To stay up to date on all things OGC, including European projects, funding opportunities, Standards development, events, and more, subscribe to the OGC Newsletter.
The post European Innovation, Global Impact appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC API – Environmental Data Retrieval v1.1 Adopted as Official Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that version 1.1 of the OGC API – Environmental Data Retrieval (EDR) Standard has been approved by the OGC Membership for adoption as an official Standard.
The Standard is part of the OGC API family of Standards that each help advance OGC’s Mission to make the world’s location information FAIR: Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable.
The OGC API – EDR Standard makes it easy to access a wide range of data through a uniform, well-defined, simple Web interface that provides users with purely the data they require while shielding them from the complexities of the underlying data storage technologies.
A major use case for an EDR API is to retrieve small subsets from large collections of environmental data, such as weather forecasts, though many other types of data can be accessed. The important aspect is that the data can be unambiguously specified by spatio-temporal coordinates.
The Standard describes a series of requirements for developing an EDR API, including lightweight query interfaces that allow users to request spatio-temporal data at a specific Position, within a Radius, within a Cube, within an Area, along a Trajectory, or through a Corridor.
Version 1.1 of the Standard offers a number of backwards-compatible enhancements. One major enhancement is support for the HTTP POST method. This enhancement will make it possible to handle requests with large payloads, such as complex filter constraints. Another enhancement is greater flexibility in selecting a default Coordinate Reference System (CRS) to be used when a client application has not indicated a preferred CRS. This enhancement will make it easier to serve data that is referenced to national or regional coordinate reference systems.
The other major enhancement is support for additional custom or categorical dimensions to use in queries in addition to the usual (x,y,z,t) continuous spatio-temporal dimensions. An example use case would be to request data for a specific wavelength or select from a specific waveband. A common meteorological use case would be to query data from a specific forecast from an ensemble of simultaneous forecasts.
The OGC API – EDR Standard supports a full range of use cases: from retrieving time-series observations to sub-setting multi-dimensional data cubes along user-supplied sampling geometries. Such sampling geometries are provided by a client through query patterns that use a set of common parameters. These query patterns provide useful building blocks to allow the composition of APIs that satisfy a wide range of geospatial data use cases. By defining a small set of query patterns, the OGC API – EDR Standard helps to simplify the design of systems, as they can be performance tuned for the supported queries – thus making it easier to build robust and scalable infrastructure.
To help users implement the OGC API – EDR Standard, an OpenAPI definition document and schema definition files have been published, alongside the Standard, on the OGC API – EDR page.
To learn more about how the family of OGC API Standards work together to provide modular “building blocks for location” that address both simple and the most complex use-cases, visit ogcapi.org.
OGC Members interested in staying up to date on further progress of this standard, or contributing to its future development, are encouraged to join the OGC API – EDR Standards Working Group via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about participating in this SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
As with any OGC Standard, the OGC API – Environmental Data Retrieval 1.1 Standard is free to download and implement. Interested parties can view and download the Standard from the OGC API – EDR page.
The post OGC API – Environmental Data Retrieval v1.1 Adopted as Official Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Welcomes Dr. Simon Cox as next Visiting Fellow
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to Welcome Dr. Simon Cox as our next Visiting Fellow. Simon will use his expertise and experience to help the organization take the new “OGC Rainbow” interoperability environment to the next level.
With its OGC Rainbow, OGC is building the most advanced interoperability framework in the geospatial domain. OGC Rainbow connects taxonomies, profiles, Standards, schemas, metadata, and other elements and enables reliable knowledge generation and decision making, all in a machine- and human-friendly environment.
Dr. Simon Cox will help OGC to further develop the conceptual model behind OGC Rainbow and review all of the underlying assumptions and use cases. Simon will also play a critical role in communicating and coordinating OGC Rainbow with other standards organizations.
“I am excited that Simon will join our work to enhance the level of interoperability seen in the geospatial domain,” said OGC Chief Technology Innovation Officer, Dr. Ingo Simonis. “Simon has excellent expertise in data modeling and extracting modeling patterns and mechanisms. I am confident that Simon will help us take the work around our ‘OGC Rainbow’ interoperability environment to the next level.”
Dr. Simon Cox worked for many years for the leading Australian science and technology organization, CSIRO. Simon has been involved in OGC activities since the year 2000, and received an OGC Gardel’s Award in 2006. Recently, Simon made substantial contributions to the joint OGC/W3C efforts on spatial data on the web.
Simon was the primary driving force behind the creation of the initial resources upon which OGC Rainbow has been built and led the establishment of the OGC Naming Authority – the group that governs OGC’s registries and Standards schemas. After retiring from CSIRO earlier this year, he has maintained an involvement in vocabulary management and publication, and in cross-domain metadata through CODATA and DDI.
“I’m looking forward to renewing my engagement with OGC,” said Simon. “I’ll bring perspectives from recent engagements in environmental and social sciences where adaptation of OGC and W3C standards to specific applications, and presentation of that to a variety of audiences, remains a challenge.”
OGC’s Visiting Fellow program was established to support OGC’s integrated standards and innovation strategy, which falls under the leadership of OGC’s Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons, and Chief Technology and Innovation Officer, Dr. Ingo Simonis. The program welcomes highly accomplished, seasoned experts from around the world to augment OGC’s leadership team with external targeted expertise and support the strategic objectives of the Consortium for durations of 3-9 months.
If you are interested in the OGC Visiting Fellow program and wish to be considered, please contact OGC using the form at ogc.org/contact.
The post OGC Welcomes Dr. Simon Cox as next Visiting Fellow appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 18:46
18:46 A Message from Prashant Shukle on Behalf of the OGC Board of Directors
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The OGC Board of Directors of the Open Geospatial Consortium congratulate Dr. Nadine Alameh on her selection as the inaugural Executive Director of the Taylor Geospatial Institute.
As her final week with the Open Geospatial Consortium draws to a close, we know that we have greatly benefitted from her transformational leadership over the last 5 years and are committed to the ongoing process of modernization within the OGC.
OGC Members and Staff work on very comprehensive and high-impact activities in the areas of Defense and Intelligence, Climate and Disasters, Health, Smart Cities and Digital Twins, the Metaverse, and advanced technology domains including Space and Earth Observation or Cloud Native Geospatial.
As the board searches for a new Chief Executive Officer, the Board and Staff are committed to ensuring that our focus will be sharp, and our momentum will not slow. We will continue to develop geospatial standards and solve interoperability issues; and serve as the leading geospatial consortium by bringing individuals and organizations together from around the world to collaborate, innovate, and develop solutions to some of the world’s toughest data and technology issues.
The Board of the OGC has started to develop a transparent, objective, merit-based process for the next Chief Executive Officer of the Open Geospatial Consortium. Please check ogc.org for any updates.
I look forward to seeing you at our in-person meetings, webinars, standard working groups, domain working groups, and at various high-level fora and research & innovation initiatives.
Should you have any questions, please send your enquiries here.
Prashant Shukle, Board Chair
On behalf of the
Open Geospatial Consortium
The post A Message from Prashant Shukle on Behalf of the OGC Board of Directors appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 Developers invited to the 2023 OGC API – Processes Virtual Code Sprint
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) invites developers to the 2023 OGC API – Processes Virtual Code Sprint to be held September 18-20, 2023, on Gitter. Registration for the code sprint is free and open to the public.

The Sprint will focus on refining the next version of the OGC API – Processes Standard and associated extensions.
The OGC API – Processes Standard supports the wrapping of computational tasks into executable processes that can be offered by a server through a Web API and be invoked by a client application. Typically, these processes combine raster, vector, coverage, and/or point cloud data with well-defined algorithms to produce new information.
Examples of computational processes that can be supported by implementations of OGC API – Processes include vector data analysis, imagery analysis, and various types of Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhanced analysis.
An OGC Sprint is a collaborative and inclusive event driven by innovative and rapid programming with minimal process and organization constraints to support the development of new applications and candidate standards.
During the virtual code sprint, there will be an opportunity for joint discussion with all participants on the goals and objectives of the event, as well as the final briefing of findings and opinions of the participants. However, the majority of the time will be spent in collaboration between participants in active coding. The virtual code sprint will run from 9:00am to 5:30pm US Eastern Time each day.
To learn more about how the family of OGC API Standards work together to provide modular “building blocks for location” that address both simple and the most complex use-cases, visit ogcapi.org.
Registration for the 2023 OGC API – Processes Virtual Code Sprint is here. The Sprint will take place in the ogc-developer/Sprints Gitter room from 9:00am to 5:30pm (US Eastern) each day from September 18-20, 2023.
To learn more about future and previous OGC code sprints, visit the OGC Code Sprints webpage or join the OGC-Events Discord Server.
The post Developers invited to the 2023 OGC API – Processes Virtual Code Sprint appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC adopts CityGML 3.0 Part 2: GML Encoding as an official OGC Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the OGC Membership have approved the OGC City Geography Markup Language (CityGML) Part 2: GML Encoding Standard for adoption as an official OGC Standard.
The CityGML 3.0 GML Encoding Standard presents the GML encoding of the concepts defined by the CityGML 3.0 Part 1: Conceptual Model (CM) Standard, which was approved as an OGC Standard in 2021. The GML encoding is compliant to OGC GML versions 3.2 and 3.3 (thus also ISO 19136). This encoding can be used to store and exchange 3D city models in the GML format as data sets or via web services.
Since its first publication by OGC in 2008, CityGML has been an open standard used for the storage and exchange of virtual 3D city models. CityGML allows the integration of urban geodata for use across a variety of applications, including urban and landscape planning; Urban Digital Twins for Smart Cities; the Metaverse; Building Information Modeling (BIM); mobile telecommunication; disaster management; 3D cadastre; tourism; vehicle & pedestrian navigation; autonomous driving and driving assistance; facility management; and energy, traffic, and environmental simulations.
CityGML defines a “City” in a broad fashion to comprise not just built structures, but also the land surface, vegetation, water bodies, city furniture, and more. Despite its name, CityGML is useful for large areas and small regions, not just cities, and can represent real-world terrain and 3D objects at different Levels Of Detail (LOD) simultaneously. CityGML enables the consistent representation of 3D urban objects across different Geographic Information Systems and users.
CityGML 3.0 is an evolution of the previous versions 1.0 and 2.0 of CityGML that further enables the cost-effective sustainable maintenance of 3D city models. While previous versions standardized a GML exchange format, CityGML 3.0 standardizes the underlying information model and can thus be implemented in a variety of technologies beyond GML. As a result, governments and companies can increase the Return On Investment (ROI) of their 3D city models by being able to put the same models into play across different technology platforms and application fields.
This Part 2 of the Standard defines how the concepts developed in Part 1 are realized using XML and GML technologies. The CityGML 3.0 GML encoding represents a full mapping of the Conceptual Model. The encoding is derived fully automatically from the UML model following the UML-to-GML encoding rules as defined by ISO 19136.
A collection of example data sets for the CityGML 3.0 GML Encoding is available from the OGC CityGML-3.0 Encodings Public GitHub Repository.
OGC Members interested in staying up to date on the progress of this standard, or contributing to its future development, are encouraged to join the CityGML Standards Working Group (SWG) via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about participating in this SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
As with any OGC Standard, the open CityGML Part 2: GML Encoding Standard is free to download and implement. Interested parties can learn more about, view, and download the Standard from OGC’s CityGML Standard Page.
The post OGC adopts CityGML 3.0 Part 2: GML Encoding as an official OGC Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Compliance Certification Available for v1.0 of the OGC API – Processes Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the Executable Test Suite (ETS) for version 1.0 of the OGC API – Processes – Part 1: Core Standard has been approved by the OGC Membership. Products that implement the Standard and pass the tests in the ETS can now be certified as OGC Compliant.
The OGC API – Processes Standard supports the wrapping of computational tasks into executable processes that can be offered by a server through a Web API and be invoked by a client application. Typically, these processes combine raster, vector, coverage, and/or point cloud data with well-defined algorithms to produce new information. Examples of computational processes that can be supported by implementations of this Standard include vector data analysis, imagery analysis, and various types of Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhanced analysis. To learn more about how the family of OGC API Standards work together to provide modular “building blocks for location” that address both simple and the most complex use-cases, visit ogcapi.org.
Implementers are invited to validate their products using the new test suite, which is available on the OGC validator tool. Testing involves submitting the endpoint of an OGC API – Processes implementation to be assessed. The validator tool sends the appropriate requests to the endpoint of the implementation and then evaluates the responses. These tests typically take only 5-10 minutes to complete. Once a product has passed the tests, the implementer can submit an application to OGC for use of the OGC Compliant trademark on their product.
To support developers with implementation of the standard, GeoLabs ZOO-Project 2.0 and Ecere GNOSIS Map Server 1.0 have been designated as reference implementations of the standard after the software products successfully passed the compliance tests.
The OGC Compliance Program offers a certification process that ensures organizations’ solutions are compliant with OGC Standards. It is a universal credential that allows agencies, industry, and academia to better integrate their solutions. OGC compliance provides confidence that a product will seamlessly integrate with other compliant solutions regardless of the vendor that created them.
More information about the OGC compliance process is available at ogc.org/compliance. Implementers of version 1.0 of the OGC API – Processes – Part 1: Core Standard – or other OGC Standards – are welcomed to validate their products using the OGC validator tool.
The post OGC Compliance Certification Available for v1.0 of the OGC API – Processes Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 18:39
18:39 A recap of the 126th OGC Member Meeting, Huntsville, AL, USA
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)From June 5-9, almost 200 geospatial innovators, influencers, and leaders from across the globe attended OGC’s 126th Member Meeting – with 100 more attending virtually. Hosted by GEOHuntsville at the beautiful Huntsville Botanical Garden in Alabama, USA, meeting attendees spent the week discussing the latest geospatial innovations and hearing how geospatial is transforming organizations and industries across the globe.
The meeting was additionally sponsored by Hexagon, OpenSensorHub (Botts Innovative Research and GeoRobotix), Ethar, Womble Bond Dickinson, and Compass-HSV.
The week saw the usual abundance of Standards Working Group (SWG) and Domain Working Group (DWG) meetings, networking & social events (including a fantastic Sunday pre-meeting gathering at the Signals Museum, hosted by Ethar), two award presentations – a Lifetime Achievement Award as well as the new Community Impact Award – and several special sessions, including a Space Standards ad hoc, an Open Science Summit, a Portrayal Workshop, a Connected Systems track, a Defense and Intelligence Track, and a Climate Workshop.
The full agenda for the 126th OGC Member Meeting is available here. Read on for an overview of the best bits, below.
 OGC CEO, Dr. Nadine Alameh (L), OGC CSO, Scott Simmons (M), and Stan Tillman from meeting sponsor, Hexagon.
Opening Session
OGC CEO, Dr. Nadine Alameh (L), OGC CSO, Scott Simmons (M), and Stan Tillman from meeting sponsor, Hexagon.
Opening Session
Opening the meetings on Monday morning was David Lucas, the Executive Director of host GEOHuntsville, who welcomed attendees and provided event context. This was followed by a welcome from the City of Huntsville Mayor, Tommy Battle.
Next, we heard from Stan Tillman, of meeting sponsor Hexagon, who provided information on the company with specific information regarding Hexagon Digital Reality capabilities. Dr. Chris Tucker, representing additional meeting sponsors OpenSensorHub participants Botts Innovative Research and GeoRobotix, then highlighted the upcoming session on Tuesday for Connected Systems.
OGC CEO Dr. Nadine Alameh then provided a CEO Welcome and described the value of recent organizational changes in OGC. Prashant Shukle, Chair of the OGC Board of Directors then gave a greeting from the Board and highlighted a commitment by the Board to more actively participate in OGC activities.
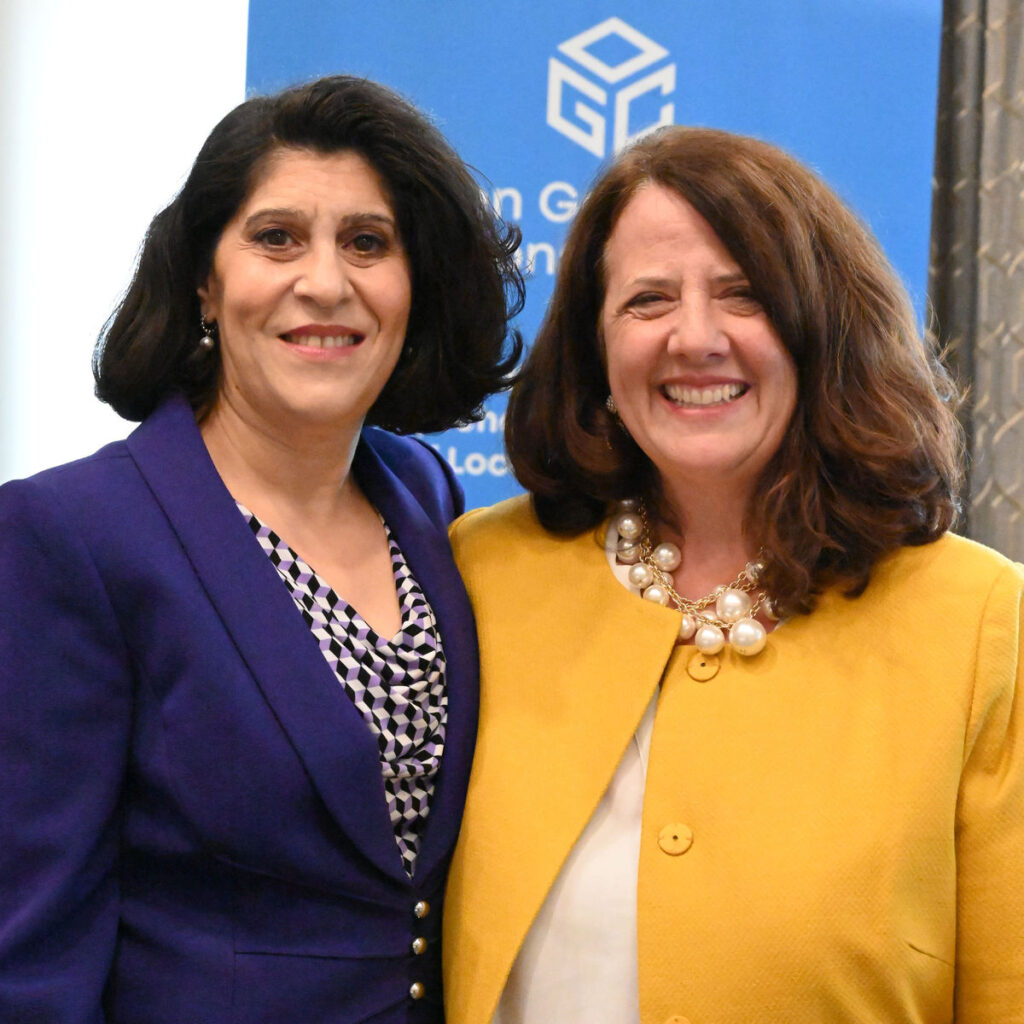 OGC CEO, Dr. Nadine Alameh (L), with Patty Mims, Director of Global National Government, Esri
OGC CEO, Dr. Nadine Alameh (L), with Patty Mims, Director of Global National Government, Esri
Nadine’s regular fireside chat followed, this time with Patty Mims, Director of Global National Government, Esri. As has become the trend for these chats, they discussed the motivation for joining the geospatial industry as well as provided advice for others to join and succeed in the community.
Trevor Taylor, Senior Director, Member Success and Development of OGC, welcomed new members and refreshed attendees on the new OGC membership model that’s now in place for new members.
I, Scott Simmons, Chief Standards Officer of OGC, then wrapped up the session by providing some logistics information for the week and describing the process to be followed in the coming weeks-to-months to roll out of the new Technical Committee Policies and Procedures. I also described the new tools in place for submitting presentation requests and special sessions for meetings.
Special SessionsThe Space Standards ad hoc continued the discussion from the 125th Member Meeting concerning where OGC should work in Space Standards, which identified a number of topical areas for Standardization as well as existing Standards covering some portions of those areas. Participants at this session identified areas of focus and proposed a new Domain Working Group (DWG) that will begin the chartering process in the coming weeks. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The Open Science Summit focused on a proposal for a new OGC Pilot project for an Open Science Persistent Demonstrator. NASA, Google, and the European Space Agency (ESA) each presented information on their own platforms. The Summit then followed with an open discussion on which other platforms might exist and what should be included. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
 Marge Cole, Director, Collaborative Solutions and Innovation Programs, OGC, speaking at the Open Science Summit
Marge Cole, Director, Collaborative Solutions and Innovation Programs, OGC, speaking at the Open Science Summit
The Portrayal Workshop: OGC has been modernizing its Standards for the portrayal of geospatial data. Numerous other communities have dependencies on the OGC Standards portfolio and need to understand the applicability of these newer Standards and how they replace the functionality of legacy Standards. The Portrayal Workshop was organized jointly with the International Cartographic Association (ICA) and was run to develop an OGC Technical Paper for “Standards supporting cartographic best practices.” OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The Connected Systems track: OGC has chartered new working groups to update and create a RESTful implementation of sensor-related Standards. The Autonomy, Sensors, Things, Robots, and Observations (ASTRO) Domain Working Group (DWG) investigates requirements and standardization targets and the Connected Systems Standards Working Group (SWG) is building the new Standards. These groups held a full-afternoon track to describe the intent of the Connected Systems API, the relationship of the work to other OGC APIs and the Sensor Web Enablement (SWE) Standards, and to demonstrate how the new Standards work in practice. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal, as well as the Demonstration here.
The Defense and Intelligence Track: The Defense and Intelligence DWG takes a broad look at the use of Standards in defense/intelligence operations as well as the requirements for interoperability that can be solved, in part, by Standards. The DWG held a full-afternoon track to explore the fundamental concepts and thus bring participants to a baseline of understanding. The session also explored where OGC members could contribute to new Standards in imagery & motion imagery as well as Space. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The Climate Workshop: OGC’s Climate Resilience DWG organized a Climate Workshop for Friday where the DWG defined the nature of its mission for resilience as the “ability of a system to compensate for impacts.” The session highlighted numerous initiatives underway in OGC and other organizations, framing them in terms of opportunities for impact. The workshop also expressed a proposed timeline for the next OGC Climate Resilience Pilot. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
Today’s Innovation/Tomorrow’s Technology and Future DirectionsThe popular Today’s Innovation/Tomorrow’s Technology and Future Directions session focused on ongoing OGC research and deployment of the nascent OGC Rainbow (borne from the OGC Definitions Server), which represents the state-of-the-art in enabling semantic interoperability.
OGC Rainbow is a web-accessible source of information about things (“Concepts”) that the OGC defines or that communities ask the OGC to host on their behalf. OGC Rainbow comprises several registries linked to common access for both human- and machine-readable representation of the data.
The OGC Definitions Server has long provided Coordinate Reference System (CRS) definitions, terminology definitions used in OGC Standards, and code lists for various domains of interest. As the capability of the OGC Rainbow increases, OGC will be registering requirements from Standards, representation of the OGC Building Blocks, and linkages to other authoritative registries. OGC Rainbow will improve consistency in the geospatial standards community and allow for expedited development of new capabilities.
Dr. Ingo Simonis and Dr. Rob Atkinson of the OGC COSI Program explained the capabilities and use cases of the OGC Rainbow and moderated open discussion amongst participants regarding the use of OGC Rainbow. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal. Stay tuned to the OGC Blog for more on the OGC Rainbow soon.
Dinner & AwardsThe always wonderful Executive Dinner was held on Wednesday night at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center – Davidson Center for Space Exploration, where attendees had the unforgettable experience of dining under an actual Saturn V rocket – one of only three in the world!
 Attendees of the Executive Dinner had the unforgettable experience of dining under an actual Saturn V Rocket
Attendees of the Executive Dinner had the unforgettable experience of dining under an actual Saturn V Rocket
At the dinner, two awards were presented: Dr. Jeff de La Beaujardiere received the OGC Lifetime Achievement Award; and Natural Resources Canada received the inaugural OGC Community Impact Award.
Dr. Jeff de La Beaujardiere was selected for the Lifetime Achievement award due to his long standing leadership, commitment, and support for the advancement and uptake of standards used for the dissemination of Earth Science information. In the OGC community, Jeff is best known as the Editor of the OGC Web Map Service (WMS) Specification: a joint OGC/ISO Standard that now supports access to millions of datasets worldwide. OGC WMS was the first in the OGC Web Services suite of Standards and is the most downloaded Standard from OGC. But most importantly, the OGC WMS Standard truly revolutionized how geospatial data is shared and accessed over the web. Jeff was also a major contributor to other OGC Standards, including the OGC Web Services Architecture, the OGC Web Map Context, OGC Web Terrain Service, and OGC Web Services Common.
The new OGC Community Impact award highlights the importance of collaboration, volunteering time and energy, advancing technologies and standards, raising awareness, and helping solve critical issues across the geospatial community. Natural Resources Canada exemplifies all of these qualities through their championing of innovation and standards. They consistently go above and beyond as both an OGC Member, and as a member of the wider geospatial community.
My well-deserved congratulations go out to both recipients!
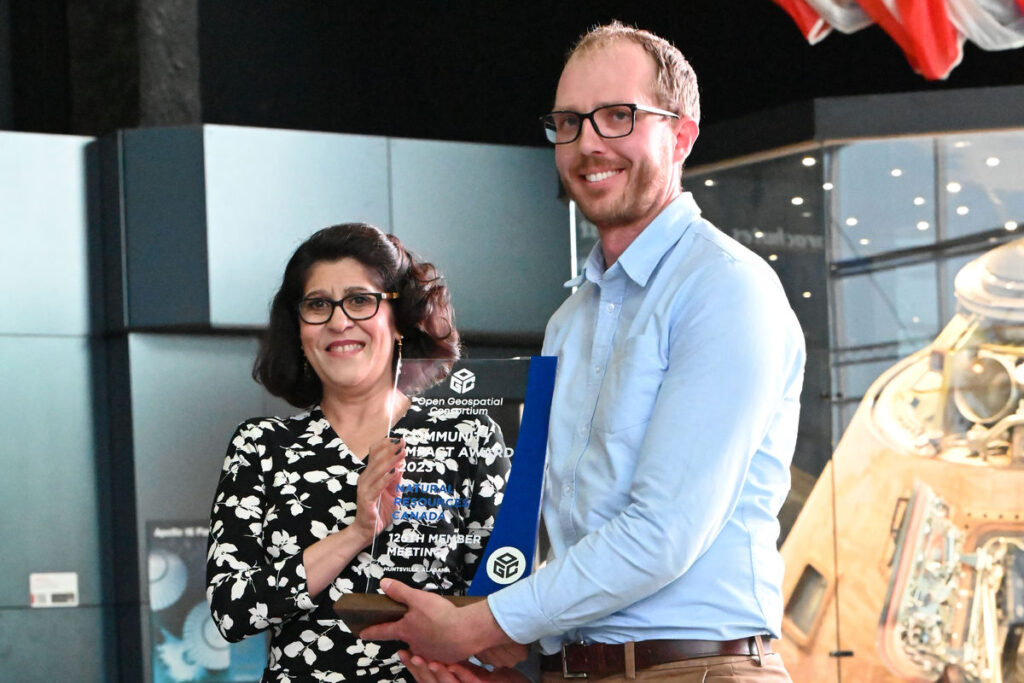 Ryan Ahola (R) accepts the inaugural OGC Community Impact Award, on behalf of Natural Resources Canada, from OGC CEO Dr. Nadine Alameh (L)
Important Things and the Closing Plenary
Ryan Ahola (R) accepts the inaugural OGC Community Impact Award, on behalf of Natural Resources Canada, from OGC CEO Dr. Nadine Alameh (L)
Important Things and the Closing Plenary
Wrapping up the week, I opened the Important Things session with a rapid, 15-minute summary of the entire meeting week that included slides and content from a large number of Working Group sessions. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The Important Things session then featured a discussion on how much OGC SWGs should accommodate developer interests and existing applications vs. optimizing their Standards work to meet the Standard requirements. OGC Members then discussed the issue and provided numerous examples of the conflict in current work. OGC Members can read the notes from the session in the Etherpad “Important-Things-2023-06”.
The Closing Plenary, though mostly focused on presentations and voting, also saw several presentations. Carsten Rönsdorf of Ordnance Survey provided a summary of the effectiveness of the model-driven standard authoring that was used for CityGML 3.0 and is now underway with MUDDI. Ali Al’Awaji highlighted the success of recent cooperation between his organization, the General Authority for Survey and Geospatial Information (GASGI) and OGC. The remainder of the session advanced a number of Standards, SWGs, and documents toward vote or publication.
Thank you to our communityThe GEOHuntsville Member Meeting was not only one of our most attended, but also one of our most memorable – with the beautiful grounds and the unforgettable Saturn V Rocket. As always it was a pleasure seeing our Members interacting, collaborating, and driving technology and standards development forward. It’s the vibrancy and enthusiasm of our community that makes OGC truly special – and my job so enjoyable. So I thank you all, once again, for your time & energy and your dedication to making OGC the world’s leading and most comprehensive community of location experts.
Be sure to join us for the 127th Member Meeting, happening September 25-29, 2023, at the Lifelong Learning Institute, Singapore. Registration and further info can be found at ogcmeet.org.
Sponsorship opportunities are also available: download this brochure or contact OGC for more info.Be sure to subscribe to the OGC Update Newsletter to stay up to date on all things OGC, including future OGC Member Meetings, funding opportunities, and how to contribute to our open Standards.

The post A recap of the 126th OGC Member Meeting, Huntsville, AL, USA appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:08
17:08 The 2023 OGC Tiling Interfaces Code Sprint – How it went!
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)On June 12-14, 2023, OGC held its 2023 Tiling Interfaces Code Sprint at OGC Strategic Member NGA’s Moonshot Labs in St. Louis, Missouri. The code sprint focused on a select set of Application Programming Interface (API), database, and encoding standards related to map tiles. An API is a standard set of documented functions that expose the capabilities supported or data offered by an application, or service to other applications.
OGC code sprints are collaborative and inclusive events that support the development and refinement of open standards by providing software developers the time and space to focus on projects that implement the standards.
By experimenting with emerging ideas in the context of geospatial standards, OGC code sprints help improve interoperability of existing standards by experimenting with new extensions or profiles, and building or enhancing software products to implement the standards.
In addition, the sprints’ mentor streams provide developers with a helping hand when learning how to use the standards and projects so that they can build a working understanding of them that will last beyond the duration of the sprint.
The mentor stream at the Tiling Interfaces Code Sprint included three entry-level tutorials that used practical use-cases to introduce participants to the standards. One tutorial focused on how to serve vector tiles using the OGC API – Tiles standard, while another focused on compliance testing, and the third provided an overview of a web-based product that implements several OGC standards.
The 2023 OGC Tiling Interfaces Code Sprint focused on the following Standards and specifications:
- OGC API – Tiles: An approved Standard that specifies building blocks for creating Web APIs that support the retrieval of geospatial information as tiles.
- OGC API – Maps: A candidate Standard that specifies building blocks for serving spatially referenced and dynamically rendered electronic maps and charts.
- Changesets API: A prototype specification based on outcomes from OGC Testbed-15 that provides the foundation for a ‘Transactional Tiles API Extension’ for OGC API – Tiles.
- Vector Tiles Extension to GeoPackage: A prototype extension of the OGC GeoPackage Standard to support the use of vector tiles.
- Variable Width Tile Matrix: A grid suited for the whole globe that keeps the data in a geographic Coordinate Reference System.
- Web Map Tile Service (WMTS): The popular OGC Standard that specifies a web service that can serve map tiles of spatially referenced data using tiled images with predefined content, extent, and resolution. The OGC WMTS Standard is the base standard for the WMTS profiles of the US National System for GEOINT (NSG) and the Defense Geospatial Information Working Group (DGIWG).
At its peak, the code sprint had 50 concurrent active users participating remotely across multiple channels on the code sprint’s online platform. In-person participation saw a dozen participants from NGA, OGC, US Army Geospatial Center, UK Defence Science & Technology Laboratory (Dstl), Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (CREAF), Pixalytics Ltd., Compass, FlightSafety International, and University of Maryland.
Screenshots of a selection of applications deployed for the code sprint are shown below.
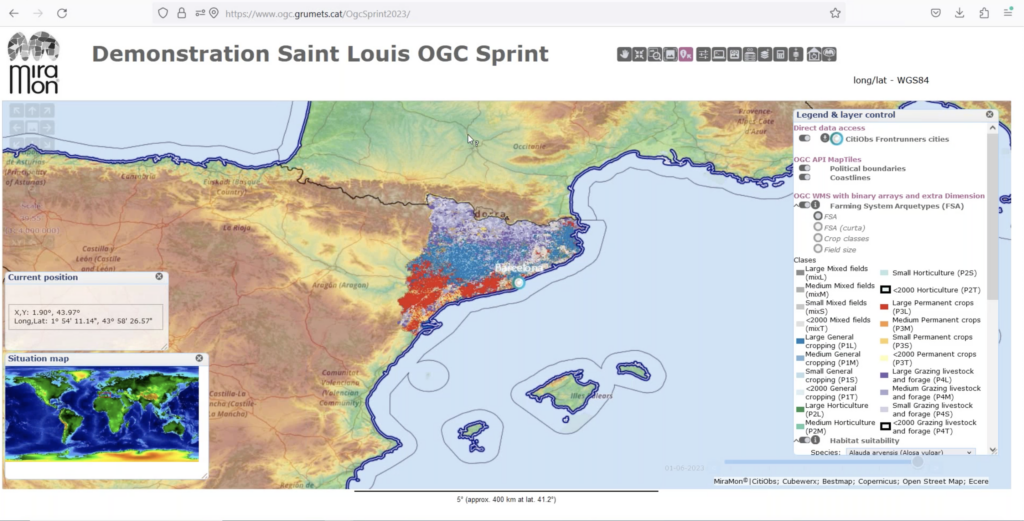 Figure 1 (click to enlarge)
Figure 1 (click to enlarge)
Figure 1 is a screenshot of the MiraMon browser accessing multiple OGC-compliant services and APIs deployed by CREAF and other participants.
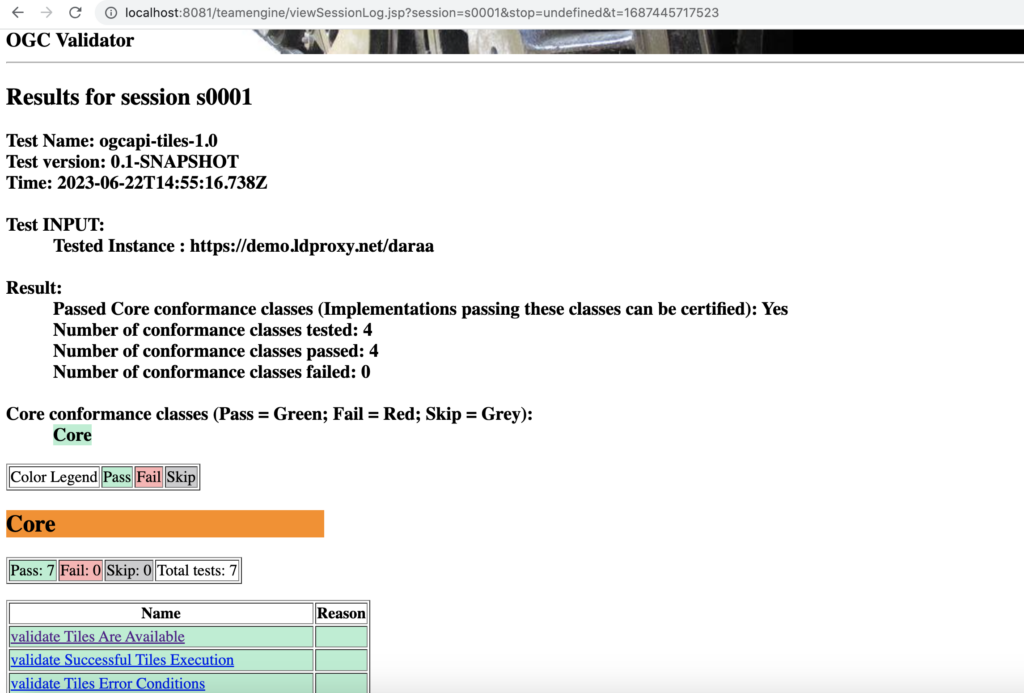 Figure 2 (click to enlarge)
Figure 2 (click to enlarge)
Figure 2 is a screenshot of TEAM Engine, the open source software used by the OGC Validator, presenting test results for a specific implementation of OGC API – Tiles.
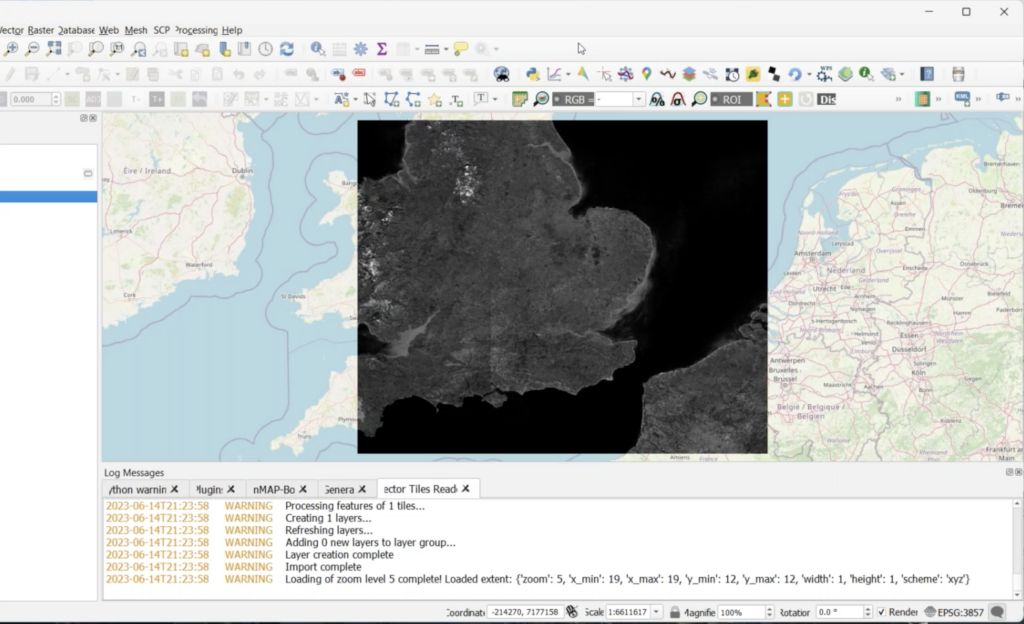 Figure 3 (click to enlarge)
Figure 3 (click to enlarge)
Figure 3 is a screenshot of the open source QGIS Desktop GIS with GDAL embedded to enable import and display of map tiles and vector tiles.
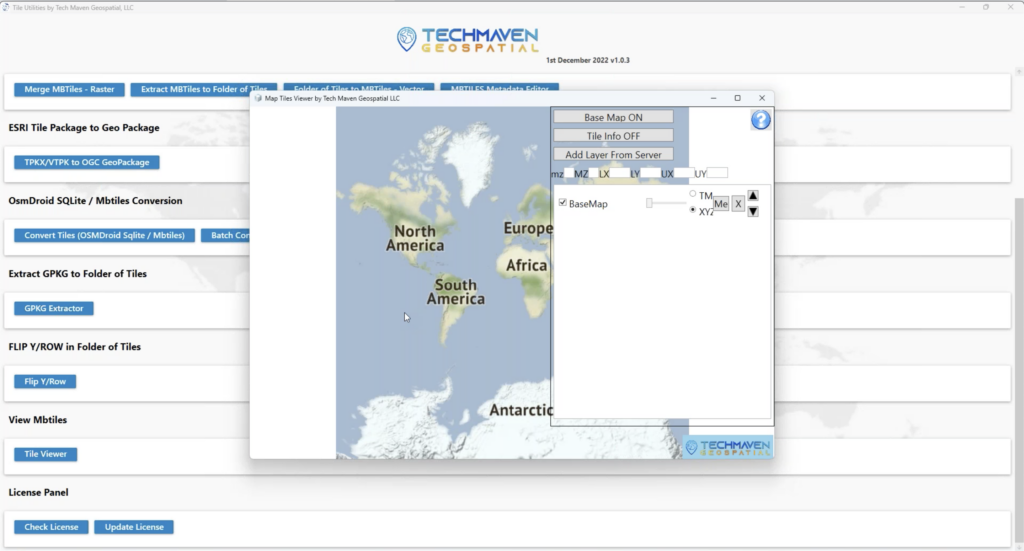 Figure 4 (click to enlarge)
Figure 4 (click to enlarge)
Figure 4 is a Map Tiles viewer by Tech Maven Geospatial.
 Figure 5 (click to enlarge)
Figure 5 (click to enlarge)
Figure 5 is a screenshot of the pygeoapi application enabled to support OGC API – Tiles.
 Figure 6 (click to enlarge)
Figure 6 (click to enlarge)
During the code sprint, personnel from the US Army Geospatial Center (AGC) presented the Releasable Basemap Tiles (RBT) product which has been in development at AGC (Figure 6). The presentation enabled participants to identify an approach for how QGIS and GDAL could support workflows that involve the downloading of vector tiles and map tiles from an OGC API and the storage of the tiles in a GeoPackage.
 Figure 7 (click to enlarge)
Figure 7 (click to enlarge)
Contains OS data © Crown copyright and database right 2023.Figure 7 shows a map created by KORTxyz from the vector tiles distribution of the Ordnance Survey Zoomstack product and accessed through an OGC API – Tiles interface.
What did we learn?The following are some of the lessons learned during the code sprint, and recorded by participants on the final day of the code sprint.
There is a need for further developer guidance documents for implementing OGC API – Tiles, particularly with regard to the placement on tileset resources. Such guidance should include clarification on the handling of relation types such as ‘conformance’ that can be represented as simple string literals and also as URLs.
There is a need to make sure there exists a well-documented user journey for people that want to use OGC API – Tiles through QGIS. For example, documentation to take a beginner from their first line of code to a more advanced stage.
Although some work has been done on vector tiles within OGC, more work is needed to advance the specification towards becoming an OGC Standard. Some of the work that could be carried out includes, for example, development of a Best Practice document. RBT could provide a foundation for such a Best Practice.
For future code sprints, it may be necessary to introduce participants to the basics of the specifications that are in focus for the code sprint ahead of the event. Further, it would be helpful to participants such as students to have specific instructions to help participants prepare for the code sprint.
Conclusions and RecommendationsThe code sprint met all of its objectives and achieved its goal of supporting the implementation of open geospatial standards within the developer community. Furthermore, the code sprint provided an environment for development and testing of prototype implementations of open standards and a starting point for developers to learn about the draft and approved standards, as well as their implementations.
The participants identified the following recommendations at the conclusion of the code sprint:
- A future code sprint that includes the OGC CDB Standard should examine how vector tiles could be embedded in such a data store.
- AGC is interested in how the World Mercator coordinate reference system (reference EPSG:3395) could support vector tiles in a GeoPackage. The question for future experimentation is whether this could be specified so that it can be implemented by any developer.
- The application of OGC API – Tiles in partitioning and indexing content from an implementation of the OGC SensorThings API standard and the OGC API – Connected Systems candidate standard could be explored in a future code sprint.
- An initiative to develop content for the OGC e-learning resource and the OGC Compliance Program could help improve interoperability between implementations of OGC Standards.
- Although OGC API – Tiles is an approved standard, there is some work to do around addressing interoperability issues in the different implementations (see for instance this Issue on the OSGeo gdal GitHub.
To learn more about – and participate in – future OGC Code Sprints, visit the OGC Code Sprints webpage or sign up to the OGC Events Newsletter.
The post The 2023 OGC Tiling Interfaces Code Sprint – How it went! appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC proud to create European Innovation Events and Open Knowledge
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is proud to co-organize and sponsor upcoming European Innovation Events such as Data Week Leipzig 2023. The Location Innovation Academy continues to grow and support Open Knowledge.
Data Week Leipzig 2023 will run next week, June 26-30, 2023, in Leipzig, Germany, and online. OGC will present its new OGC European Innovation Days event and more at the event. Data Week Leipzig is an innovative networking and exchange event that highlights scientific, economic, and social perspectives of data and its use, and where industry, citizens, science, and public authorities can enter into dialogue. Special topics of Data Week Leipzig 2023 are Semantic Interoperability, the European Green Deal, NetZero Cities, sustainable, resilient development, and the Location Innovation Academy (see below). Digital strategies will be presented and discussed from the European to the local Leipzig City level. The event will be streamed to viewers worldwide.
Findings of the AD4GD (All Data for Green Deal) and GeoE3 Projects will be included in the topics of Monday’s European Innovation Day at Data Week. Several sessions on Data Spaces, Digital Twins, and Urban Planning will be held across Monday and Tuesday, while Wednesday will offer several workshops on Semantic Interoperability and the new “OGC Rainbow” environment – which represents the state-of-the-art in enabling semantic interoperability.
The Growing Location Innovation Academy
Starting as a hub for the distribution of knowledge and skills related to the publication and use of location-based information, the Location Innovation Academy is expanding its horizons and finding a larger audience, with a view to provide the foundation for the future OGC Academy. The Academy was presented during last week’s Open Data & Open Knowledge Workshop, hosted by GEO. The workshop emphasized the importance of open knowledge and open academies that provide not just information but also grow students’ ability to correctly interpret the available information to support better and more informed decision-making.Don’t miss the hybrid hands-on session providing detailed insights about the Location Innovation Academy during the European Innovation Days at Data Week Leipzig 23 on Tuesday June 27 @ 17:00 CEST.
 Learn more at academy.ogc.org
Learn more at academy.ogc.org
GeoE3 recently published a blog post entitled “Interested in new technologies of data services?” that outlines the free Data Service Management course offered by the Location Innovation Academy. The course teaches students everything they need to know about OGC API standards and how they can be implemented to manage geospatial data services more efficiently. This course and others offered by the Academy address the need, identified during GeoE3, to lower the barrier of entry for new users of APIs.
More information on the academy and the courses offered is available on GeoE3’s Location Innovation Academy information page. The Location Innovation Academy is hosted by OGC at academy.ogc.org.
For information and registration for the European Innovation Days, including the Semantic Interoperability and Location Innovation Academy sessions, see the Data Week Leipzig 23 website. For other events see the GeoE3 events and OGC events webpages.
The post OGC proud to create European Innovation Events and Open Knowledge appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC CEO Dr. Nadine Alameh receives 24th Annual Women in Technology Leadership Award
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is pleased to announce that OGC CEO, Dr. Nadine Alameh, has received the 24th Annual Women in Technology Leadership Award in the Non-Profit and Academia category, which honors women who demonstrate exemplary leadership traits and have achieved success in a non-profit organization or educational institution.
The Women in Technology’s Annual Leadership Awards seek to “recognize and honor female leaders whose achievements, mentorship and contributions to the community align with the WIT mission of advancing women in technology from the classroom to the boardroom” by honoring and celebrating female professionals who have found success in entrepreneurial, STEM, government, and corporate industries while inspiring colleagues, partners, and their community.
“These awards are a cornerstone of the WIT mission to advance women in technology from the classroom to the boardroom,” said Amber Hart, President of WIT and the Co-Owner/Founder, The Pulse of GovCon, in a press release for the awards. “Recognizing the success of these women provides a vision for current and future leaders of what is possible with determination and focus and highlights the role of mentorship and sponsorship in building a successful and meaningful career.”
In the nomination letter for the award, Chair of the OGC Board, Jeff Harris, Vice Chair, Prashant Shukle, and Board member, Zaffar Sadiq Mohamed-Ghouse, said that the OGC board nominated Nadine for her “outstanding global leadership of the Open Geospatial Consortium and its 500 members through a period of profound change.
“When Nadine assumed the role of Chief Executive Officer, she articulated a new vision and role for the OGC – one where it had to be relevant at the speed of change. To that end, she has worked tirelessly in pursuit of this vision as she mobilized some of the world’s largest technology companies, developed and developing national governments, and small- and medium-sized businesses and startups. That she delivered in a not-for-profit entity and with a steely resolve to ensure the global public interest – not only speaks of the scale of her achievements but also its impact on the global public good.”
The 24th Annual Leadership Awards were presented at a Gala on Thursday, May 18, 2023, at the Hyatt Regency in Reston, VA, USA.
The post OGC CEO Dr. Nadine Alameh receives 24th Annual Women in Technology Leadership Award appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 Dr. Jeff de La Beaujardiere receives OGC Lifetime Achievement Award
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that Dr. Jeff de La Beaujardiere has been selected as the latest recipient of the OGC Lifetime Achievement Award. The announcement was made last night during the Executive Dinner in the U.S. Space & Rocket Center at the 126th OGC Member Meeting in GeoHuntsville, AL.
Jeff has been selected for the award due to his long standing leadership, commitment, and support for the advancement and uptake of standards used for the dissemination of Earth Science information.
“I’m so happy that Jeff has been selected to receive the OGC Lifetime Achievement Award,” said OGC CEO, Dr. Nadine Alameh. “Jeff is more than a champion for standards, more than an OGC Gardels award winner, and more than the WMS editor and promoter: Jeff is a role model for many of us in geospatial circles, and has directly and indirectly influenced generations of interoperability enthusiasts to collaborate, to innovate, and to solve critical problems related to our Earth. From OGC and myself, I offer our congratulations and thank Jeff for his technical work – and for being such an inspiration to so many!”
For more than 25 years, Jeff’s support of open standards and OGC’s FAIR mission has improved access to Earth science information for countless users and decision-makers around the globe. Since 1995, Jeff has focused on improving public access to scientific data by pushing for it to be discoverable, accessible, documented, interoperable, citable, curated for long-term preservation, and reusable by the broader scientific community, external users, and decision-makers.
In the OGC community, Jeff is best known as the Editor of the OGC Web Map Service (WMS) Specification: a joint OGC/ISO Standard that now supports access to millions of datasets worldwide. OGC WMS was the first in the OGC Web Services suite of Standards and is the most downloaded Standard from OGC. But most importantly, the OGC WMS Standard truly revolutionized how geospatial data is shared and accessed over the web.
Jeff was also a major contributor to other OGC Standards, including the OGC Web Services Architecture, the OGC Web Map Context, OGC Web Terrain Service, and OGC Web Services Common.
Jeff’s journey with Standards – and his engagement with OGC – started back in 1998 when NASA was leading the effort to implement the Digital Earth program. At that time, Jeff championed interoperability standards as fundamental to realizing the Digital Earth vision. As part of his journey, he has provided leadership to the Geospatial Applications and Interoperability (GAI) Working Group of the U.S. Federal Geographic Data Committee and to the OGC Technical Committee.
In 2002 and 2003, Jeff served as Portal Manager for Geospatial One-Stop, a federal electronic government initiative. He led a team of experts in defining the requirements, architecture, and competitive solicitation for a Portal based on open standards and led an OGC interoperability initiative in developing and demonstrating a working implementation. This was a fast-paced, high-stakes effort involving many companies and agencies building on what today is the OGC Collaborative Solution & Innovation Program.
Jeff has received several awards for his leadership and impact in the many communities that he has participated in throughout his career, including the 2013 OGC Kenneth D. Gardels Award, the 2023 ESIP President’s Award, and the 2003 Falkenberg Award at AGU which honors “a scientist under 45 years of age who has contributed to the quality of life, economic opportunities, and stewardship of the planet through the use of Earth science information and to the public awareness of the importance of understanding our planet.”
With this lifetime achievement award, OGC recognizes and celebrates Jeff’s lifetime of service, and his steadfast support of FAIR geospatial information for the benefit of open science, and society.
The post Dr. Jeff de La Beaujardiere receives OGC Lifetime Achievement Award appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.

