Vous pouvez lire le billet sur le blog La Minute pour plus d'informations sur les RSS !
Canaux
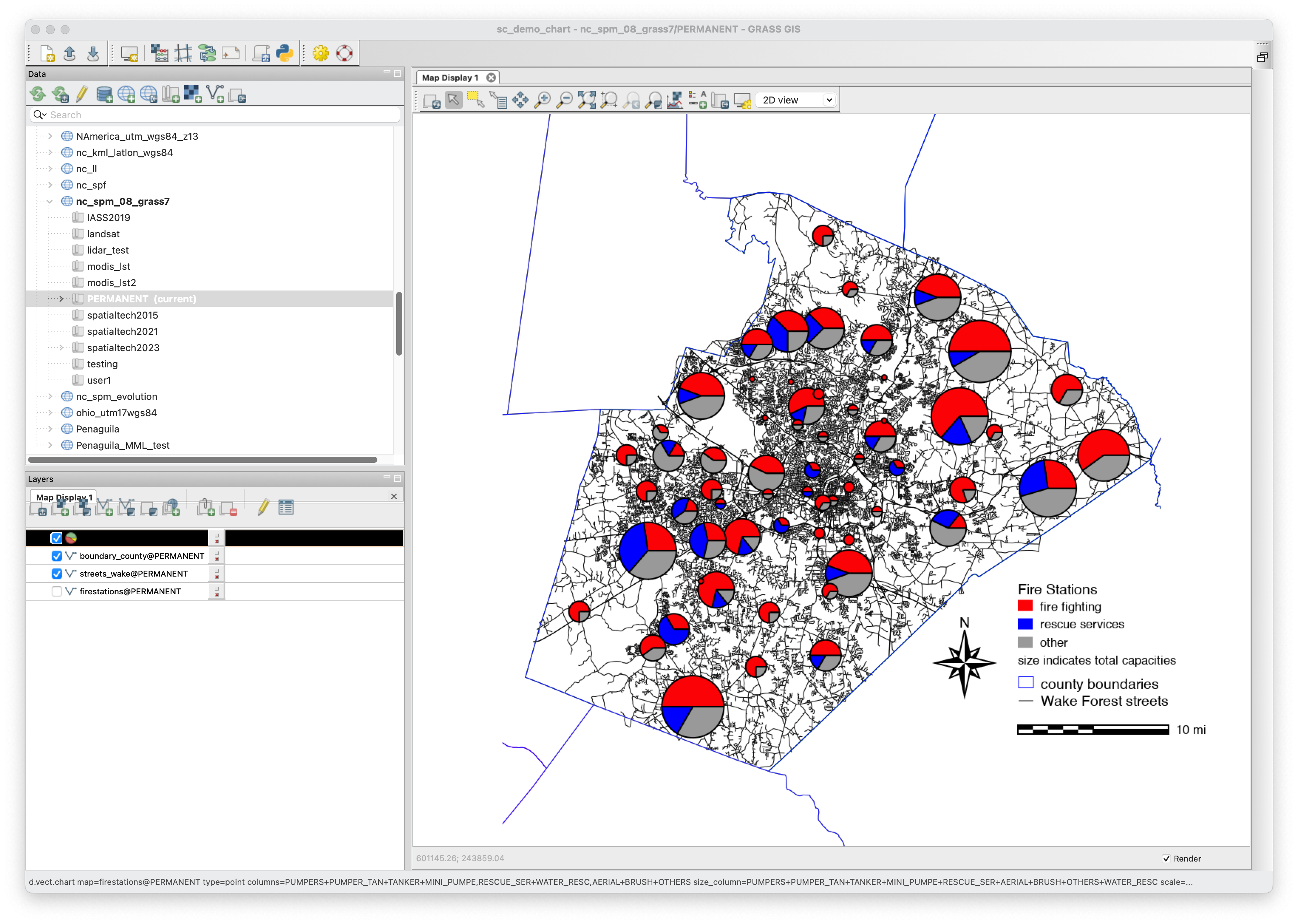
6119 éléments (1853 non lus) dans 50 canaux
 Dans la presse
(1672 non lus)
Dans la presse
(1672 non lus)
-
 Cybergeo
(1611 non lus)
Cybergeo
(1611 non lus) -
 Mappemonde
(60 non lus)
Mappemonde
(60 non lus) -
 Dans les algorithmes
(1 non lus)
Dans les algorithmes
(1 non lus)
 Du côté des éditeurs
(24 non lus)
Du côté des éditeurs
(24 non lus)
-
 Toute l’actualité des Geoservices de l'IGN
(15 non lus)
Toute l’actualité des Geoservices de l'IGN
(15 non lus) -
 arcOpole - Actualités du Programme
arcOpole - Actualités du Programme
-
 arcOrama
(9 non lus)
arcOrama
(9 non lus) -
 Neogeo
Neogeo
 Toile géomatique francophone
(110 non lus)
Toile géomatique francophone
(110 non lus)
-
Géoblogs (GeoRezo.net) (5 non lus)
-
 UrbaLine (le blog d'Aline sur l'urba, la géomatique, et l'habitat)
UrbaLine (le blog d'Aline sur l'urba, la géomatique, et l'habitat)
-
 Séries temporelles (CESBIO)
(2 non lus)
Séries temporelles (CESBIO)
(2 non lus) -
 Datafoncier, données pour les territoires (Cerema)
Datafoncier, données pour les territoires (Cerema)
-
 Cartes et figures du monde
Cartes et figures du monde
-
 SIGEA: actualités des SIG pour l'enseignement agricole
SIGEA: actualités des SIG pour l'enseignement agricole
-
 Data and GIS tips
Data and GIS tips
-
 ReLucBlog
ReLucBlog
-
 L'Atelier de Cartographie
L'Atelier de Cartographie
-
My Geomatic
-
 archeomatic (le blog d'un archéologue à l’INRAP)
archeomatic (le blog d'un archéologue à l’INRAP)
-
 Cartographies numériques
Cartographies numériques
-
 Carnet (neo)cartographique
Carnet (neo)cartographique
-
 GEOMATIQUE
GEOMATIQUE
-
 Évènements – Afigéo
(12 non lus)
Évènements – Afigéo
(12 non lus) -
 Afigéo
(12 non lus)
Afigéo
(12 non lus) -
 Geotribu
(50 non lus)
Geotribu
(50 non lus) -
 Conseil national de l'information géolocalisée
(9 non lus)
Conseil national de l'information géolocalisée
(9 non lus) -
 Icem7
Icem7
-
Makina Corpus (1 non lus)
-
 Oslandia
(1 non lus)
Oslandia
(1 non lus) -
 CartONG
(2 non lus)
CartONG
(2 non lus) -
 GEOMATICK
(6 non lus)
GEOMATICK
(6 non lus) -
 Geomatys
(3 non lus)
Geomatys
(3 non lus) -
 Les Cafés Géo
(1 non lus)
Les Cafés Géo
(1 non lus) -
 L'Agenda du Libre
(3 non lus)
L'Agenda du Libre
(3 non lus) -
 Conseil national de l'information géolocalisée - Actualités
(3 non lus)
Conseil national de l'information géolocalisée - Actualités
(3 non lus)
 Géomatique anglophone
(35 non lus)
Géomatique anglophone
(35 non lus)
-
 All Points Blog
All Points Blog
-
 Directions Media - Podcasts
Directions Media - Podcasts
-
 Navx
Navx
-
James Fee GIS Blog
-
 Maps Mania
(19 non lus)
Maps Mania
(19 non lus) -
 Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)
Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)
-
 Planet OSGeo
(16 non lus)
Planet OSGeo
(16 non lus)
 Géomatique anglophone
Géomatique anglophone
-
 13:36
13:36 Jorge Sanz: MSF Mapathon at Universitat de València
sur Planet OSGeo Last week for the first time since the pandemic I attended a Mapathon in person. With the geomaticblog.net retired, this is my first geospatial post on my own website ?.
What’s a mapathon? For those that don’t know the term, a mapathon is a gathering of volunteers to do some remote mapping with the objective of improve the cartography of an area of the world that does not have a proper map.
Last week for the first time since the pandemic I attended a Mapathon in person. With the geomaticblog.net retired, this is my first geospatial post on my own website ?.
What’s a mapathon? For those that don’t know the term, a mapathon is a gathering of volunteers to do some remote mapping with the objective of improve the cartography of an area of the world that does not have a proper map. -
 12:30
12:30 Jackie Ng: Announcing: mapguide-rest 1.0 RC6
sur Planet OSGeo6 years later, I have finally put out another release of mapguide-rest!
The reason for finally putting out a new release (besides being long overdue!), is that I needed a solid verification of the vanilla SWIG API binding work for MapGuide Open Source 4.0 and mapguide-rest was just the ideal project that touches almost every nook and cranny of the MapGuide API. So if mapguide-rest still works with the PHP binding in MapGuide Open Source 4.0, that is as good of an endorsement to the reliability and readiness of these bindings.
For this release of mapguide-rest, it is compatible with the version of PHP that comes with:
- MapGuide Open Source 3.1.2 (PHP 5.6)
- MapGuide Open Source 4.0 Beta 1 (PHP 8.1)
Download
Special thanks to Gordon Luckett and Scott Hamiester for assistance in internal testing of many internal builds of mapguide-rest that finally culminated in this long-overdue release.
Now that this is out of the way, it is back to MapGuide development proper and getting closer to the 4.0 release. -
 2:00
2:00 MapTiler: GeoCamp ES 2023
sur Planet OSGeoGeoCamp ES is a non-profit, free-to-attend, and self-financed national conference of the international collective Geoinquietos. To talk and learn about earth sciences, open geodata services, free software, and GIS applications, especially around the OSGeo community. -
 2:00
2:00 MapTiler: GeoCamp ES 2023
sur Planet OSGeoGeoCamp ES is a non-profit, free-to-attend, and self-financed national conference of the international collective Geoinquietos. To talk and learn about earth sciences, open geodata services, free software, and GIS applications, especially around the OSGeo community. -
 16:50
16:50 From GIS to Remote Sensing: Tutorial: Using Remotior Sensus in Copernicus JupyterLab
sur Planet OSGeo This is a tutorial about Remotior Sensus, a Python package that allows for the processing of remote sensing images and GIS data.
This is a tutorial about Remotior Sensus, a Python package that allows for the processing of remote sensing images and GIS data.
In particular, this tutorial describes the use of Remotior Sensus in Copernicus JupyterLab, which is a Jupyter Notebook service in a web-based environment, offering several tools for working with the Copernicus Data Space.This service can be accessed at this link [https:]] after a free registration to the Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem (CDSE).
The Jupyter Notebooks are available in 3 flavors: Small (2 CPU cores and 4GB RAM), Medium (2 CPU cores and 8GB RAM) and Large (4 CPU cores and 16GB RAM). As stated in the documentation, to ensure the fair use of resources by the CDSE users, it is recommended to start with the Small flavor and switch to a bigger only in case of issues with kernel crashing due to the lack of available memory.
Therefore, the Copernicus JupyterLab offers a great opportunity to use Copernicus data in a cloud environment. In this tutorial, we are going to see how to:- Download and preprocess Sentinel-2 images.
- Create a BandSet and prepare a training input
- Run a Random Forest classification
-
 15:31
15:31 Free and Open Source GIS Ramblings: Mapping Neo4j spatial nodes with GeoPandas
sur Planet OSGeoIn the recent post Setting up a graph db using GTFS data & Neo4J, we noted that — unfortunately — Neomap is not an option to visualize spatial nodes anymore.
GeoPandas to the rescue!
But first we need the neo4j Python driver:
pip install neo4j
Then we can connect to our database. The default user name is
neo4jand you get to pick the password when creating the database:from neo4j import GraphDatabase URI = "neo4j://localhost" AUTH = ("neo4j", "password") with GraphDatabase.driver(URI, auth=AUTH) as driver: driver.verify_connectivity()Once we have confirmed that the connection works as expected, we can run a query:
QUERY = "MATCH (p:Stop) RETURN p.name AS name, p.location AS geom" records, summary, keys = driver.execute_query( QUERY, database_="neo4j", ) for rec in records: print(rec)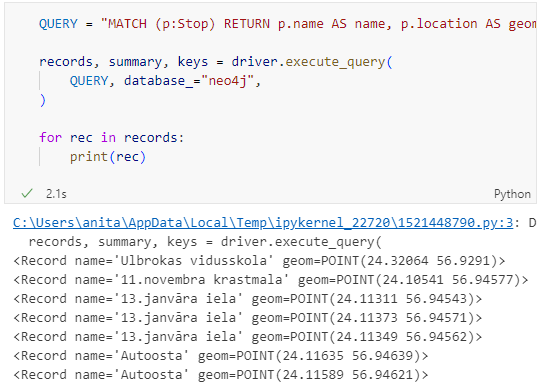
Nice. There we have our GTFS stops, their names and their locations. But how to put them on a map?
Conveniently, there is a to_db() function in the Neo4j driver:
import geopandas as gpd import numpy as np with driver.session(database="neo4j") as session: tx = session.begin_transaction() results = tx.run(QUERY) df = results.to_df(expand=True) df = df[df["geom[].0"]>0] gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame( df['name'], crs=4326, geometry=gpd.points_from_xy(df['geom[].0'], df['geom[].1'])) print(gdf) tx.close()Since some of the nodes lack geometries, I added a quick and dirty hack to get rid of these nodes because — otherwise —
gdf.explore()will complain about None geometries.

You can find this notebook at: [https:]]
Next step will have to be the relationships. Stay posted.
-
 1:19
1:19 Sean Gillies: 2024 Bear 100 registration
sur Planet OSGeoIn my previous post I said that I was going to register for the 2024 Bear 100 and I did. I was logged into UltraSignup promptly at 8 am on Friday and am glad, because this race apparently filled up within the day. 2024, let's fucking go!

Brunch at Upper Richards Hollow, 2023-09-29
-
 16:54
16:54 From GIS to Remote Sensing: Tutorial: Random Forest Classification Using Remotior Sensus
sur Planet OSGeo This is a tutorial about Remotior Sensus, a Python package that allows for the processing of remote sensing images and GIS data.In the last few months Remotior Sensus was frequently update to fix and integrate new functions, in particular for the integration with the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin for QGIS.
This is a tutorial about Remotior Sensus, a Python package that allows for the processing of remote sensing images and GIS data.In the last few months Remotior Sensus was frequently update to fix and integrate new functions, in particular for the integration with the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin for QGIS.
In this tutorial we are going to use Remotior Sensus to perform the Random Forest classification of a Copernicus Sentinel-2 image, which involves the following main steps:- Create a BandSet using an image
- Load a training input
- Perform the random forest classification
-
 12:44
12:44 QGIS Blog: Plugin Update Sept-Nov 2023
sur Planet OSGeoThis autumn, from September to November, 84 new plugins have been published in the QGIS plugin repository.
Here’s the quick overview in reverse chronological order. If any of the names or short descriptions piques your interest, you can find the direct link to the plugin page in the table below:
SOSIexpressions Expressions related to SOSI-data Puentes Run external Python files inside QGIS. UA CRS Magic ?????? ??????? ???????? ??? ?????????? ???? FilterMate FilterMate is a Qgis plugin, a daily companion that allows you to easily explore, filter and export vector data QWC2_Tools QGIS plug-in designed to publish and manage the publication of projects in a QWC2 instance. The plugin allows you to publish projects, delete projects and view the list of published projects. QGIS Fast Grid Inspection (FGI) This plugin aims to allow the generation and classification of samples from predefined regions. QDuckDB This plugin adds a new data prodivder that can read DuckDB databases and display their tables as a layer in QGIS. CIGeoE Toggle Label Visibility Toggle label visibility CIGeoE Merge Areas Centro de Informação Geoespacial do Exército Drainage the hydro DEM analysis with the TauDEM Postcode Finder The plugin prompts the user to select the LLPG data layer from the Layers Panel and enter a postcode. The plugin will search for the postcode, if found, the canvas will zoom to all the LLPG points in the postcode. Multi Union This plugin runs the UNION MULTIPLE tool, allowing you to use up to 6 polygon vector layers simultaneously. FLO-2D MapCrafter This plugin creates maps from FLO-2D output files. Download raster GEE download_raster_gee GisCarta Manage your GisCarta data TENGUNGUN To list up and download point cloud data such as “VIRTUAL SHIZUOKA” LADM COL UV Plugin de Qgis para la evaluación de calidad en el proceso de captura y mantenimiento de datos conformes con el modelo LADM-COL ohsomeTools ohsome API, spatial and temporal OSM requests for QGIS Social Burden Calculator This plugin calculates social burden Show Random Changelog Entry on Launch Shows a random entry in the QGIS version’s visual changelog upon QGIS launch Fotowoltaika LP Wyznaczanie lokalizacji pod farmy fotowoltaiczne LP KICa – KAN Imagery Catalog KICa, is QGIS plugin Kan Imagery Catalog, developed by Kan Territory & IT to consult availability of images in an area in an agnostic way, having as main objective to solve the need and not to focus on suppliers. In the beginning, satellite imagery providers (free and commercial) are incorporated, but it is planned to incorporate drone imagery among others. Risk Assessment Risk assessment calculation for forecast based financing ViewDrone A QGIS plugin for viewshed analysis in drone mission planning qgis2opengis Make Lite version of OpenGIS – open source webgis Quick Shape Update Automatic update of the shapes length and/or area in the selected layer CoolParksTool This plugin evaluates the cooling effect of a park and its impact on buildings energy and thermal comfort Nahlížení do KN Unofficial integration for Nahlížení do Katastru nemovitostí. PyGeoRS PyGeoRS is a dynamic QGIS plugin designed to streamline and enhance your remote sensing workflow within the QGIS environment. D4C Plugin This plugin allows the manbipulation from QGis of Data4Citizen datasets (Open Data platform based on Drupal and CKan) Avenza Maps’s KML/KMZ File Importer This plugin import features from KML e KMZ files from Avenza Maps Histogram Matching Image histogram matching process PV Prospector Displays the PV installation potential for residential properties. The pv_area layer is derived from 1m LIDAR DSM, OSMM building outlines and LLPG data. Save Attributes (Processing) This plugin adds an algorithm to save attributes of selected layer as a CSV file Artificial Intelligence Forecasting Remote Sensing This plugin allows time series forecasting using deep learning models. Salvar Pontos TXT Esse plugin salvar camada de pontos em arquivo TXT QGIS to Illustrator with PlugX The plugin to convert QGIS maps to import from Illustrator. With PlugiX-QGIS, you can transfer maps designed in QGIS to Illustrator! QCrocoFlow A QGIS plugin to manage CROCO projectsqcrocoflow Soft Queries This plugin brings tools that allow processing of data using fuzzy set theory and possibility theory. TerrainZones This Plugin Identifies & Creates Sub-Irrigation Zones Consolidate Networks Consolidate Networks is a a Qgis plugin bringing together a set of tools to consolidate your network data. AWD Automatic waterfalls detector SAGis XPlanung Plugin zur XPlanung-konformen Erfassung und Verwaltung von Bauleitplänen Monitask a SAM (facebook segment anything model and its decendants) based geographic information extraction tool just by interactive click on remote sensing image, as well as an efficient geospatial labeling tool. PLATEAU QGIS Plugin Import the PLATEAU 3D City Models (CityGML) used in Japan — PLATEAU 3D??????CityGML?????QGIS??????? FLO-2D Rasterizor A plugin to rasterize general FLO-2D output files. Geoportal Lokalizator PL: Wtyczka otwiera rz?dowy geoportal w tej samej lokacji w której u?ytkownik ma otwarty canvas QGIS-a. EN: The plugin opens the government geoportal in the same location where the user has the QGIS canvas open (Poland only). BorderFocus clicks on the edge center them on the canvas LANDFILL SITE SELECTION LANDFILL SITE SELECTION Bearing & Distance This plugin contains tools for the calculation of bearing and distances for both single and multiple parcels. Moisture and Water Index 2.0 Este complemento calcula el índice NDWI con las imágenes del Landsat 8. K-L8Slice Este nombre combina el algoritmo k-means que se utiliza para el agrupamiento (K) con “Landsat 8”, que es el tipo específico de imágenes satelitales utilizadas, y “Slicer”, que hace referencia al proceso de segmentación o corte de la imagen en diferentes clusters o grupos de uso del suelo. EcoVisioL8 Este complemento fue diseñado para automatizar y optimizar la obtención de índices SAVI, NDVI y SIPI, así como la realización de correcciones atmosféricas en imágenes Landsat 8. QGIS Animation Workbench A plugin to let you build animations in QGIS Catastro con Historia Herramienta para visualizar el WMS de Catastro en pantalla partida con historia. RechercheCommune Déplace la vue sur l’emprise de la commune choisie. Sentinel2 SoloBand Sentinel2 SoloBand is a plugin for easily searching for individual bands in Sentinel-2 imagery. CIGeoE Right Angled Symbol Rotation Right Angled Symbol Rotation CIGeoE Node Tool Tool to perform operations over nodes of a selected feature, not provided by similar tools and plugins. Spatial Distribution Pattern This plugin estimates the Spatial Distribution Pattern of point and linear features. Webmap Utilities This plugin provides tools for clustered and hierarchical visualization of vector layers, creation of Relief Shading and management of scales using zoom levels. Simstock QGIS Allows urban building energy models to be created and simulated within QGIS Fast Point Inspection Fast Point Inspection is a QGIS plugin that streamlines the process of classifying point geometries in a layer. Layer Grid View The Layer Grid Plugin provides an intuitive dockable widget that presents a grid of map canvases. Kadastr.Live Toolbar ????? ??????? ?? ????? Kadastr.Live ?? ??????????? ???????. S+HydPower Plugin designed to estimate hydropower generation. QollabEO Collaborative functions for interaction with remote users. digitizer digitizer NetADS NetADS est un logiciel web destiné à l’instruction dématérialisée des dossiers d’urbanisme. Runoff Model: RORB Build a RORB control vector from a catchment FlexGIS Manage your FlexGIS data LXExportDistrict Export administrative district PostGIS Toolbox Plugin for QGIS implementing selected PostGIS functions Chasse – Gestion des lots Fonctions permettant de définir la surface cadastrale des lots de chasse et d’extraire la liste des parcelles concernées par chaque lot de chasse, sous forme de fichier Excel®. Time Editor Used to facilitate the editing of features with lifespan information RST This plugin computes biophysical indices Japanese Grid Mesh Create common grid squares used in Japan. ???????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????CSV???????????????????????????????????????? Panoramax Upload, load and display your immersive views hosted on a Panoramax instance. StereoPhoto Permet la visualisation d’images avec un système stéréoscopique CIGeoE Merge Multiple Lines Merge multiple lines by coincident vertices and with the same attribute names and values. CIGeoE Merge Lines Merge 2 lines that overlap (connected in a vertex) and have same attribute names and values. Nimbo’s Earth Basemaps Nimbo’s Earth Basemaps is an innovative Earth observation service providing cloud-free, homogenous mosaics of the world’s entire landmass as captured by satellite imagery, updated every month. OpenHLZ An Open-source HLZ Identification Processing Plugin Selection as Filter This plugin makes filter for the selected features
-
 19:39
19:39 How OGC Contributes to FAIR Geospatial Data
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)Standards are a key element of the FAIR Principles of Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reusability. As such, the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) has been supporting the FAIR Principles for geospatial information since its formation 30 years ago.
Following the more recent codification of the FAIR principles, the growing recognition of their potential to improve data production, storage, exchange, and processing is seeing them being used to support and enhance recent technological developments such as artificial intelligence, crowdsourcing, data spaces, digital twins, cloud computing, and beyond. This blog post, therefore, offers an overview of select OGC standards and components that support FAIRness in geospatial data.
Within the whole OGC Standards suite, we can broadly distinguish two types of Standards: data format and transfer standards that facilitate data exchange between systems; and semantic interoperability standards that support a common understanding of the meaning of data. For example, OGC Standards that define interoperable geometrical information formats, such as 3D Tiles, GML, GeoPackage, GeoTiff, or KML, support FAIRness by facilitating data Access and Reuse.
Communication Standards
Starting with OGC Web Map Service (WMS) 1.0 in 2000, the suite of OGC Web Services Standards grew to become OGC’s most popular and successful suite of Standards. Services that implement OGC Web Services Standards give access to different kinds of data through the web. Most OGC Web Services provide instructions on how to post a message or build a query URL that gives access to the data behind the service. The URL contains an action to perform and parameters to modify the action and specify the form of the result.
While perfectly functional, the OGC Web Services Standards do not completely follow modern practices on the Web. In particular they do not focus on resources but on operations. To correct that issue, the OGC is evolving the OGC Web Services into the OGC APIs – open web APIs that define resources and use HTTP methods to retrieve them. OGC APIs have diverse functionalities, as explained below.
Communication Standards for Finding DataThe Catalog Service for the Web (CSW) is an OGC Web Service that provides the capacity to query a collection of metadata and find the data or the services that the user requires. Deploying a CSW (e.g. a GeoNetwork instance) is a way to comply with the FAIR sub-principle “F4. (Meta)data are registered or indexed in a searchable resource.” CSW is compatible with Dublin Core and ISO 19115 metadata documents. An interesting characteristic of the GeoNetwork is its capability to store attachments to the metadata. This provides a way to store the actual data as an attachment and link it to the distribution section of an ISO 19115. This ensures not only Findability of the metadata but also Findability of the data. In the Open Earth Monitor (OEMC) project, CSW can be effectively used to store metadata about the in-situ data and some of the results of the pilots, making them Findable on the web. The original Remote Sensing data is offered through a SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC).
The OGC API – Records Standard is an alternative to CSW that uses the aforementioned resource-oriented architecture. It gives a URL to each and every metadata/data record stored in the catalog, making it compliant with the FAIR sub-principle “F1. (Meta)data are assigned a globally unique and persistent identifier.” The OGC API – Records Standard is still in its draft phase and the authors are making efforts to exploit STAC good practices and make the two compatible.
For flexibility, in the CSW and OGC API – Records Standards, a metadata record is not obligatory, though it is desirable in many cases. This is useful for improved findability, but also for preservation purposes when the dataset may no longer be available. This ensures compatibility with the FAIR sub-principle “A2. Metadata are accessible, even when the data are no longer available.”
Communication Standards for Accessing DataThe OGC Web Feature Service (WFS) and the Web Coverage Service (WCS) give access to feature or coverage data independently of the data’s data model or schema. Implementations of these services are based on Open Standards that can be implemented for free. This complies with the FAIR sub-principle “A1.1 The protocol is open, free, and universally implementable.” It is possible to get the whole resource or a subset of it based on spatial or thematic queries. However, these services are based on a service-oriented architecture and do not necessarily provide a URI for each resource.
The newer OGC API – Features and OGC API – Coverages Standards, though, provide similar functionality with a resource-oriented architecture. They provide a URI for each resource they expose. This makes the OGC API Standards, as well as the SensorThings API, compliant to the FAIR sub-principle “A1. (Meta)data are retrievable by their identifier using a standardized communications protocol.” OGC Web Services and OGC APIs both use the HTTP protocol over the Internet and can make use of the current standards and practices for authentication and authorization, such as OpenID Connect.
However, the resource-oriented architecture of the OGC API Standards means they are better positioned to adopt best practices for authentication and authorization. In this paradigm, authorization on geospatial resources can be fine-tuned for each resource URI in the same way as any other resource on the Web. As such, OGC API – Features, OGC API – Coverages, and The Sensor Things API comply with the FAIR sub-principle “A1.2 The protocol allows for an authentication and authorization procedure, where necessary.”
Semantic Interoperability Standards The OGC RAINBOW
The OGC RAINBOW
To better support the “Interoperable” FAIR principle as it applies semantic interoperability, OGC is implementing the OGC RAINBOW (formerly the OGC Definitions Server) as a Web accessible source of information about concepts and vocabularies that OGC defines or that communities ask the OGC to host on their behalf. It applies FAIR principles to the key concepts that underpin interoperability in systems using OGC specifications.
The OGC Registry for Accessible Identifiers of Names and Basic Ontologies for the Web (RAINBOW) is a linked-data server, published and maintained by OGC, used to manage and publish reference vocabularies, standard definitions with profiles, ontologies, and resources. It is intended to be a node in an interoperable ecosystem of resources published by different communities. It supports a wide spectrum of resources and allows more value to be realized from data. It can be accessed at opengis.net/def.
OGC RAINBOW is implemented using Linked Data principles that provide enhanced findability, making it compliant with the FAIR sub-principles “F1. (Meta)data are assigned a globally unique and persistent identifier” and “F4: (Meta)data are registered or indexed in a searchable resource.” It is accessed using the HTTP protocols over the Internet, so is also compliant with “A1. (Meta)data are retrievable by their identifier using a standardised communication protocol” and “A1.1 The protocol is open, free, and universally implementable.”
The set of concepts stored in the RAINBOW or in other vocabularies can be used by data and metadata to comply with the FAIR sub-principles “I1. (Meta)data use a formal, accessible, shared, and broadly applicable language for knowledge representation” and “I2. (Meta)data use vocabularies that follow FAIR principles.”
The OGC SensorThings APIThe OGC SensorThings API is an open and free standard that complies to the FAIR sub-principle “A1.1 The protocol is open, free, and universally implementable.” It incorporates a data model that includes two properties that allow for linking to URLs for “units of measurement” and “observed properties” (e.g. references to variable definitions) that makes it compliant with the FAIR sub-principle “I2. (Meta)data use vocabularies that follow FAIR principles.” However, other services and APIs, such as OGC API – Features and OGC API – Coverages, do not specify how this could be done in practice, so more work needs to be done in that respect.
On the other hand, the new OGC APIs use link mechanisms to connect datasets, resources, and resource collections to other resources for different purposes, making them compliant with the FAIR sub-principle “I3 (Meta)data include qualified references to other (meta)data.”
Similarly, the new OGC SensorThings API plus (STAplus) Standard includes an additional element called “Relation” that allows for relating an observation to other internal or external observations. It also adds an element called “License” associated with the datastream or observation group that complies with the FAIR sub-principle “R1.1. (Meta)data are released with a clear and accessible data usage license.” Further, the STA data model can be extended to domain-specific areas by subclassing some of the entities, such as “Thing” and “Observation,” allowing it to meet the FAIR sub-principle “R1.3. (Meta)data meet domain-relevant community standards.”
STAplus includes many considerations for secure operations and can support authentication and authorization through the implementation of business logic, making it compliant with the FAIR sub-principle “A1.2. The protocol allows for an authentication and authorization procedure where necessary.”
Other Standard Thematic Data ModelsOGC also offers Standards that define thematic data models and knowledge representations. For example, WaterML is an information model for the representation of water observations data. In addition, PipelineML defines concepts supporting the interoperable interchange of data pertaining to oil and gas pipeline systems. The PipelineML Core addresses two critical business use-cases that are specific to the pipeline industry: new construction surveys and pipeline rehabilitation.
Another example is the Land and Infrastructure Conceptual Model (LandInfra) for land and civil engineering infrastructure facilities. Subject areas include facilities, projects, alignment, road, railway, survey, land features, land division, and “wet” infrastructure (storm drainage, wastewater, and water distribution systems). CityGML is intended to represent city objects in 3D city models. The (upcoming) Model for Underground Data Definition and Integration (MUDDI) represents information about underground utilities. IndoorGML offers a data model to represent indoor building features. Finally, GeoSciML is a model of geological features commonly described and portrayed in geological maps, cross sections, geological reports and databases. This standard describes a logical model for the exchange of geological map data, geological time scales, boreholes, and metadata for laboratory analyses.
The existence of these Standards can help each thematic sector to comply with the FAIR Interoperability sub-principle “I1. (Meta)data use a formal, accessible, shared, and broadly applicable language for knowledge representation.” As well as these standards, connecting their vocabularies to information systems or databases would significantly increase their usefulness and encourage the principle of Reusability “R1.(Meta)data are richly described with a plurality of accurate and relevant attributes” and sub-principle “R1.3 (Meta)data meet domain-relevant community standards.”
FAIR in Everything We DoOGC’s Mission, to “Make location information Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR),” places the FAIR Principles at the heart of everything we do. This post has shown how OGC Standards explicitly address the FAIR Principles to contribute to FAIR geospatial data.
The Standards shown here were chosen due to their popularity and utility, but represent only a small portion of what’s available from OGC. You can see the full suite of OGC Standards at ogc.org/standards.
For more detailed information on OGC API Standards, including developer resources, news of upcoming code sprints, or to learn how the family of OGC API Standards work together to provide modular “building blocks for location” that address both simple and the most complex use-cases, visit ogcapi.org.
The post How OGC Contributes to FAIR Geospatial Data appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 2:00
2:00 GeoServer Team: GeoServer installation methods on Windows
sur Planet OSGeoGeoSpatial Techno is a startup focused on geospatial information that is providing e-learning courses to enhance the knowledge of geospatial information users, students, and other startups. The main approach of this startup is providing quality, valid specialized training in the field of geospatial information.
( YouTube | LinkedIn | Facebook | Reddit | X )
GeoServer installation methods: “Windows Installer” and “Web Archive”GeoServer installation methods: “Windows Installer” and “Web Archive” In this session, we will talk about how to install GeoServer software by two common methods in Windows. If you want to access the complete tutorial, simply click on the link.
IntroductionGeoServer can be installed on different operating systems, since it’s a Java based application. You can run it on any kind of operating system for which exists a Java virtual machine. GeoServer’s speed depends a lot on the chosen Java Runtime Environment (JRE). The latest versions of GeoServer are tested with both OracleJRE and OpenJDK. These versions are:
- Java 17 for GeoServer 2.23 and above
- Java 11 for GeoServer 2.15 and above
- Java 8 for GeoServer 2.9 to GeoServer 2.22
- Java 7 for GeoServer 2.6 to GeoServer 2.8
- Java 6 for GeoServer 2.3 to GeoServer 2.5
- Java 5 for GeoServer 2.2 and earlier
But remember that the older versions are unsupported and won’t receive fixes nor security updates, and contain well-known security vulnerabilities that have not been patched, so use at own risk. That is true for both GeoServer and Java itself.
There are many ways to install GeoServer on your system. This tutorial will cover the two most commonly used installation methods on Windows.
- Windows Installer
- Web Archive
The Windows installer provides an easy way to set up GeoServer on your system, as it requires no configuration files to be edited or command line settings.
Installation- GeoServer requires a Java environment (JRE) to be installed on your system, available from Adoptium for Windows Installer, or provided by your OS distribution. For more information, please refer to this link: [https:]
Consider the operating system architecture and memory requirements when selecting a JRE installer. 32-bit Java version is restricted to 2 GB memory, while the 64-bit version is recommended for optimal server memory. Utilizing JAI with the 32-bit JRE can enhance performance for WMS output generation and raster operations.
- Install JRE by following the default settings and successfully complete the installation.
- Navigate to the GeoServer.org and download the desired version of GeoServer.
- Launch the GeoServer installer and agree to the license.
- Enter the path to the JRE installation and proceed with the installation. The installer will attempt to automatically populate this box with a JRE if it is found, but otherwise you will have to enter this path manually.
- Provide necessary details like the GeoServer data directory, administration credentials, and port configuration.
- Review the selections, install GeoServer, and start it either manually or as a service.
- Finally, navigate to localhost:8080/geoserver (or wherever you installed GeoServer) to access the GeoServer Web administration interface.
GeoServer can be uninstalled in two ways:
- By running the uninstall.exe file in the directory where GeoServer was installed
- By standard Windows program removal
GeoServer is packaged as a web-archive (WAR) for use with an application server such as Apache Tomcat or Jetty. It has been mostly tested using Tomcat, and so is the recommended application server. There are reasons for installing it such as it is widely used, well-documented, and relatively simple to configure. GeoServer requires a newer version of Tomcat (7.0.65 or later) that implements Servlet 3 and annotation processing. Other application servers have been known to work, but are not guaranteed.
Installation- Make sure you have a JRE installed on your system, then download Apache Tomcat from its website [https:] For the Windows installation package, scroll down and choose the 32bit/64bit Windows Service Installer option.
- Configure Tomcat by selecting components, setting up a username and password, and specifying memory settings. So, before start the Tomcat service, you have to configure the memory settings that will use for Java VM. To do it, open the Tomcat9w from the bin folder, then click on the Java tab. This tab allows for configuration of memory settings, including initial and maximum memory pool sizes. Recommended values are 512MB for the initial memory pool and 1024MB for the maximum memory pool.
- Start Tomcat service and verify its functionality, then navigate to localhost:8080, and get the Tomcat9 web page.
- Navigate to the GeoServer.org and Download page. Select Web Archive on the download page from the version of GeoServer that you wish to download.
- Deploy the GeoServer web archive as you would normally. Often, all that is necessary is to copy the GeoServer.war file to the Tomcat’s webapps directory, then the application will be deployed automatically.
- Now to access the Web administration interface, open a browser and navigate to localhost:8080 and press Manager App button. Enter the username and password of apache tomcat. Click on the start button for the GeoServer. Once it has started, click the GeoServer link. This will take you to the GeoServer web page.
Stop the container application. Remove the GeoServer webapp from the container application’s webapps directory. This will usually include the GeoServer.war file as well as a GeoServer directory.
Difference between GEOSERVER.war and GEOSERVER.exe?- The ‘GeoServer.exe’ NSIS installer registers GeoServer as a Windows Service, which uses the Jetty application server to run GeoServer. The ‘GeoServer.war’ is a platform independent web-archive package to be deployed in your own application server (we recommend Apache Tomcat). Using the ‘GeoServer.exe’ installer is a reliable way to setup GeoServer as a windows background service. The downside is the included Jetty application server is managed using text files (jetty.ini) once installed.
- Use of ‘GeoServer.war’ web-archive is provided to install into your own application server (we recommend Apache Tomcat as the market leader, with excellent documentation and integration options). A single application server may support several web application allowing GeoServer to be run alongside your own java web application.
-
 12:03
12:03 Marco Bernasocchi: New QGIS Courses dates for 2024
sur Planet OSGeoWe published our new dates for all courses in 2024 and are looking forward to your participation

- Cours QGIS de base, 10.01. et 17.01.2024 à Lausanne in French
- Cours QGIS avancé, 24.01. et 31.01.2024 à Lausanne in French
- INTERLIS Webinar, 07.03.24 Online in German
- Modelbaker Kurs, 14.03.24 in Zürich in German
- QGIS Kurs Einsteiger, 22.05 und 29.05.2024 in Zürich in German
- QGIS Kurs Fortgeschrittene, 05.06 und 12.06.2024 in Zürich in German
- QGIS Kurs Einsteiger, 30.10 und 06.11.2024 in Bern in German
- QGIS Kurs Fortgeschrittene, 13.11 und 20.11.2024 in Bern in German
- QGIS Kurs Fortgeschrittene, 13.11 und 20.11.2024 in Bern in German
You can find all course information by clicking on the corresponding link
Subscribe now -
 19:57
19:57 Free and Open Source GIS Ramblings: Analyzing mobility hotspots with MovingPandas & CARTO
sur Planet OSGeoToday, I want to point out a blog post over at
written together with my fellow co-authors and EMERALDS project team members Argyrios Kyrgiazos and Helen McKenzie.

In this blog post, we walk you through a trajectory hotspot analysis using open taxi trajectory data from Kaggle, combining data preparation with MovingPandas (including the new OutlierCleaner illustrated above) and spatiotemporal hotspot analysis from Carto.
-
 16:47
16:47 gvSIG Team: Free workshop on ‘Introduction to gvSIG,’ using version 2.6 and its new icon set at 19th gvSIG Conference
sur Planet OSGeoOn November 30, 2023, during the 19th International gvSIG Conference, a free workshop will be held to learn to use version 2.6 of gvSIG, showcasing the new icon set.
To participate in the workshop, simply register using the following link: Workshop Registration.

Version 2.6 comes with an improved default icon set, replacing the one used since its initial versions.
This workshop will cover the main tools of the application, creating views, loading vector and raster layers, both locally and remotely, editing them graphically and alphanumeric, applying geoprocessing, and creating maps. All of this will be done using the new icon set, providing a refreshed version of gvSIG.
Whether you’ve used gvSIG before or it’s your first time, you won’t want to miss this workshop.
To follow it, you’ll need to download the portable version 2.6 of gvSIG for your operating system: Windows 64 – Windows 32 – Linux 64 – Linux 32
You’ll have to extract it to a folder without spaces. For example, you can create a folder called ‘gvSIG’ in C:\ (on Windows) or in the user’s home directory (on Linux), place the zip file inside, and extract it there.
You’ll also need to download the cartography to be used: Workshop Cartography ‘Introduction to gvSIG 2.6’
-
 2:06
2:06 GeoTools Team: GeoTools 30.1 released
sur Planet OSGeo The GeoTools team is pleased to the release of the latest stable version of GeoTools 30.1:geotools-30.1-bin.zip geotools-30.1-doc.zip geotools-30.1-userguide.zip geotools-30.1-project.zip This release is also available from the OSGeo Maven Repository and is made in conjunction with GeoServer 2.24.1. The release was made by Jody Garnett (GeoCat).Release -
 23:31
23:31 Free and Open Source GIS Ramblings: Setting up a graph db using GTFS data & Neo4J
sur Planet OSGeoIn a recent post, we looked into a graph-based model for maritime mobility data and how it may be represented in Neo4J. Today, I want to look into another type of mobility data: public transport schedules in GTFS format.
In this post, I’ll be using the public GTFS data for Riga since Riga is one of the demo sites for our current EMERALDS research project.
The workflow is heavily inspired by Bert Radke‘s post “Loading the UK GTFS data feed” from 2021 and his import Cypher script which I used as a template, adjusted to the requirements of the Riga dataset, and updated to recent Neo4J changes.
Here we go.
Since a GTFS export is basically a ZIP archive full of CSVs, we will be making good use of Neo4Js CSV loading capabilities. The basic script for importing the stops file and creating point geometries from lat and lon values would be:
LOAD CSV with headers FROM "file:///stops.txt" AS row CREATE (:Stop { stop_id: row["stop_id"], name: row["stop_name"], location: point({ longitude: toFloat(row["stop_lon"]), latitude: toFloat(row["stop_lat"]) }) })This requires that the stops.txt is located in the import directory of your Neo4J database. When we run the above script and the file is missing, Neo4J will tell us where it tried to look for it. In my case, the directory ended up being:
C:\Users\Anita\.Neo4jDesktop\relate-data\dbmss\dbms-72882d24-bf91-4031-84e9-abd24624b760\importSo, let’s put all GTFS CSVs into that directory and we should be good to go.
Let’s start with the agency file:
load csv with headers from 'file:///agency.txt' as row create (a:Agency { id: row.agency_id, name: row.agency_name, url: row.agency_url, timezone: row.agency_timezone, lang: row.agency_lang });… Added 1 label, created 1 node, set 5 properties, completed after 31 ms.
The routes file does not include agency info but, luckily, there is only one agency, so we can hard-code it:
load csv with headers from 'file:///routes.txt' as row match (a:Agency {id: "rigassatiksme"}) create (a)-[:OPERATES]->(r:Route { id: row.route_id, shortName: row.route_short_name, longName: row.route_long_name, type: toInteger(row.route_type) });… Added 81 labels, created 81 nodes, set 324 properties, created 81 relationships, completed after 28 ms.
From stops, I’m removing non-existent or empty columns:
load csv with headers from 'file:///stops.txt' as row create (s:Stop { id: row.stop_id, name: row.stop_name, location: point({ latitude: toFloat(row.stop_lat), longitude: toFloat(row.stop_lon) }), code: row.stop_code });… Added 1671 labels, created 1671 nodes, set 5013 properties, completed after 71 ms.
From trips, I’m also removing non-existent or empty columns:
load csv with headers from 'file:///trips.txt' as row match (r:Route {id: row.route_id}) create (r)<-[:USES]-(t:Trip { id: row.trip_id, serviceId: row.service_id, headSign: row.trip_headsign, direction_id: toInteger(row.direction_id), blockId: row.block_id, shapeId: row.shape_id });… Added 14427 labels, created 14427 nodes, set 86562 properties, created 14427 relationships, completed after 875 ms.
Slowly getting there. We now have around 16k nodes in our graph:
Finally, it’s stop times time. This is where the serious information is. This file is much larger than all previous ones with over 300k lines (i.e. times when an PT vehicle stops).
This requires another tweak to Bert’s script since
using periodic commitis not supported anymore:The PERIODIC COMMIT query hint is no longer supported. Please use CALL { … } IN TRANSACTIONS instead.So I ended up using the following, based on [https:]] ::auto load csv with headers from 'file:///stop_times.txt' as row CALL { with row match (t:Trip {id: row.trip_id}), (s:Stop {id: row.stop_id}) create (t)<-[:BELONGS_TO]-(st:StopTime { arrivalTime: row.arrival_time, departureTime: row.departure_time, stopSequence: toInteger(row.stop_sequence)})-[:STOPS_AT]->(s) } IN TRANSACTIONS OF 10 ROWS;… Added 351388 labels, created 351388 nodes, set 1054164 properties, created 702776 relationships, completed after 1364220 ms.
As you can see, this took a while. But now we have all nodes in place:


The final statement adds additional relationships between consecutive stop times:
call apoc.periodic.iterate('match (t:Trip) return t', 'match (t)<-[:BELONGS_TO]-(st) with st order by st.stopSequence asc with collect(st) as stops unwind range(0, size(stops)-2) as i with stops[i] as curr, stops[i+1] as next merge (curr)-[:NEXT_STOP]->(next)', {batchmode: "BATCH", parallel:true, parallel:true, batchSize:1});This fails with:
There is no procedure with the name apoc.periodic.iterate registered for this database instance. Please ensure you've spelled the procedure name correctly and that the procedure is properly deployed.So, let’s install APOC. That’s a plugin which we can install into our database from within Neo4J Desktop:
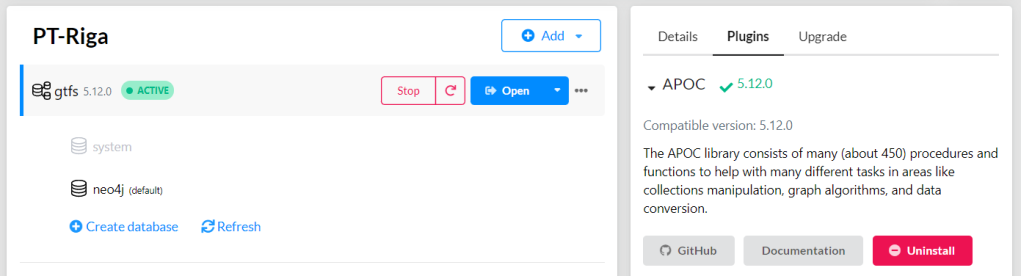
After restarting the db, we can run the query:

No errors. Sounds good.
Let’s have a look at what we ended up with. Here are 25 random Trips. I expanded one of them to show its associated StopTimes. We can see the relations between consecutive StopTimes and I’ve expanded the final five StopTimes to show their linked Stops:

I also wanted to visualize the stops on a map. And there used to be a neat app called Neomap which can be installed easily:

However, Neomap does not seem to be compatible with the latest Neo4J:

So this final step will have to wait for another time.
-
 19:49
19:49 gvSIG Team: Taller gratuito sobre “Introducción a gvSIG”, con la versión 2.6 y su nuevo juego de iconos en las 19as Jornadas gvSIG
sur Planet OSGeoEl día 30 de noviembre de 2023, durante las 19as Jornadas Internacionales gvSIG, se realizará un taller gratuito sobre el manejo de la versión 2.6 de gvSIG, con el nuevo juego de iconos.
Para seguir el taller solo deberás registrarte desde el siguiente enlace: Inscripción taller.
La versión 2.6 incluye por defecto un nuevo juego de iconos mejorado, sustituyendo al que llevaba desde sus versiones iniciales.
En este taller se repasarán las principales herramientas de la aplicación, aprendiendo a crear vistas, cargar capas vectoriales y raster, locales y remotas, a editarlas, tanto gráfica como alfanuméricamente, a aplicar geoprocesamiento y a generar mapas. Todo ello se realizará con el nuevo juego de iconos, que da una versión renovada a gvSIG.
Tanto si ya has utilizado gvSIG previamente, como si es tu primera vez, no puedes perderte este taller.
Para poder seguirlo, deberás descargarte la versión 2.6 portable de gvSIG, según tu sistema operativo: Windows 64 – Windows 32 – Linux 64 – Linux 32
Se deberá descomprimir en una carpeta sin espacios ni acentos ni eñes. Se puede crear por ejemplo una carpeta “gvSIG” en C:\ (en Windows) o en el home de usuario (en Linux), dejar el zip dentro, y descomprimir ahí.
Se deberá también descargar la cartografía a utilizar: Cartografía taller “Introducción a gvSIG 2.6”
-
 2:00
2:00 GeoServer Team: GeoServer 2.24.1 Release
sur Planet OSGeoGeoServer 2.24.1 release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is a stable release of GeoServer recommended for production use. GeoServer 2.24.1 is made in conjunction with GeoTools 30.1, and GeoWebCache 1.24.1.
Thanks to Jody Garnett (GeoCat) for making this release.
Release notesImprovement:
- GEOS-11152 Improve handling special characters in the Simple SVG Renderer
- GEOS-11153 Improve handling special characters in the WMS OpenLayers Format
- GEOS-11154 Improve handling special characters in the MapML HTML Page
- GEOS-11155 Add the X-Content-Type-Options header
- GEOS-11173 Default to using [HttpOnly] session cookies
- GEOS-11176 Add validation to file wrapper resource paths
- GEOS-11188 Let DownloadProcess handle download requests whose pixel size is larger than integer limits
- GEOS-11189 Add an option to throw a service exception when nearest match “allowed interval” is exceeded
- GEOS-11193 Add an option to throw an exception when the time nearest match does not fall within search limits
Bug:
- GEOS-11074 GeoFence may not load property file at boot
- GEOS-11166 OGC API Maps HTML representation fail without datetime parameter
- GEOS-11184 ncwms module has a compile dependency on gs-web-core test jar
- GEOS-11190 GeoFence: align log4j2 deps
- GEOS-11196 NPE in VectorDownload if ROI not defined
- GEOS-11200 GetFeatureInfo can fail on rendering transformations that generate a different raster
- GEOS-11203 WMS GetFeatureInfo bad WKT exception for label-geometry
- GEOS-11206 Throw nearest match mismatch exceptions only for WMS
For the complete list see 2.24.1 release notes.
Community Module Updates OAuth2 OpenID-Connect improvementsTwo improvements have been made to the community module for OAuth2 OpenID-Connect authentication:
- GEOS-11209 Open ID Connect Proof Key of Code Exchange (PKCE)
- GEOS-11212 ODIC accessToken verification using only JWKs URI
In addition the module includes an
OIDC_LOGGINGprofile and updated documentation covering new settings and troubleshooting guidance.Thanks Jody Garnett for these improvements on behalf of GeoBeyond.
note: Over the course of 2024 the OAuth2 plugins will need to be rewritten for spring-framework 6. Interested parties are encouraged to reach out to geoserver-devel email list; ideally we would like to see this functionality implemented and included as part of GeoServer.
About GeoServer 2.24 SeriesAdditional information on GeoServer 2.24 series:
- GeoServer 2.24 User Manual
- State of GeoServer 2.24 (foss4g-na presentation)
- Control remote HTTP requests sent by GeoTools/GeoServer
- Multiple CRS authority support, planetary CRS
- Extensive GeoServer Printing improvements
- Upgraded security policy
Release notes: ( 2.24.1 | 2.24.0 | 2.24-RC )
GeoServer is an Open Source Geospatial Foundation project supported by a mix of volunteer and service provider activity. We reply on sponsorship to fund activities beyond the reach of individual contributors.
-
 19:47
19:47 KAN T&IT Blog: Destacada participación de Julia Martinuzzi y Walter Shilman en el Side Event de UN-GGIM Américas
sur Planet OSGeoEl pasado 20 de octubre, nuestra Directora de Operaciones (COO), Julia Martinuzzi, y nuestro Director de Tecnología (CTO), Walter Shilman, asumieron roles clave durante la Décima Sesión de la Comisión de las Naciones Unidas para América Latina y el Caribe (ECLAC) celebrada en Santiago de Chile. Su destacada participación se centró en la organización y liderazgo del Side Event titulado «Open Source technologies for geospatial information management and their role in the implementation of the IGIF.»
Este evento, coordinado por el capítulo argentino de OSGeo – Geolibres, reunió a destacados expertos de la región para compartir sus conocimientos sobre enfoques sostenibles y accesibles para abordar los desafíos geoespaciales.
La discusión se centró esencialmente en la implementación del Marco Integrado de Información Geoespacial (IGIF), resaltandola importancia de la accesibilidad y sostenibilidad, con un énfasis primordial en la aplicación de tecnologías de código abierto.
Los participantes exploraron temas clave, como la integración de datos estadísticos y geoespaciales, destacando cómo las tecnologías de código abierto fomentan la colaboración y mejoran la toma de decisiones. Además, se examinó el papel esencial de la geoinformación y las tecnologías de código abierto en la gestión de desastres.
El evento concluyó resaltando la necesidad de difundir y promover el uso de tecnologías de código abierto entre los países miembros de UN-GGIM, subrayando su poder en la Gestión de Información Geoespacial. La colaboración e intercambio de conocimientos entre expertos y principiantes fueron identificados como impulsores clave para un uso más efectivo de la información geoespacial en diversas aplicaciones, desde la planificación urbana hasta la gestión de desastres.
En ese momento, Julia Martinuzzi y Walter Shilman lideraron de manera destacada, contribuyendo significativamente al buen desarrollo del evento. Esperamos que esta experiencia positiva siga siendo una fuente de nuevas ideas y trabajo conjunto en el manejo de información geoespacial en América Latina y el Caribe.

Presentación en el Side Event sobre «Open Source technologies for geospatial information management and their role in the implementation of the IGIF,»
Les compartimos la presentación del evento para que todos puedan acceder.
Presentación Side Event: «Open Source technologies for geospatial information management and their role in the implementation of the IGIF»
UN-GGIM-Americas-Side-Event-ENDescarga -
 16:05
16:05 SIG Libre Uruguay: Un nuevo reconocimiento a gvSIG
sur Planet OSGeo
-
 16:00
16:00 OGC Compliance Certification now available for the GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the Executable Test Suite (ETS) for version 1.0 of the OGC GeoPose Data Exchange Standard has been approved by the OGC Membership. Products that implement OGC GeoPose 1.0 and pass the tests in the ETS can now be certified as OGC Compliant.
The OGC Compliance Program offers a certification process that ensures organizations’ solutions are compliant with OGC Standards. It is a universal credential that allows agencies, industry, and academia to better integrate their solutions. OGC Compliance provides confidence that a product will seamlessly integrate with other compliant solutions regardless of the vendor that created them.
Implementers of the GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard are invited to validate their products using the new test suite in the OGC validator tool. Testing involves submitting an OGC GeoPose 1.0 document produced by the product being assessed. These tests typically take only 5-10 minutes to complete. Once a product has passed the test, the implementer can apply to use the ‘OGC Compliant’ trademark on their product.
OGC GeoPose is a free and open Implementation Standard for exchanging the location and orientation of real or virtual geometric objects (“Poses”) within reference frames anchored to Earth’s surface (“Geo”) or within other astronomical coordinate systems. The Standard specifies a JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) encoding for representing conformant poses.
The GeoPose Standard specifies a number of conformance classes, most being optional. One conformance class is defined for each corresponding set of Structural Data Units (SDUs), where each SDU is linked to the Logical Model as an alias for a class or attribute. The following conformance classes from the OGC GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard (OGC 21-056r11) are supported by the ETS:
- Basic-YPR (Yaw-Pitch-Roll) SDU JSON
- Basic-Quaternion SDU JSON – Permissive
- Advanced SDU JSON
- Graph SDU JSON
- Chain SDU JSON
- Regular Series SDU JSON
- Stream SDU JSON
Some of the products implementing the GeoPose Standard that have already been certified as OGC Compliant include Away Team Software’s 3D Compass 1, OpenSitePlan’s SolarPose 1.0, and Ethar Inc.’s GeoPose C# Library 1.0. These products apply GeoPose in a wide variety of applications, such as Augmented Reality (AR), mobile Location Based Services (LBS), web APIs, and more. To implement GeoPose in your product, please refer to the OGC GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard document, freely available from OGC. Additional documentation is also available on the GeoPose website.
More information about the OGC compliance process, and how it can benefit your organization, is available at ogc.org/compliance. Implementers of the OGC GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard – or other OGC Standards – can validate their products now using the OGC Validator Tool.
The post OGC Compliance Certification now available for the GeoPose 1.0 Data Exchange Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 12:25
12:25 gvSIG Team: El Proyecto GVSIG, impulsado por la Generalitat Valenciana y la Asociación GVSIG, galardonado como mejor proyecto de software de Europa en los OSOR Awards
sur Planet OSGeo
El Proyecto GVSIG, una iniciativa conjunta de la Generalitat Valenciana y la Asociación GVSIG, ha sido distinguido con el primer premio en los OSOR Awards. Este galardón reconoce los logros excepcionales que ha logrado el proyecto GVSIG a nivel internacional y reflejan el compromiso continuo de la Generalitat Valenciana con la innovación y la colaboración.
Los OSOR Awards han sido organizados por el Observatorio de Software Libre (OSOR) de la Comisión Europea con motivo de su 15 aniversario, y han querido destacar los mejores proyectos impulsados por las administraciones públicas de toda Europa. En este contexto, GVSIG ha destacado entre todas las nominaciones, convirtiéndose en el ganador de los premios, en los que se ha destacado su impacto global y su contribución al desarrollo tecnológico europeo.
Según los organizadores de los premios se recibieron más de cien candidaturas de 23 países. Tras una primera fase, el jurado seleccionó los seis mejores proyectos, donde GVSIG compartía opciones con proyectos de España, Dinamarca, Italia y Francia. Durante el evento organizado en el día de ayer en Bruselas, los seis proyectos tuvieron que defender su candidatura ante el jurado de la Comisión Europea. Finalmente fue anunciado el ganador: el proyecto GVSIG presentado conjuntamente por la Generalitat Valenciana y la Asociación GVSIG.El Proyecto GVSIG es un catálogo de herramientas informáticas para gestión de información geográfica que desde su nacimiento en 2004 ha ido ganado reconocimiento por su versatilidad y utilidad en una variedad de sectores, desde la gestión de recursos naturales hasta la planificación urbana. La Generalitat Valenciana ha desempeñado un papel fundamental tanto en su impulso inicial como en el respaldo continuo al proyecto. La Asociación GVSIG, por su parte, ha desempeñado un papel esencial en la promoción y difusión de esta plataforma a nivel internacional, facilitando la generación y crecimiento de un sector empresarial valenciano especialista en tecnologías de información geográfica. Un ejemplo de colaboración público-privada que ahora obtiene el reconocimiento de Europa.
Este prestigioso galardón no solo reconoce el éxito del Proyecto GVSIG, sino que también destaca el compromiso de la Generalitat Valenciana y la Asociación GVSIG con la promoción de soluciones tecnológicas abiertas y accesibles, fomentando la innovación y la colaboración como motor de desarrollo.
GVSIG da solución a todas las necesidades relacionadas con la geolocalización y la administración del territorio. En la Generalitat Valenciana se multiplican sus usuarios y entre los diversos ejemplos de uso se encuentran desde aplicaciones para ayudar a proteger las praderas fanerógamas, la conocida posidonia, evitando fondear en zonas protegidas a aplicaciones de gestión del registro vitivinícola, pasando por soluciones para fomentar la movilidad sostenible mediante un planificador de rutas más versátil que el propio Google Maps o aplicaciones para analizar los accidentes de tráfico.
Si su uso es transversal en la Generalitat Valenciana, otro tanto ocurre a nivel global. Son innumerables las entidades de todo tipo que utilizan esta tecnología valenciana. En la presentación de los OSOR Awars se citaron varias de ellas. A nivel supranacional entidades como Naciones Unidas la han adoptado como tecnología de referencia en usos tan destacados como facilitar la seguridad de las misiones de los Cascos Azules en sus desplazamientos ante ataques terroristas. A nivel nacional ha sido igualmente adoptada, contando casos tan significativos como el del Gobierno de Uruguay, donde GVSIG es la base tecnológica para todos los proyectos de gestión y difusión de información territorial del país, habiendo servido también para crear un sistema único de direcciones. En Uruguay ha sido tal el nivel de adopción que en la educación secundaria es utilizada para el aprendizaje de las materias relacionadas con la geografía. Su uso a nivel regional y local nos lleva a citar ejemplos como el del Estado de Tocantins en Brasil, donde se ha convertido en la plataforma de gestión geográfica y estadística o el Gobierno de Córdoba en Argentina, donde es utilizada para analizar los datos de criminalidad y seguridad ciudadana. Y donde todavía está más implantada es en las administraciones locales, donde GVSIG está siendo adoptada a gran velocidad por decenas de ayuntamientos de toda España; los últimos han sido los Ayuntamientos de Alicante, Albacete, Cartagena y Talavera de la Reina. Solo en la Comunidad Valenciana el número de ayuntamientos que confían en GVSIG es innumerable: Cullera, Onda, Picassent, L’Eliana, La Pobla de Vallbona, Nàquera, Alzira, Benicarló… e igualmente otras entidades valencianas han adoptado GVSIG como el Consorcio Provincial de Bomberos de Valencia, donde su uso se centra en la gestión de emergencias. Y más allá de la administración pública, cuya relación con el territorio es directa, GVSIG también ha entrado a formar parte de las soluciones informáticas que utilizan empresas que trabajan con información geoposicionada, como es el caso de Repsol que hace un uso extensivo de GVSIG en su división de energías renovables.
El premio otorgado a la Generalitat Valenciana y a la Asociación GVSIG se suma a otros galardones obtenidos anteriormente, de entidades tan diversas como el Diario Expansión o la NASA.
GVSIG es un referente en lo que se ha denominado Infraestructuras de Datos Espaciales, la puesta en marcha de plataformas que permitan a las administraciones públicas compartir su información geográfica mediante estándares.
El impacto del proyecto tiene numerosas derivadas, a nivel académico se imparte formación en GVSIG en universidades de todo el mundo, se publican anualmente cientos de artículos científicos donde se utiliza GVSIG como herramienta de los investigadores, se multiplican las conferencias y eventos donde se presentan todo tipo de proyectos desarrollados con GVSIG.
GVSIG, un proyecto basado en el conocimiento libre, ejemplo de colaboración público-privada que sitúa a Valencia como uno de los indiscutibles polos de referencia en el ámbito de la geomática, la tecnología aplicada a la dimensión geográfica de la información. El premio obtenido ayer es un reconocimiento a todo el camino recorrido.
Recientemente ha sido nominado al Premio Nacional de Ciencias Geográficas, todavía por resolver. Lo que nos han confirmado fuentes de la Asociación gvSIG es que esta candidatura ha recibido más de 150 cartas de apoyo de entidades de todo el mundo, desde el Departamento de Transporte de Washington al Ordnance Survey, la agencia cartográfica del Reino Unido. -
 10:24
10:24 gvSIG Team: The GVSIG Project, driven by the Generalitat Valenciana and the GVSIG Association, awarded as the best software project in Europe at the OSOR Awards
sur Planet OSGeo
The GVSIG Project, a joint initiative of the Generalitat Valenciana and the GVSIG Association, has been honored with the first prize at the OSOR Awards. This award recognizes the exceptional achievements of the GVSIG project on an international level and reflects the ongoing commitment of the Generalitat Valenciana to innovation and collaboration.
The OSOR Awards were organized by the Observatory of Open Source Software (OSOR) of the European Commission on the occasion of its 15th anniversary, aiming to highlight the best projects driven by public administrations throughout Europe. In this context, GVSIG stood out among all nominations, becoming the winner of the awards, emphasizing its global impact and contribution to European technological development.
According to the award organizers, over a hundred nominations from 23 countries were received. After an initial phase, the jury selected the top six projects, where GVSIG competed alongside projects from Spain, Denmark, Italy, and France. During the event held yesterday in Brussels, the six projects had to defend their candidacy before the European Commission’s jury. Finally, the winner was announced: the GVSIG project jointly presented by the Generalitat Valenciana and the GVSIG Association.
The GVSIG Project is a catalog of computer tools for geographic information management that, since its inception in 2004, has gained recognition for its versatility and usefulness in various sectors, from natural resource management to urban planning. The Generalitat Valenciana has played a fundamental role in both its initial promotion and continuous support for the project. The GVSIG Association, in turn, has played an essential role in promoting and disseminating this platform internationally, facilitating the generation and growth of a Valencian business sector specializing in geographic information technologies. An example of public-private collaboration that now receives recognition from Europe.
This prestigious award not only acknowledges the success of the GVSIG Project but also highlights the commitment of the Generalitat Valenciana and the GVSIG Association to promoting open and accessible technological solutions, fostering innovation and collaboration as drivers of development.
GVSIG addresses all needs related to geolocation and territory management. Its users in the Generalitat Valenciana are multiplying, and among various use cases are applications to help protect seagrass meadows, such as the well-known posidonia, by avoiding anchoring in protected areas, applications for managing the vineyard registry, and solutions to promote sustainable mobility through a route planner more versatile than Google Maps itself, or applications to analyze traffic accidents.
If its use is widespread in the Generalitat Valenciana, the same is true globally. Countless entities of all kinds use this Valencian technology. Several were mentioned in the presentation of the OSOR Awards. At the supranational level, entities like the United Nations have adopted it as a reference technology for prominent uses, such as enhancing the security of Blue Helmets’ missions during their travels in the face of terrorist attacks. Nationally, it has been similarly adopted, with significant cases such as the Government of Uruguay, where GVSIG is the technological basis for all territorial information management and dissemination projects in the country, also serving to create a unique addressing system. In Uruguay, its adoption is so extensive that it is used in secondary education for learning subjects related to geography. Its use at the regional and local levels leads to examples such as the State of Tocantins in Brazil, where it has become the platform for geographic and statistical management, or the Government of Córdoba in Argentina, where it is used to analyze crime and public safety data. It is even more deeply entrenched in local administrations, with GVSIG being rapidly adopted by dozens of municipalities throughout Spain, including the recent additions of the municipalities of Alicante, Albacete, Cartagena, and Talavera de la Reina. In the Valencian Community alone, the number of municipalities trusting GVSIG is countless: Cullera, Onda, Picassent, L’Eliana, La Pobla de Vallbona, Nàquera, Alzira, Benicarló, and many other Valencian entities have also adopted GVSIG, such as the Provincial Fire Consortium of Valencia, where its use focuses on emergency management. Beyond the public administration, whose relationship with the territory is direct, GVSIG has also become part of the computer solutions used by companies working with geopositioned information, such as Repsol, which extensively uses GVSIG in its renewable energy division.
The award granted to the Generalitat Valenciana and the GVSIG Association adds to other accolades previously obtained from diverse entities such as Diario Expansión or NASA.
GVSIG is a reference in what is called Spatial Data Infrastructures, the implementation of platforms that allow public administrations to share their geographic information through standards.
The impact of the project has numerous ramifications; academically, GVSIG training is offered at universities worldwide, hundreds of scientific articles are published annually using GVSIG as a tool by researchers, and conferences and events showcasing various projects developed with GVSIG abound.
GVSIG, a project based on free knowledge, is an example of public-private collaboration that positions Valencia as one of the undisputed reference hubs in the field of geomatics, technology applied to the geographic dimension of information. The award obtained yesterday is recognition for the entire journey taken.
Recently, it has been nominated for the National Geographic Sciences Award, still pending resolution. Sources from the GVSIG Association have confirmed that this candidacy has received more than 150 letters of support from entities worldwide, from the Department of Transportation in Washington to the Ordnance Survey, the cartographic agency of the United Kingdom.
-
 11:18
11:18 gvSIG Team: Program of 19th International gvSIG Conference (online) is now available, and registration (free of charge) period is open
sur Planet OSGeoFree registration period for the 19th International gvSIG Conference is now open. The Conference is an online event, and it will be held from November 29th to 30th.
The full program of the Conference is available on the event website, where registration to the different sessions can be done.

The webinar platform allows to connect to the webinars from any operating system, and in case you can’t follow them, you will be able to watch them at the gvSIG Youtube channel later.
In reference to workshops, all the information about cartography and gvSIG version to install will be published at the gvSIG blog before the conference.
Don’t miss it!
-
 11:09
11:09 gvSIG Team: Programa e inscripciones gratuitas abiertas para las 19as Jornadas Internacionales gvSIG (online)
sur Planet OSGeoYa están abiertas las inscripciones gratuitas para las 19as Jornadas Internacionales gvSIG, que se celebrarán de forma online los días 29 y 30 de noviembre.
El programa completo está disponible en la página web del evento, desde donde se puede realizar la inscripción a cada una de las ponencias.

La plataforma de webinar permite conectarse desde cualquier sistema operativo, y en caso de no poder seguirlos en directo se podrán ver a posteriori, ya que se publicarán en el canal de Youtube del proyecto al igual que en años anteriores.Respecto a los talleres, en el blog de gvSIG informaremos sobre la cartografía a descargar para seguirlos, así como de la versión de gvSIG a instalar.
-
 16:52
16:52 SIG Libre Uruguay: Las TIG ante los nuevos retos globales en un contexto cambiante. Actas de la XVIII CONFIBSIG 2023. Cáceres, 16-19 de mayo de 2023
sur Planet OSGeo
Descarga de la publicación aquí
-
 4:50
4:50 Sean Gillies: Bear 100 retro
sur Planet OSGeoAfter the race I needed some time to deal with my disappointment about rolling my ankle and dropping out at mile 61. Then I got busy looking for a new job. Writing up a retrospective that I could use in the future was delayed. Here it is, at last. I hope it's interesting and useful to others. This kind of retrospective is something I've learned to use at work. It's roughly organized around what went well, what could be better, lessons learned, in the areas of preparation and training, planning, and execution.
First of all, the race itself was great! Other runners I know said it was, and they were right. It was very well run. The aid stations were well stocked and operated smoothly. The course was beautiful and well marked. I felt constantly challenged, safe, and encouraged. I won't forget the super runnable single track down into Leatham Hollow, the springy soil made of pine needles, the ferns, and the view of the cliffs on the sunny slope. I lived just a few miles away for 10 years, but I'd never been on that trail before. The shady side of the canyon was super lush and green, almost Pacific Northwestern compared to Colorado's Front Range foothills. My memory of arriving at the Upper Richards Hollow aid station is another favorite. After a tough climb out of a wooded canyon, we were greeted on the flat bench above by an aid station volunteer holding a tray of cool, moist towels! They invited us to freshen up and enjoy a fancy brunch at clothed tables served by volunteers in tuxedo t-shirts. More than one of us expressed the feeling that it was way too early to be having hallucinations.
Much went according to plan, or better. My summer training volume was adequate and I did plenty of hiking and running on similar terrain at a similar, or higher, elevation. 4.5 weeks of fine tuning and tapering suited me well. I started the race feeling fresh. Flying to Salt Lake City and driving to Logan worked well for me. I was able to close my eyes and snooze while others transported me from Fort Collins to SLC. After landing, I had a sentimental and tasty lunch at Red Iguana, one of my favorite restaurants. In Logan, I enjoyed an entire day of hanging out with my aunt and her dog before race day.
My simple race plan was fine. I started out aiming to leave aid stations at the times that previous 36 hour finishers have, and did that. I aimed to slow down less than the typical 36 hour finisher after 40 miles, and achieved that, too. It was a good pacing plan for finishing in less than 36 hours. At each aid station I knew how many 100 calorie portions of food I should be picking up, and how many drink bottles to fill, and this was a fine fueling and hydration plan. I didn't bonk, cramp, or run out of drinks at any point, thanks to the water drop above Temple Fork.
We had exceptionally good weather on race day and night, so flaws in my equipment choices didn't surface like they might have. Tony Grove was, in fact, a good place to have a change of clothes, pants, and a sweater. Temple Fork would have been too early for warm layers. Franklin Basin would have been too late.
My feet suffered less in 60 miles of the Bear than in any of my previous 100K runs. I lubed them well before the start and changed socks at 28 and 50 miles. I had no blisters and no hot spots. I started the race in a pair of newish HOKA Mafate Speed 4 and they were fine. In the weeks before the race I had some persistent soreness on the top of my right foot and was concerned about a stress injury, but this didn't get any worse during the Bear.
I had no crew at the race, but found good company on the trail multiple times. Sometimes with other people making their own first 100 mile attempt. Sometimes with people going for their third or fourth Bear finish. I heard hilarious stories about the extreme hallucinations you can experience after 48 hours without sleep. I met a guy who graduated from Cache Valley's other high school a year after I graduated from Logan High. I ran with a woman who lost her colon to cancer a year ago. I spent four hours on the trail before Tony Grove with a guy from Boulder who runs a molecular biology center at CU. We run many of the same routes in Rocky Mountain National Park.
Now for the things that didn't go as well. Some flaws in my training and overall fitness were exposed by the Bear's long and rough downhills. I should lose at least 10 pounds. 15 might be better. I can feel the extra weight in my knees and the sensation compounded over 20+ hours. Also, I feel like I've lost foot speed and spatial sense over the last year or so. Three years ago my favorite fitness trainer went out of business and exercises like skaters and box jumps fell out of my repertoire. I believe that I can improve my proprioception by bringing these kinds of exercises back. If I can, I should be better able to dodge impacts instead of absorbing them.
My stomach was fine at the Bear, but I struggled with lower intestinal trouble from miles 20-40. I had to make a lot of stops in the trees, used up my supply of toilet paper, and had to resort to various leaves. Burdock is my friend in this situation. It wasn't the end of the world, but was a distraction. I don't know what the cause was. In the interest of keeping things simple, I had decided to go with the race's drinks instead of bringing, and mixing, my own, but I didn't train with them beforehand. Gnarly Fuel2O treated me well enough at Kettle Moraine, so I felt safe at the Bear. I started the race with 3 bottles of GU Roctane because I spaced packing some Tailwind mix for my initial bottles. I've never tried this stuff before. It has more ingredients than Taillwind or VFuel, my staples, including taurine. Maybe that was the culprit? I can only speculate. As I said, this was not a problem that would have prevented me from finishing.
Long descents in the dark made my brain and eyes tired. I was not fully prepared for this. I had a 350 lumen light on my belt and 500 lumens on my head. This was fine for 9 hours at Kettle Moraine in June, but not great for 12 hours at the Bear. I'll bring more light next time. Why spend energy trying to figure out mysteries on the trail that could be solved by better illumination?
Without a crew, my stop at Tony Grove to change clothes and get set for seven more hours of night running was overly long. I wonder if I'd left 20-30 minutes earlier I might have reached Franklin Basin without incident? At the very least, I'd have reached Franklin Basin that much sooner. A crew wouldn't have helped earlier, but would have helped at 50 miles when I was trying to change clothes, stay warm, and get fed simultaneously. It was mentally tiring at a moment where I was already mentally tired.
I've mentioned before that I left Tony Grove alone at 11 pm and had a sprained ankle at 1 pm. I was out there by myself and am not sure what happened. I could have fallen asleep on my feet; this has been known to happen. Having a pacer could have helped get me to Franklin Basin and beyond in good shape. Being able to follow someone with fresh eyes and a fresh mind would have helped with the issues I mentioned two paragraphs above. It's always easier to follow than to break trail. Even without a pacer, if I'd been in a small group I could have done some leading and some following. This would have been good. And I think getting out of Tony Grove earlier would have made it more likely to join such a group.
In hindsight, I should have had some plan for resting or napping. At 20 hours, I was more groggy than I expected, perhaps because I was alone with nothing but my breath, footsteps, and sleepy thoughts. Recently, a friend of mine shared his tactic of laying down on the trail for short naps, to be woken by the next runner 5-10 minutes behind. This issue is very connected to the previous ones. With less exertion, there is less need to nap. Even if I solve other problems, I bet I'll still run into the need to shut my eyes at 3 or 4 am. I'm going to think about this for next year.
Lastly on the could-have-gone-better front, how about my reaction to my ankle injury? My fuzzy recollection is that I came to full consciousness with a painful and unstable ankle in the dark at 1 am, a mile from the Franklin Basin aid station. I was concerned and went gingerly over that mile, and my plan was to try 15-20 minutes of elevation and compression before deciding whether to continue. I wasn't otherwise physically tired, hungry, or thirsty. My ankle became more swollen and painful while I was off my feet, and after 30 minutes I concluded that I could could not continue.
What if I had not stopped and just grabbed some hot food and kept going? The worst case scenario would have been hiking some small way toward the next aid station and having to return to Franklin Basin, with some damage done to my ankle. What if I had been able to hobble 8 miles to the Logan River aid station and continue slowly from there? I've run through mild sprains several times this year, and have endured worse grade 2 sprains than this one, yes, but not this year. Being alone out there make it harder to push on. If I was pacing myself, I may have been able to convince myself to take a shot at continuing. I think dropping out was 99% the right decision overall. My chance of making it another 8 miles to Logan River was maybe 50%, though? It's hard to say.
I learned two lessons. The TSA says no hiking poles allowed in carry on luggage! I had to leave mine behind at DEN and get new poles at the Farmington REI after leaving SLC. I won't make this mistake again.
While I was mentally prepared for the possibility of dropping out of the race, I did not have any plan for getting back to town after I did so! After two hours of sitting by the campfire at Franklin Basin I did finally meet someone who was heading directly back down the canyon to Logan.
As I said earlier, things mostly went my way. Except for some bad luck and a misstep I believe I would have finished. Registration for the 2024 edition of the Bear opens on December 1. I'm going to try again with more or less the same simple plan, stronger ankles, more light, and fewer distractions.
-
 2:41
2:41 Sean Gillies: Status update
sur Planet OSGeoFinally, I have a professional update. I started work at TileDB on Wednesday. I'll be working from Fort Collins alongside colleagues around the world. I know a slice of TileDB's market, dense multi-dimensional arrays like earth observation data, well, but have a lot to learn about genetic data, embeddings, and storing graphs in adjacency matrices. I expect this to be both challenging and fun. I'll post more about it once I'm settled in.
I'll be resuming work on open source projects, which I've paused while job hunting, soon!
-
 2:00
2:00 PostGIS Development: PostGIS Patch Releases
sur Planet OSGeoThe PostGIS development team is pleased to provide bug fix and performance enhancements 3.4.1, 3.3.5, 3.2.6, 3.1.10, 3.0.10 for the 3.4, 3.3, 3.2, 3.1, 3.0 stable branches.
-
 14:00
14:00 Free and Open Source GIS Ramblings: Adding basemaps to PyQGIS maps
sur Planet OSGeoIn the previous post, we investigated how to bring QGIS maps into Jupyter notebooks.
Today, we’ll take the next step and add basemaps to our maps. This is trickier than I would have expected. In particular, I was fighting with “invalid” OSM tile layers until I realized that my QGIS application instance somehow lacked the “WMS” provider.
In addition, getting basemaps to work also means that we have to take care of layer and project CRSes and on-the-fly reprojections. So let’s get to work:
from IPython.display import Image from PyQt5.QtGui import QColor from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication from qgis.core import QgsApplication, QgsVectorLayer, QgsProject, QgsRasterLayer, \ QgsCoordinateReferenceSystem, QgsProviderRegistry, QgsSimpleMarkerSymbolLayerBase from qgis.gui import QgsMapCanvas app = QApplication([]) qgs = QgsApplication([], False) qgs.setPrefixPath(r"C:\temp", True) # setting a prefix path should enable the WMS provider qgs.initQgis() canvas = QgsMapCanvas() project = QgsProject.instance() map_crs = QgsCoordinateReferenceSystem('EPSG:3857') canvas.setDestinationCrs(map_crs) print("providers: ", QgsProviderRegistry.instance().providerList())
To add an OSM basemap, we use the xyz tiles option of the WMS provider:
urlWithParams = 'type=xyz&url=https://tile.openstreetmap.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png&zmax=19&zmin=0&crs=EPSG3857' rlayer = QgsRasterLayer(urlWithParams, 'OpenStreetMap', 'wms') print(rlayer.crs()) if rlayer.isValid(): project.addMapLayer(rlayer) else: print('invalid layer') print(rlayer.error().summary())If there are issues with the WMS provider,
rlayer.error().summary()should point them out.
With both the vector layer and the basemap ready, we can finally plot the map:
canvas.setExtent(rlayer.extent()) plot_layers([vlayer,rlayer])

Of course, we can get more creative and style our vector layers:
vlayer.renderer().symbol().setColor(QColor("yellow")) vlayer.renderer().symbol().symbolLayer(0).setShape(QgsSimpleMarkerSymbolLayerBase.Star) vlayer.renderer().symbol().symbolLayer(0).setSize(10) plot_layers([vlayer,rlayer])
And to switch to other basemaps, we just need to update the URL accordingly, for example, to load Carto tiles instead:
urlWithParams = 'type=xyz&url=http://basemaps.cartocdn.com/dark_all/{z}/{x}/{y}.png&zmax=19&zmin=0&crs=EPSG3857' rlayer2 = QgsRasterLayer(urlWithParams, 'Carto', 'wms') print(rlayer2.crs()) if rlayer2.isValid(): project.addMapLayer(rlayer2) else: print('invalid layer') print(rlayer2.error().summary()) plot_layers([vlayer,rlayer2])
You can find the whole notebook at: [https:]]
-
 10:00
10:00 Lutra consulting: 3D Tiles in QGIS
sur Planet OSGeoEarlier this year, in collaboration with North Road we were awarded a grant from Cesium to introduce 3D tiles support in QGIS. The feature was developed successfully and shipped with QGIS 3.34.
In this blog post, you can read more about how to work with this feature, where to get data and how to display your maps in 2D and 3D. For a video demo of this feature, you can watch Nyall Dawson’s presentation on Youtube.
What are 3D tiles?3D tiles are a specification for streaming and rendering large-scale 3D geospatial datasets. They use a hierarchical structure to efficiently manage and display 3D content, optimising performance by dynamically loading appropriate levels of detail. This technology is widely used in urban planning, architecture, simulation, gaming, and virtual reality, providing a standardised and interoperable solution for visualising complex geographical data.
Examples of 3D tiles:
Data from Swisstopo [https:]
Washington - 3D Surface Model (Vricon, Cesium) 3D tiles in QGIS
To be able to use 3D tiles in QGIS, you need to have QGIS 3.34 or later. You can add a new connection to a 3D tile service from within the Data Source Manager under Scene:
Adding a new 3D tile service from Data Source Manager in QGIS
Alternatively, you can add the service from your Browser Panel:
3D tiles data provider in the Browser panel
To test the feature, you can use the following 3D tiles service:
Name: Bathurst URL: [https:]
Creating a new connection to a 3D tiles service
You can then add the map from the newly generated connection to QGIS:
Adding a new 3D tiles to QGIS
By default, the layer is styled using texture, but you can change it to see the wireframe mesh behind the scene:
3D tiles’ mesh wireframe
You can change the mesh fill and line symbols similar to the vector polygons. Alternatively, you can use texture colors. This will render each mesh element with the average value of the full texture. This is ideal when dealing with a large dataset and want to get a quick overview of the data:
3D tiles with texture color for meshes
To view the data in 3D, you can open a new 3D map. Similar to 2D map, by zooming in/out, finer resolution tiles will be fetched and displayed:
Using data from Cesium ionCesium ion is a cloud-based platform for managing and streaming 3D geospatial data. It simplifies data management, visualisation, and sharing.
To add 3D tiles from Cesium ion, you need to first sign up to their service here: [https:]
Under Asset Depot, you will see a catalogue of publicly available datasets. You can also upload your own 3D models (such as OBJ or PLY), georeference them and get them converted to 3D tiles.
You can also add one of the existing tile service under [https:]] and select the tile service and then click on Add to my assets:
Adding an existing dataset to your Cesium ion assets
You can use the excellent Cesium ion plugin by North Road from the QGIS repository to add the data to QGIS:
Adding Cesium ion assets to QGIS Working with Google 3D data
In addition to accessing Google Photorealistic 3D tiles from Cesium ion, you can also add the tiles directly in QGIS. First you will need to follow the instructions below and obtain API keys for 3D tiles: [https:]]
During the registration process, you will be asked to add your credit card details. Currently (November 2023), they do not charge you for using the service.
Once you have obtained the API key, you can add Google tiles using the following connection details:
Adding Google Photorealistic tiles in QGIS Notes and remarks
- Adjusting map extents for large scenes
When dealing with large scenes, map extents should be set to a smaller area to be able to view it in 3D. This is the current limitation of QGIS 3D maps as it cannot handle scenes larger than 500 x 500 km.
To change the map extent, you can open Project Properties and under View Settings change the extent. In the example below, the map extent has been limited only to a part of London, so we can view Google Photorealistic tiles in the 3D map without rendering issues.
Limiting project extent in QGIS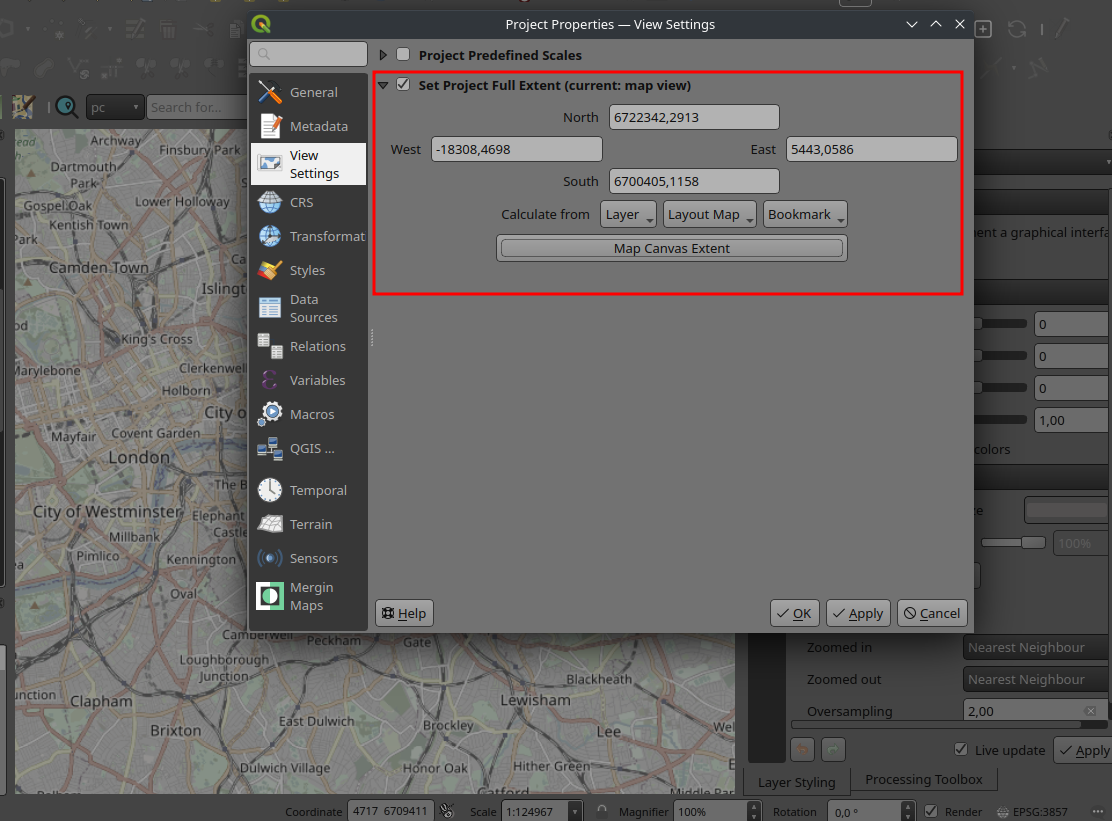
3D tiles from Google in QGIS
- Network cache size
If you are handling a large dataset, it is recommended to increase network cache size to 1 GB or more. The default value in QGIS is much lower and it results in slower rendering of the data.
Increasing Cache size in QGIS for faster rendering
- Overlaying other 3D data
When you try to overlay other data sets on top of a global 3D tiles, the vertical datum might not match and hence you will see the data in the wrong place in a 3D map. To fix the issue, you may need to use elevation offsetting to shift the data along the Z axis under Layer Properties:
Offsetting elevation of a layer in QGIS Future works
This is the first implementation of the 3D tiles in QGIS. For the future, we would like to add more features for handling and creation of the 3D tiles. Our wishlist in no particular order is:
- Globe view: QGIS 3D cannot handle large scenes or unprojected views.
- More advanced styling of meshes: as an example, users will be able to create their own style.
- 3D In-door navigation: as an example users will be able to navigate inside buildings and potentially it will bring BIM data closer to QGIS
- Generation of 3D tiles inside QGIS: adding a processing tool in QGIS to generate 3D Tiles from your map data.
Styling of 3D tiles (image from [https:]
If you would like to see those features in QGIS and want to fund the efforts, do not hesitate to contact us.
-
 20:16
20:16 Free and Open Source GIS Ramblings: MovingPandas v0.17 released!
sur Planet OSGeo
Over the last couple of months, I have not been posting release announcements here, so there is quite a bit to catch up.
The latest v0.17.2 release is now available from conda-forge.
New features (since 0.14):
- Improved MovingFeatures MF-JSON support
- New OutlierCleaner #334
- Faster stop detection #316
- New arrow markers to indicate trajectory direction in plots fb1174b
- Distance, speed, and acceleration unit handling #295
- New aggregation parameter (agg) for to_traj_gdf() 5745068
- New get_segments_between() for TrajectoryCollection #287
Behind the scenes:
- We now have a dedicated Github organization: [https:]] that houses all related repositories
- And we finally added [https] support to the website
As always, all tutorials are available from the movingpandas-examples repository and on MyBinder:

If you have questions about using MovingPandas or just want to discuss new ideas, you’re welcome to join our discussion forum.
-
 16:09
16:09 OGC India Forum 2023: Key Highlights from Hyderabad
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)A meeting of the OGC India Forum was held on October 18, 2023, in Hyderabad, where over 40 experts from government, industry, and academia met to discuss the future of geospatial technologies in India. With its booming tech industry, Hyderabad provided an apt backdrop for discussions on innovation and standards in the geospatial realm.
The event was supported by the following organizations: The Association of Geospatial Industries (AGI India), which represents India’s geospatial private sector capabilities; the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the national standards body that underpins technical excellence; and Geospatial World, a media company and the host for GeoSmart India 2023, where the forum was organized.
A pivotal moment at the event was the unveiling of the OGC India Forum’s new Charter, heralding a renewed commitment to advancing geospatial standards and innovation within the Indian context. Also at the Forum, OGC and AGI India renewed their partnership in line with the policy priorities of India.
 Harsha Madiraju, OGC, and Sreeramam GV, AGI India, exchanging the partnership agreement.
Harsha Madiraju, OGC, and Sreeramam GV, AGI India, exchanging the partnership agreement.
The forum facilitated a series of expert-led panels, dissecting the latest trends, challenges, and opportunities in the geospatial and Earth Observation sectors. It provided a platform for participants to contribute insights and actively shape the Forum’s committees and future directives.
Emphasizing the Economic Value of Geospatial StandardsHarsha Madiraju, Lead – OGC India Forum, set the stage with a presentation on the economic impact of standards in geospatial technologies. Citing the 2012 ISO publication on Standards and Economic Growth, he highlighted the positive correlation between the proliferation of standards and national economic development. This underscores the importance of investment in geospatial interoperability and its tangible benefits to industries and economies.
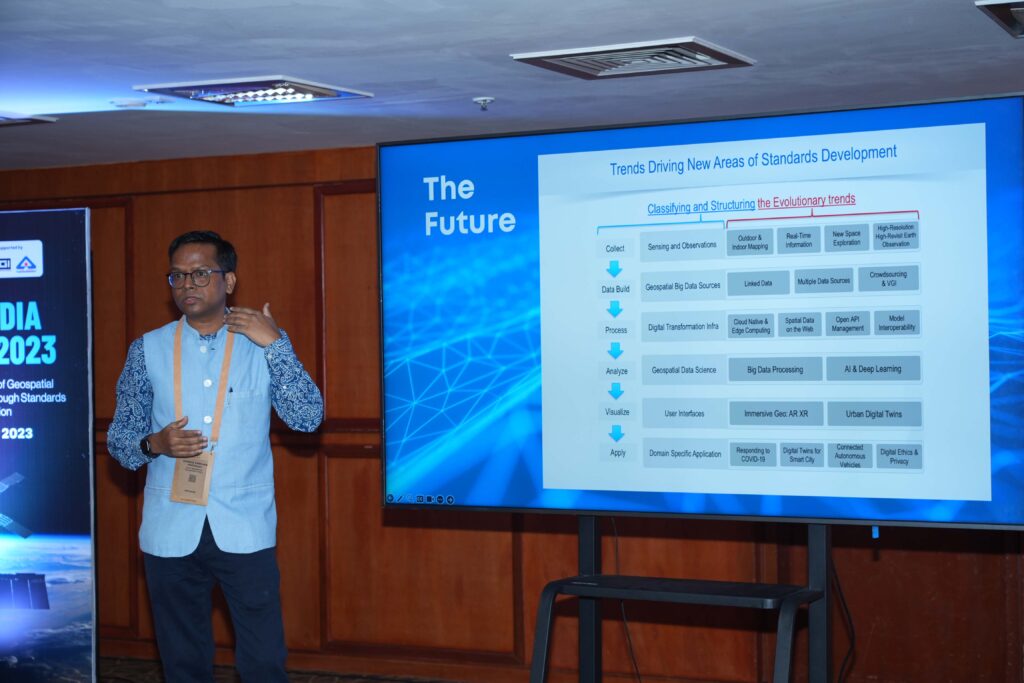 Harsha Madiraju, Lead – OGC India Forum, delivering his opening address.
Harsha Madiraju, Lead – OGC India Forum, delivering his opening address.
From the Indian Context, Harsha said that we need proven methodologies and best practices for implementing Standards in India’s diverse and complex landscape. From this perspective, he said, the “Guide to the Role of Standards in Geospatial Information Management” prepared by ISO/TC 211, OGC, and IHO, and endorsed by UN-GGIM, provides a reliable framework around geospatial standards implementation. Quoting the guide, he said the Indian community can refer to the Goal-based Approach to geospatial standards implementation, where different maturity levels from Tier 1 to Tier 4 are prescribed.
 Goal-based Approach to geospatial standards implementation
Goal-based Approach to geospatial standards implementation
Harsha said about the interoperability scenario in India: “Our data and systems are not yet fully interoperable, and our community is at varying stages of maturity compared to more developed geospatial ecosystems. The opportunity here is immense. It’s not just about sharing maps: it’s about evolving towards a spatially enabled nation where we can take advantage of the authoritative datasets coming up for India.”
He further called for collaboration by saying “In a country like India, with its unique challenges and opportunities, the role of standards in accelerating the maturity of our technology ecosystems is crucial. At OGC India Forum, we aim to work on standards, compliance, and innovation. It’s not just the responsibility of a few: it’s a collective endeavor. Your expertise and contributions can shape the future of geospatial technology in India.”
Concluding his talk, he said, “We have the framework, the global endorsement, and, most importantly, a community willing to drive change. Let’s invest wisely in standards to shape a future that benefits us all.”
Panels and Discussions for India – Tech Trends, Adoption of Standards, and Academic Perspectives.The event then proceeded with three panels on the following topics:
Panel on Geospatial and Earth Observation Technology Innovation in IndiaThe panel discussed India’s contributions to geospatial and Earth Observation technologies and the possible advancements that may come from the Indian government, private sector, and especially start-ups. The session also discussed the untapped sectors and applications that these technologies could significantly impact. Finally, the discussions identified key challenges in technology adoption and scalability and discussed how the community can help overcome these challenges.
 Panelists on Geospatial and Earth Observation Technology Innovation in India, along with along with AGI and OGC Staff (on the right side)
Panelists on Geospatial and Earth Observation Technology Innovation in India, along with along with AGI and OGC Staff (on the right side)
Rajesh Mathur, Esri India, said that federated GIS architecture is a new paradigm enabling collaboration and data sharing. According to him, India’s National Geospatial Policy 2022 is a progressive and transformational initiative that will accelerate the adoption of geospatial technologies by encouraging collaboration and data sharing among all the stakeholders. This opens up exciting opportunities for GIS deployment – both on the Cloud and in a federated architecture. Data partnerships enabled by Standards and interoperability will allow users from multiple organizations to collaborate and share content through trusted and secure workflows.
Shubham Sharma, GalaxEye Space, said that the OGC India Forum provided a great platform to interact with the panel members and the audience with diverse experiences. With discussions ranging from the evolution of technology in the geospatial sector to standardization, the discussions centred around the implementation of OGC standards in India. With the continued expansion of the geospatial sector, Open Standards will pave a smoother road for building scalable and sustainable products.
S S Raja Shekar, National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), said OGC standards have changed how geospatial data and applications are handled, providing simple solutions to complex exchanges of data and services. A growing focus on standards in the space domain and in sectors of priority to the country where geospatial applications are critical is needed. This session also brought perspectives and ideas from entrepreneurs and proved to be highly constructive.
Akshay Loya, Founder & CEO of GISKernel Technologies, said “I was asked how I envision the evolution of the geospatial industry in India. My response was straightforward: we, as young founders, can share our insights alongside esteemed figures on a platform like OGC India Forum, which is a significant evolution in our industry.”
Panel on Geospatial and Earth Observation Standards in IndiaThe second panel examined the current adoption of BIS/ISO and OGC standards in India, focusing on areas where they are most – and least – implemented. The panel also discussed the avenues available for contributing to geospatial and Earth Observation Standards, both at a national and international level. The session then also delved into the compliance and procurement aspects.
 Speakers at the Panel on Geospatial and Earth Observation Standards
Speakers at the Panel on Geospatial and Earth Observation Standards
Abhiroop Bhatnagar, Lead, Platform at Aereo, said “I would like to share the message regarding the importance of cloud-native geospatial formats. The essential property of cloud-native formats is that they allow data delivery directly from cloud-based storage to clients without involving any compute in between – for example consider direct requests to S3 from web browsers. The world is quickly transitioning towards a cloud-based data-delivery paradigm. Under this new paradigm, if we have to ensure scalability along with preserving efficiency, it is critical to utilize cloud-native geospatial formats. In that respect, Cloud-optimized GeoTIFF has already been accepted as an OGC standard and is well-supported by the ecosystem. We at Aereo have already integrated support for COGs in our WebGIS platform, Aereo Cloud. We actively promote it as the preferred format for raster data within the industry and the government.”
Ashish Tiwari, Joint Director of the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), said that ISO/TC211 and OGC have a strong history of collaboration on geospatial standards. BIS, through the Geospatial Information Sectional Committee, has adopted over twelve Standards and is working on adopting fourteen more. BIS looks forward to collaborating with the OGC community, as this will be valuable in many areas where BIS can understand recent trends and best practices.
Participating in this session, Vishnu Chandra, Former Deputy Director General & HOG -NIC, Geospatial Technology Services Division, said that open geospatial Standards are the core foundation of geospatial information interoperability and play a crucial role through open geospatial APIs for the exchange of data and Service Delivery. OGC India Forum can play a critical role in bringing the global OGC standards to India in collaboration with various government, industry, and academic stakeholders.
OGC standards have a significant role given the context of the Indian National Geospatial Policy 2022, which calls for the creation of the National Geospatial Foundation around 14 Thematic Areas to support UN-GGIM objectives associated with the UN Sustainable Development Goals. These themes also have relevance in digital public infrastructures and platforms for specific governance, planning, and service delivery in the Indian context. Therefore, each data theme needs Standards implemented across the entire geospatial information value chain.
Panel providing Perspectives from Academia & Research on Innovation and Standards in IndiaThe final panel discussed the current awareness and usage of geospatial and Earth Observation Standards in academic programs and research projects. The discussions explored the extent to which Standards are integrated into educational curricula. The panel also delved into how academic and research institutions can contribute to standards development, implementation testing, and even lead the creation of new standards.
 Speakers at the Panel Providing Perspectives from Academia & Research
Speakers at the Panel Providing Perspectives from Academia & Research
Dr. Sanjay Chaudhary, Professor and Associate Dean, Ahmedabad University, School of Engineering and Applied Science, said “There is a lack of interest in geospatial technologies in India from the students in the broader computer science and IT community. Helping them understand the value and opportunities available in this sector will be important. With the evolution of OGC Standards into APIs and the availability of developer resources, we can make these students learn and invest in this direction, which will be valuable to their professions and bring skilled resources to India.”
Professor Dr. Karbhari Vishwanath Kale, Vice-Chancellor of Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, Raigad, Maharashtra, said “Through our engagement with the Bureau of Indian Standards, I have been making personal efforts to bring awareness in our professional circles on the value and importance of Standards. As an OGC Member, our university closely follows the development of international Standards by OGC. Some of our core interests lie in the intersection of multi- and hyper-spectral sensor data for agriculture, material detection, disaster management, and health care. We must invest in developing sensors and data dissemination platforms and make applications and data more broadly available, specifically in agriculture. In line with the Indian National Education Policy 2020, our university has set goals to establish and design the course curriculum with a research lab where IoT, sensors, and Standards can be brought together for the overall benefit of end users. We look forward to collaborating with the international network of OGC and taking this on.”
Dr. Sumit Sen, GISE Hub, IIT Bombay, said “Our Hub is established as an interdisciplinary project funded by the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, to enable the research and development of geospatial technology solutions. In turn, our hub works with many academic and research organizations to further fundamental research in GIScience. Standards and Interoperability is one of the focus areas, and we continue to work closely with OGC and other stakeholders like IIT Kanpur, IIT Tirupati, and IIIT Hyderabad in enabling the geospatial community with the right skills on OGC Standards and APIs. The Winter School is one of India’s unique learning programs on geospatial standards. It is a fifteen-day on-campus training program supported by OGC Staff and Members. It provides hands-on and practical training on OGC Standards to India’s government, private, and research organizations. The 2023 program will be on the OGC API Stack. We will continue our international engagement and work closely with the OGC India Forum community.”
Next StepsThe OGC India Forum 2023 event was a success. The event concluded with a broader agreement around the need to identify areas of engagement in the coming days. It was agreed that there is a need for partnerships and to organize events, training programs, and policy roundtables on geospatial standards, in collaboration with OGC Members and Partners in India and the broader community.
The post OGC India Forum 2023: Key Highlights from Hyderabad appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:27
17:27 Markus Neteler: Translating Open Source Software with Weblate: A GRASS GIS Case Study
sur Planet OSGeoOpen source software projects thrive on the contributions of the community, not only for the code, but also for making the software accessible to a global audience. One of the critical aspects of this accessibility is the localization or translation of the software’s messages and interfaces. In this context, Weblate (https://weblate.org/) has proven to be a powerful tool for managing these translations, especially for projects such as GRASS GIS, which is part of OSGeo (Open Source Geospatial Foundation).
What is Weblate?Weblate is an open source translation management system designed to simplify the translation process of software projects. It provides an intuitive web interface that allows translators to work without deep technical knowledge. This ease of use combined with robust integration capabilities makes Weblate a popular choice for open source projects.
GRASS GIS and LocalizationGRASS GIS ( [https:]] ), a software suite for managing and analyzing geospatial data, is used worldwide and therefore needs to be available in many languages. The project uses Weblate, hosted by OSGeo, to manage and facilitate its translation work (see OSGeo-Weblate portal).
Marking messages for translationBefore translation work can begin, the messages to be translated must be marked for translation in the GRASS GIS source code. This is done with the gettext macro _(“…”). GNU gettext is a GNU library for the internationalization of software. Here is a simplified overview of the process:
- Identify the strings to be translated: The developers identify the strings in the source code that need to be translated. These are usually user messages, while debug messages are not marked for translation.
- Use the gettext macro: The identified strings are packed into a gettext macro. For example, a string “Welcome to GRASS GIS” in the source code would be changed to _(“Welcome to GRASS GIS”). This change indicates that the string should be used for translation.
- Extraction and template generation: Tools such as xgettext are used to extract these marked strings from the source code and create a POT (Portable Object Template) file. This file is used as a template for all translations. In the GRASS GIS project the template language is English.
There are three template files in the GRASS GIS project: one with the graphical user interface (GUI) messages, one with the library functions (libs) and one with the modules (mods).
Connecting the software project to WeblateWhile the POT files could be transferred to Weblate manually, we chose the automated option. The OSGeo Weblate instance is directly connected to the GRASS GIS project via git (GitHub) using the Weblate version control integration.
How it works in practice:
- Developer makes a commit to the GRASS GIS repo on GitHub
- A GitHub webhook makes a call to weblate.osgeo.org – note that it has it’s own local git repo for GRASS GIS, as it does for other OSGeo projects, with translations being managed in this Weblate instance. This local git repo is updated when the webhook is fired.
- As messages are translated in OSGeo-Weblate, they are eventually pushed to the Weblate Github fork of GRASS GIS (the push frequency is set to 24 hours by default, i.e., new translations are collected over a day), and Weblate then triggers a pull request to the main GRASS GIS repo on GitHub.
For technical background on the OSGeo Weblate installation, see the related OSGeo-SAC Weblate page.
Translation process in WeblateHere is how the typical translation process looks like:
- Translator registration: Registration (via OSGeo-ID) and login to the Weblate instance.
- Language selection: Select the language to be translated. If a language does not exist yet, it can be added with the approval of the project managers.
- Translation interface: Weblate provides an easy-to-use web interface where translators can view the original texts and enter their translations. If activated, machine translation can also be used here (DeepL, Google Translate, etc.). The Weblate translation memory helps to quickly translate identical and similar sentences.
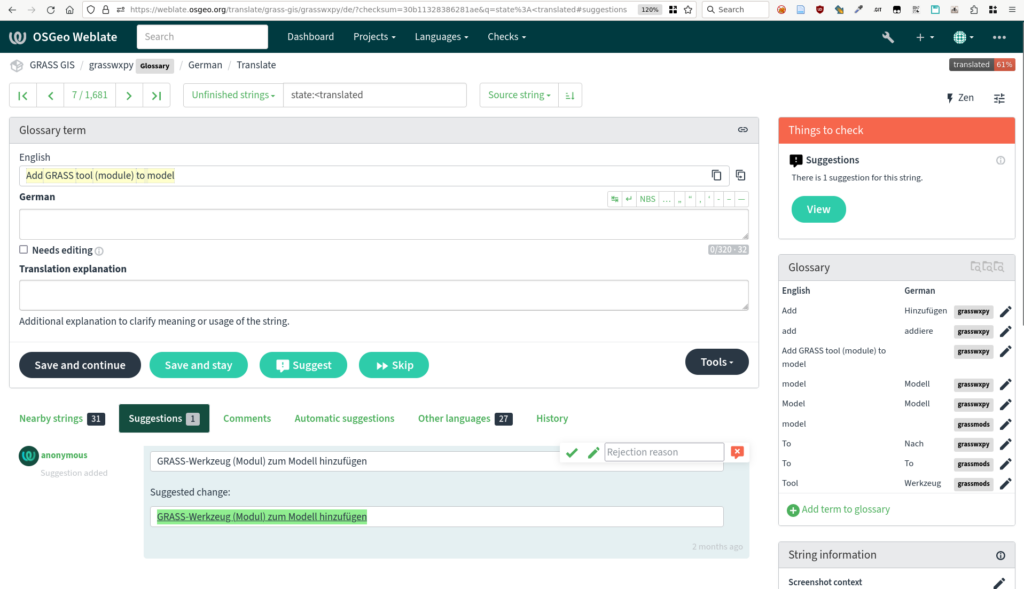
GRASS GIS messages in Weblate
- Together we are better: translators can discuss translations, resolve conflicts and suggest improvements. Weblate also offers quality checks to ensure consistency and accuracy. Translations in different languages can be compared in tabular form.
Message translation comparison in Weblate (GRASS GIS project example)
- Integration with source code: Once translations are completed and checked, they are written back into the GRASS GIS source code (see above). Weblate supports automatic synchronization with source code repositories.
- Continuous updates: As the source code evolves, new strings can be marked for translation and Weblate is automatically updated to reflect these changes.
Pull request with new translations opened by Weblate in GRASS GIS Github repository
Benefits for the GRASS GIS projectBy using Weblate, GRASS GIS benefits from the following advantages:
- Streamlined translation workflow: The process from tagging strings to integrating translations is efficient and manageable.
- Community engagement: Weblate’s ease of use encourages more community members to participate in the translation process.
- Quality and Consistency: Weblate ensures high quality translations through integrated quality checks and collaboration tools.
- Up-to-date localization: Continuous synchronization with the source code repository ensures that translations are always up-to-date.
The integration of Weblate into the GRASS GIS development workflow underlines the importance of localization in open source software. By using tools such as gettext for message tagging and Weblate for translation management, GRASS GIS ensures that it remains accessible and usable for a global community, embodying the true spirit of open source software.
ThanksThanks to Regina Obe from OSGeo-SAC for her support in setting up and maintaining the OSGeo-Weblate instance and for her explanations of how things work in terms of Weblate/GitHub server communication.
The post Translating Open Source Software with Weblate: A GRASS GIS Case Study appeared first on Markus Neteler | Geospatial Analysis | Remote sensing | GRASS GIS.
-
 4:01
4:01 Sean Gillies: Wellsville fall colors
sur Planet OSGeoAfter crashing out of the Bear, I picked myself up by going for a short hike in the Wellsville Mountains. This range frames Cache Valley on the west side and is covered with bigtooth maple.

The Wellsville Range draped in red maples.
The colors made my jaw drop. I lived in Cache Valley for 10 years and don't remember a better show.

Closeup on pink and red maple leaves.

Dark red chokecherry leaves.
Hobbling through this landscape and seeing the color change as the sunlight fluctuated improved my mood by several hundred percent.

View across a sunlit pasture to red maple covered slopes under a partly stormy sky.
-
 2:00
2:00 Ian Turton's Blog: Is GeoJSON a spatial data format?
sur Planet OSGeoIs GeoJSON a good spatial data format?A few days ago on Mastodon Eli Pousson asked:
Can anyone suggest examples of files that can contain location info but aren’t often considered spatial data file formats?
He suggested EXIF, Iván Sánchez Ortega followed up with spreadsheets, and being devilish I said GeoJSON.
This led to more discussion, with people asking why I thought that, so I instead of being flippant I thought about it. This blog post is the result of those thoughts which I thought were kind of obvious but from things people have said since may be aren’t that obvious.
I’ve mostly been a developer for most of my career so my main interest in a spatial data format is that:
- it stores my spatial data as I want it to,
- it’s fast to read and to a lesser extent, write.
- It’s easy to manage.
One, seems to be obvious, if I store a point then ask for it back I want to get that point back (to the limit of the precision of the processor’s floating point). If a format can’t manage that then please don’t use it. This is not common but Excel comes to mind as a program that takes good data and trashes it. If it isn’t changing gene names into dates then it’s reordering the dbf file to destroy your shapefile. GeoJSON also can fail at this as the standard says that I must store the data in WGS:84 (lon/lat), which is fine if that is the format that I store my data in already, but suppose I have some high quality OSGB data that is carefully surveyed to fractions of a millimetre and the underlying code does a conversion to WGS:84 in the background and further the developer wanted to save space and limited the number of decimal places to say 6 (OK, that was me) when it gets converted back to OSGB I’m looking at centimetres (or worse) but given the vagaries of floating point representation I may not be able to tell.
Two, comes from being a GeoServer developer, a largish chunk of the time taken to draw a web map (or stream out a WFS file) is taken up by reading the data from the disk. Much of the rest of the time is converting the data into a form that we can draw. Ideally, we only want to read in the features needed for the map the user has requested (actually, ideally we want to not read in most of the data by having it already be in the cache, but that is hard to do). So we like indexed datasets both spatial indexes and attribute indexes can help substantially speed up map drawing. As the size of spatial datasets increases the time taken to fetch the next feature from the store becomes more and more important. An index allows the program to skip to the correct place in the file for either a specific feature or for features that are in a specific place or contain a certain attribute with the requested value. This is a great time saver, imagine trying to look something up in a big book by using the index compared to paging through it reading each page in turn.
After one or more indexes the main thing I look for in a format is a binary format that is easy to read (and write). GeoJSON (and GML) are both problematic here as they are text formats (which is great in a transfer format) and so for every coordinate of every spatial object the computer has to read in a series of digits (and punctuation) and convert that into an actual binary number that it can understand. This is a slow operation (by computer speeds anyway) and if I have a couple of million points in my coastline file then I don’t want to do 4 million slow operations before I even think of drawing something.
Three, I have to interact with users on a fairly regular basis and in a lot of cases these are not spatial data experts. If a format comes with up to a dozen similarly named files (that are all important) that a GIS will refuse to process unless you guess which is the important one then it is more of a pain than a help. And yes shapefile I’m looking at you. If your process still makes use of Shapefiles please, please stop doing that to your users (and the support team) and switch over to GeoPackages which can store hundreds of data sets inside a single file, All good GIS products can process them by now, they have been an OGC standard for nearly 10 years. If you don’t think that shapefiles are confusing go and ask your support team how often they have been sent just the
.shpfile (or 11 files but not the.sbn) or how often they have seen people who have deleted all the none.shpfiles to save disk space.My other objection to GeoJSON is that I don’t know what the structure (or schema) of the data set is until I have read the entire file. That last record could add several bonus attributes, in fact any (or all) of the records could do that, from a parsers view it is a nightmare. At least GML provides me with a fixed schema and enforces it through out the file.
When I’m storing data (as opposed to transferring it) I use PostGIS, it’s fast and accurate, can store my data in whatever projection I chose and is capable of interfacing with any GIS program I am likely to use, and if I’m writing new code then it provides good, well tested libraries in all the languages I care about so I don’t have to get into the weeds of parsing binary formats. If I fetch a feature from PostGIS it will have exactly the attributes I was expecting no more or less. It has good indexes and a nifty DSL (SQL) that I can use to express my queries that get dealt with by a cool query optimiser that knows way more than I do about how to access data in the database.
If for some reason I need to access my data while I’m travelling or share it with a colleague then I will use a GeoPackage which is a neat little database all packaged up in a single file. It’s not a quick as PostGIS so I wouldn’t use it for millions of records but for most day to day GIS data sets it’s great. You can even store you QGIS styles and project in it to make it a single file project transfer format.
One final point, I sometimes see people preaching that we should go cloud native (and often serverless) by embracing “modern” standards like GeoJSON and COGs. GeoJSON should never be used as a cloud native storage option (unless it’s so small you can read it once and cache it in memory in which case why are you using the cloud) as it is large (yes, I know it compresses well) and slow to parse (and slower still if you compressed it first) and can’t be indexed. So that means you have to copy the whole file from a disk on the far side of a slow internet connection. I don’t care if you have fibre to the door it is still slow compared to the disk in your machine!

-
 22:04
22:04 KAN T&IT Blog: Simplificá tu Análisis Geoespacial con KICa, el Innovador Plugin de QGIS para acceder a catálogos de Imágenes
sur Planet OSGeoPièce jointe: [télécharger]
KICa, «Kan Imagery Catalog», es un plugin para QGIS. Esta herramienta innovadora simplifica el acceso a catálogos de imágenes satelitales, en un principio, utilizando metodología estándar como es STAC (sigla en inglés de Catálogos de Recursos Espacio- Temporales) el cual es un lenguaje único para el acceso a catálogos de imágenes satelitales de una manera estándar y uniforme. Esto nos permite tener un objetivo agnóstico basado en la posibilidad de centrarnos en la necesidad de resolver nuestro análisis geoespacial sobre una zona y no tener que estar buscando cada uno de los proveedores por separado.
En un principio se incorporan proveedores de imágenes satelitales (gratuitas y comerciales), pero está previsto, en las siguientes versiones, incorporar imágenes de drones, vuelos entre otros recursos que faciliten el análisis geoespacial. Hoy podrán observar que están disponible los proveedores como UP42 o Sentinel Hub, dentro de una región geográfica definida por el usuario.
Con este potente plugin, los usuarios tienen la capacidad de explorar de manera eficiente los catálogos disponibles, así como consultar pisadas (footprints) y vistas rápidas (quicklooks) de las imágenes que se encuentran en su área de interés para estimar su uso sin la necesidad de ser descargada la imagen completa para su análisis.
Así, este plugin se convierte en una herramienta esencial para todos aquellos que trabajan con datos geoespaciales, ya que les proporciona un acceso rápido y sencillo a imágenes satelitales, facilitando tanto el análisis como la visualización de datos. No importa si sos un profesional en el campo de la geoinformación, un científico de datos o un entusiasta de la cartografía; «KICa» enriquecerá tu flujo de trabajo y mejorará tus capacidades de exploración y utilización de imágenes satelitales.
Nuestra solución es de código abierto y colaborativa, por lo que te invitamos a visitar nuestro repositorio donde podrás ver más documentación, reportar bugs y nuevas mejoras, y también contribuir en el código con tus “push request”.
¡Optimizá tus proyectos geoespaciales con esta valiosa herramienta!
#satellite #QGIS #SentinelHub #Copernicus #Sentinel -
 20:03
20:03 Free and Open Source GIS Ramblings: Bringing QGIS maps into Jupyter notebooks
sur Planet OSGeoEarlier this year, we explored how to use PyQGIS in Juypter notebooks to run QGIS Processing tools from a notebook and visualize the Processing results using GeoPandas plots.
Today, we’ll go a step further and replace the GeoPandas plots with maps rendered by QGIS.
The following script presents a minimum solution to this challenge: initializing a QGIS application, canvas, and project; then loading a GeoJSON and displaying it:
from IPython.display import Image from PyQt5.QtGui import QColor from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication from qgis.core import QgsApplication, QgsVectorLayer, QgsProject, QgsSymbol, \ QgsRendererRange, QgsGraduatedSymbolRenderer, \ QgsArrowSymbolLayer, QgsLineSymbol, QgsSingleSymbolRenderer, \ QgsSymbolLayer, QgsProperty from qgis.gui import QgsMapCanvas app = QApplication([]) qgs = QgsApplication([], False) canvas = QgsMapCanvas() project = QgsProject.instance() vlayer = QgsVectorLayer("./data/traj.geojson", "My trajectory") if not vlayer.isValid(): print("Layer failed to load!") def saveImage(path, show=True): canvas.saveAsImage(path) if show: return Image(path) project.addMapLayer(vlayer) canvas.setExtent(vlayer.extent()) canvas.setLayers([vlayer]) canvas.show() app.exec_() saveImage("my-traj.png")When this code is executed, it opens a separate window that displays the map canvas. And in this window, we can even pan and zoom to adjust the map. The line color, however, is assigned randomly (like when we open a new layer in QGIS):
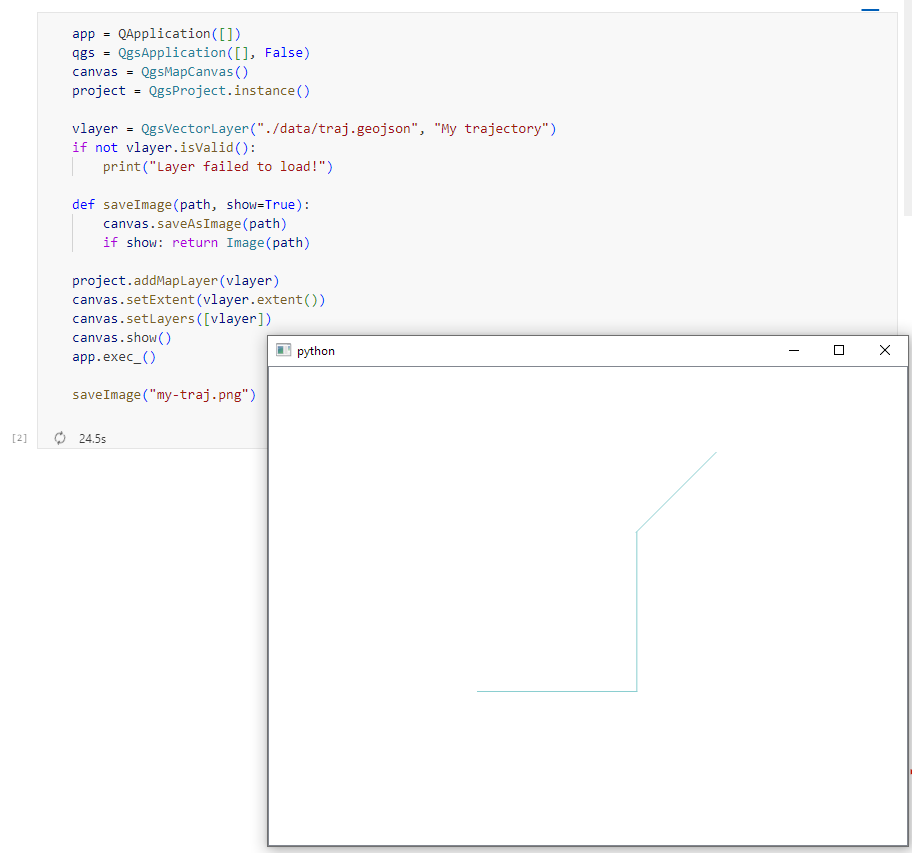
To specify a specific color, we can use:
vlayer.renderer().symbol().setColor(QColor("red")) vlayer.triggerRepaint() canvas.show() app.exec_() saveImage("my-traj.png")
But regular lines are boring. We could easily create those with GeoPandas plots.
Things get way more interesting when we use QGIS’ custom symbols and renderers. For example, to draw arrows using a QgsArrowSymbolLayer, we can write:
vlayer.renderer().symbol().appendSymbolLayer(QgsArrowSymbolLayer()) vlayer.triggerRepaint() canvas.show() app.exec_() saveImage("my-traj.png")
We can also create a QgsGraduatedSymbolRenderer:
geom_type = vlayer.geometryType() myRangeList = [] symbol = QgsSymbol.defaultSymbol(geom_type) symbol.setColor(QColor("#3333ff")) myRange = QgsRendererRange(0, 1, symbol, 'Group 1') myRangeList.append(myRange) symbol = QgsSymbol.defaultSymbol(geom_type) symbol.setColor(QColor("#33ff33")) myRange = QgsRendererRange(1, 3, symbol, 'Group 2') myRangeList.append(myRange) myRenderer = QgsGraduatedSymbolRenderer('speed', myRangeList) vlayer.setRenderer(myRenderer) vlayer.triggerRepaint() canvas.show() app.exec_() saveImage("my-traj.png")
And we can combine both QgsGraduatedSymbolRenderer and QgsArrowSymbolLayer:
geom_type = vlayer.geometryType() myRangeList = [] symbol = QgsSymbol.defaultSymbol(geom_type) symbol.appendSymbolLayer(QgsArrowSymbolLayer()) symbol.setColor(QColor("#3333ff")) myRange = QgsRendererRange(0, 1, symbol, 'Group 1') myRangeList.append(myRange) symbol = QgsSymbol.defaultSymbol(geom_type) symbol.appendSymbolLayer(QgsArrowSymbolLayer()) symbol.setColor(QColor("#33ff33")) myRange = QgsRendererRange(1, 3, symbol, 'Group 2') myRangeList.append(myRange) myRenderer = QgsGraduatedSymbolRenderer('speed', myRangeList) vlayer.setRenderer(myRenderer) vlayer.triggerRepaint() canvas.show() app.exec_() saveImage("my-traj.png")
Maybe the most powerful option is to use data-defined symbology. For example, to control line width and color:
renderer = QgsSingleSymbolRenderer(QgsSymbol.defaultSymbol(geom_type)) exp_width = 'scale_linear("speed", 0, 3, 0, 7)' exp_color = "coalesce(ramp_color('Viridis',scale_linear(\"speed\", 0, 3, 0, 1)), '#000000')" # [https:] renderer.symbol().symbolLayer(0).setDataDefinedProperty( QgsSymbolLayer.PropertyStrokeWidth, QgsProperty.fromExpression(exp_width)) renderer.symbol().symbolLayer(0).setDataDefinedProperty( QgsSymbolLayer.PropertyStrokeColor, QgsProperty.fromExpression(exp_color)) renderer.symbol().symbolLayer(0).setDataDefinedProperty( QgsSymbolLayer.PropertyCapStyle, QgsProperty.fromExpression("'round'")) vlayer.setRenderer(renderer) vlayer.triggerRepaint() canvas.show() app.exec_() saveImage("my-traj.png")
Find the full notebook at: [https:]]
-
 2:00
2:00 Georg Heiler: Introduction to Geostatistics
sur Planet OSGeoGeorg Heiler: Introduction to Geostatistics -
 10:12
10:12 GRASS GIS: Apply Now for Student Grants
sur Planet OSGeoWe would like to announce a unique paid opportunity for students to contribute to GRASS GIS! GRASS GIS will offer a number of student grants for projects that include development of GRASS documentation, tests, new features or geospatial tools and bug fixing. Check the suggested topics on the Student Grant wiki. Why to apply? Experience: Gain hands-on experience in a thriving open-source community. Mentorship: Work alongside experienced developers who will guide you throughout your journey.
-
 16:00
16:00 OGC and Joint Research Centre renew Collaboration Agreement to enhance Geospatial Standards
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) and the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission (JRC) have renewed their collaboration agreement to enhance the development and use of geospatial standards.
The ongoing collaboration enables JRC to more effectively contribute to the OGC Standards process and facilitate the consideration of European objectives, requirements, and policies during the development of international open geospatial standards.
The agreement formalizes the partners’ collaboration in the field of development, application, maintenance, and promotion of international open geospatial standards and best practices that support the implementation of EU policies, for example, INSPIRE, European Data Spaces, Open Data, and Earth Observation, including Copernicus and Galileo.
Further, the agreement will enable OGC and JRC to jointly organize workshops for exchanging scientific and technological information on topics of mutual interest, for example, spatial law and policy, Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) Best Practices, and emerging technologies (e.g. metaverse, digital twins, cloud/edge computing, platforms, and Artificial Intelligence (AI)).
“We at OGC are pleased to continue our collaboration with the JRC,” commented Ingo Simonis, Ph.D, OGC Chief Technology Innovation Officer. “With the modernization of national and international spatial data infrastructures, the semantic enhancement of existing data offerings, and the development of cross-domain yet flexible solutions for heterogeneous communities, we have many core activities in common. Bringing the JRC and OGC communities together allows us to address these important topics far more efficiently.”
About JRC
The European Commission’s Joint Research Centre provides independent, evidence-based knowledge and science, supporting EU policies to positively impact society.?It plays a key role at multiple stages of the EU policy cycle.
It works closely with research and policy organisations in the Member States, with the European institutions and agencies, and with scientific partners in Europe and internationally, including within the United Nations system. In addition, the JRC offers scientific expertise and competences from a very wide range of disciplines in support of almost all EU policy areas.The post OGC and Joint Research Centre renew Collaboration Agreement to enhance Geospatial Standards appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 18:14
18:14 SIG Libre Uruguay: web gratuito «Asociación con EOS Data Analytics: Ventajas de su red de socios y soporte».
sur Planet OSGeo
Todo tipo de empresas y organizaciones orientadas a la agricultura están invitadas a asistir al seminario web, así como periodistas, activistas, y ecologistas interesados en la agricultura de precisión. Cuándo: 21 de noviembre Hora: 9 AM CST / 4 PM CET Los ponentes del seminario web serán: Dmytro Svyrydenko, Ejecutivo de cuentas, EOSD?
Pablo Ezequiel Escudero, Socio gerente, Agro Gestión
Esteban Moschin, Consultor de Negocios Independiente, Agro Gestión
Pablo Astudillo, Gerente General, BM Monitoring
Daniel Marulanda, Director General de Tecnología, GeoSatLos ponentes debatirán sobre los siguientes temas: Beneficios del Programa de socios y soporte de EOSDA.
Transformación de la agricultura en Argentina en los últimos 10 años. Cómo cambió en este tiempo el servicio de consultoría agrícola.
La agricultura de precisión en España. Gestores y asesores agrícolas y su rol en la transformación de la agricultura en el país.
El rol de los consultores y asesores agrícolas en Chile. Requisitos principales de los clientes para cubrir todas sus necesidades.
Solución de marca blanca, qué ventajas tiene y proyecto con la FAO. Recomendaciones para los clientes que quieren pasarse a marca blanca.Para obtener más información, presione aquí. Idioma: Español Duración: 1,5 horas. -
 19:41
19:41 SIG Libre Uruguay: Tercera edición del curso online gratuito del BID: Cartografía y Geografía Estadística
sur Planet OSGeo
El curso está dirigido al personal y/o profesionales del mundo de la estadística y de la geografía que estén interesados en conocer cómo se utilizan los mapas para las investigaciones de campo y cuál es el papel que juega la cartografía y las ciencias geográficas como apoyo a la ciencia estadística. No es necesario que se cuente con conocimientos previos muy especializados en manejo de herramientas de Sistemas de Información Geográfica (SIG). Click en la imagen para más información.
-Este curso es auto-regulado y no cuenta con clases o sesiones sincrónicas-
-Este curso no tiene el acompañamiento de un tutor/a-
-
 23:17
23:17 Free and Open Source GIS Ramblings: Exploring a hierarchical graph-based model for mobility data representation and analysis
sur Planet OSGeoToday’s post is a first quick dive into Neo4J (really just getting my toes wet). It’s based on a publicly available Neo4J dump containing mobility data, ship trajectories to be specific. You can find this data and the setup instructions at:
Maryam Maslek ELayam, Cyril Ray, & Christophe Claramunt. (2022). A hierarchical graph-based model for mobility data representation and analysis [Data set]. Zenodo. [https:]
I was made aware of this work since they cited MovingPandas in their paper in Data & Knowledge Engineering: “The implementation combines several open source tools such as Python, MovingPandas library, Uber H3 index, Neo4j graph database management system”
Once set up, this gives us a database with three hierarchical levels:

Neo4j comes with a nice graphical browser that lets us explore the data. We can switch between levels and click on individual node labels to get a quick preview:


Level 2 is a generalization / aggregation of level 1. Expanding the graph of one of the level 2 nodes shows its connection to level 1. For example, the level 2 port node “Audierne” actually refers to two level 1 nodes:
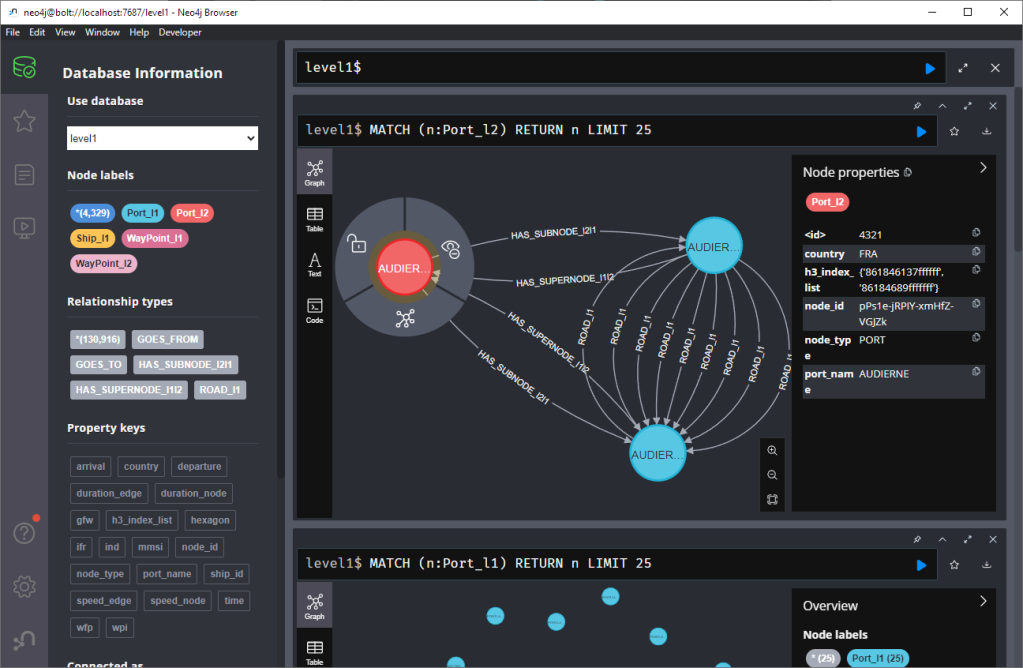
Every “road” level 1 relationship between ports provide information about the ship, its arrival, departure, travel time, and speed. We can see that this two level 1 ports must be pretty close since travel times are only 5 minutes:

Further expanding one of the port level 1 nodes shows its connection to waypoints of level1:

Switching to level 2, we gain access to nodes of type Traj(ectory). Additionally, the road level 2 relationships represent aggregations of the trajectories, for example, here’s a relationship with only one associated trajectory:

There are also some odd relationships, for example, trajectory 43 has two ends and begins relationships and there are also two road relationships referencing this trajectory (with identical information, only differing in their automatic <id>). I’m not yet sure if that is a feature or a bug:
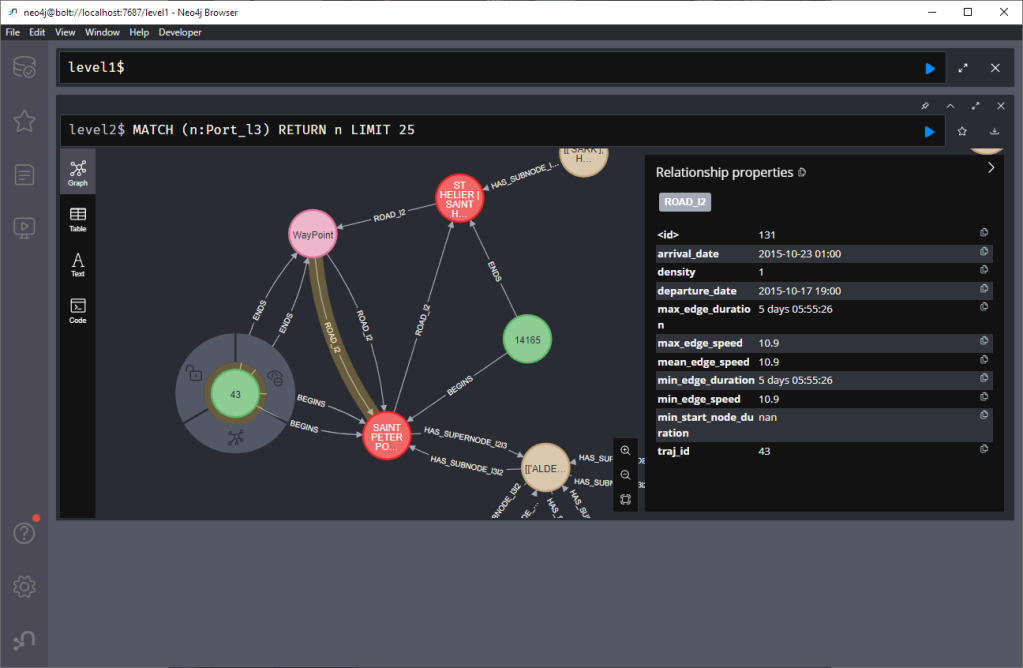
On level 1, we also have access to ship nodes. They are connected to ports and waypoints. However, exploring them visually is challenging. Things look fine at first:
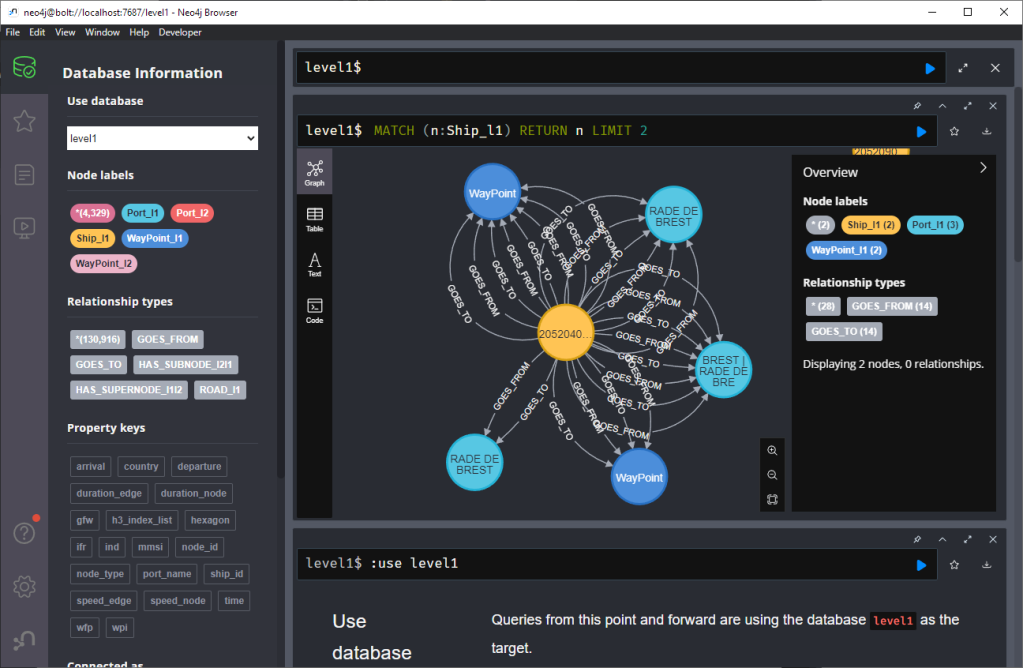
But after a while, once all relationships have loaded, we have it: the MIGHTY BALL OF YARN ™:

I guess this is the point where it becomes necessary to get accustomed to the query language. And no, it’s not SQL, it is Cypher. For example, selecting a specific trajectory with id 0, looks like this:
MATCH (t1 {traj_id: 0}) RETURN t1
But more on this another time.
This post is part of a series. Read more about movement data in GIS.
-
 17:10
17:10 From GIS to Remote Sensing: Downloading free satellite images using the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin: the Download product tab
sur Planet OSGeoThis is part of a series of video tutorials focused on the tools of the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (SCP).In this tutorial, the Download products tab is illustrated, which allows for downloading free satellite images such as Landsat and Sentinel-2.You can find more information in the user manual at this link.
Following the video tutorial.
For any comment or question, join the Facebook group or GitHub discussions about the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin.
-
 11:07
11:07 QGIS Blog: QGIS 3.34 Prizren is released!
sur Planet OSGeoWe are pleased to announce the release of QGIS 3.34 Prizren!
Installers for Windows and Linux are already out. QGIS 3.34 comes with tons of new features, as you can see in our visual changelog. QGIS 3.34 Prizren is named after this year’s FOSS4G host city.
We would like to thank the developers, documenters, testers and all the many folks out there who volunteer their time and effort (or fund people to do so). From the QGIS community we hope you enjoy this release! If you wish to donate time, money or otherwise get involved in making QGIS more awesome, please wander along to qgis.org and lend a hand!
QGIS is supported by donors and sustaining members. A current list of donors who have made financial contributions large and small to the project can be seen on our donors list. If you would like to become a sustaining member, please visit our page for sustaining members for details. Your support helps us fund our six monthly developer meetings, maintain project infrastructure and fund bug fixing efforts.
QGIS is Free software and you are under no obligation to pay anything to use it – in fact we want to encourage people far and wide to use it regardless of what your financial or social status is – we believe empowering people with spatial decision making tools will result in a better society for all of humanity.
-
 19:20
19:20 SIG Libre Uruguay: Premios Osor: gvSIG seleccionado entre los 6 mejores proyectos Open Source de la Comisión Europea
sur Planet OSGeo -
 19:15
19:15 SIG Libre Uruguay: XIII Jornada Educativa en Teledetección en el Ámbito del Mercosur
sur Planet OSGeo -
 17:50
17:50 gvSIG Batoví: GIS DAY EN FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS FORESTALES (UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE MISIONES)
sur Planet OSGeo
Con mucho gusto y honor Felipe Sodré Barros (Mgtr. Ecología y Biodiversidad) les hace la invitación a las actividades por el día SIG (GIS Day) organizado por sus alumnos de la Tecnicatura en SIG y Teledetección.

En una de ellas, tendremos la participación de Antoni Pérez Navarro, a quien agradecemos por la participación!

Existe un formulario de inscripción para facilitar la comunicación por si se necesita hacer algún cambio
-
 17:38
17:38 SIG Libre Uruguay: GIS Day en Facultad de Ciencias Forestales (Universidad Nacional de Misiones)
sur Planet OSGeo
Con mucho gusto y honor Felipe Sodré Barros (Mgtr. Ecología y Biodiversidad) les hace la invitación a las actividades por el día SIG (GIS Day) organizado por sus alumnos de la Tecnicatura en SIG y Teledetección.

En una de ellas, tendremos la participación de Antoni Pérez Navarro, a quien agradecemos por la participación!

Existe un formulario de inscripción para facilitar la comunicación por si se necesita hacer algún cambio
-
 15:00
15:00 Climate, Disaster, and Emergency Communities invited to Innovation Days 2023
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) invites anyone involved in climate resilience, disaster response, and emergency management to attend OGC Innovation Days 2023. The event will be held December 5-7 at the American Red Cross Headquarters in Washington, D.C. Attendance is free for OGC Members using this link.
OGC Innovation Days 2023 brings together diverse members of the climate, disaster, and emergency resilience and response communities to explore what OGC-enabled geospatial technologies have made possible and to ask: what do we need to do next?
This multi-day event will benefit anyone interested or involved in climate resilience, disaster response, or emergency management by providing an opportunity to learn about the latest geospatial data and technology developments from the OGC community, contribute to shaping future work, and interact with stakeholders from industry, government, research, and the private sector.
OGC has for many years been developing solutions that support climate and disaster resilience and response, from supporting the development of FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) climate resilience information systems, to empowering first responders with the information they need, when they need it.
But to most effectively address the multi-faceted challenges of the changing climate and associated disasters, we want to hear about the problems being faced by city-managers, community members, first responders, climate scientists, insurers, government bodies, and others, as they respond to the changing climate and associated disasters – so that we can use OGC’s collective expertise to address them.
By bringing the climate, disaster, and emergency communities together, OGC Innovation Days 2023 provides a unique opportunity for attendees to meet people facing similar challenges to their own and learn about the solutions that worked for them, while guiding OGC towards creating impactful free and open solutions where none currently exist.
The event runs across three days: a day of panels and discussions, a day of demonstrations, and a day exclusively for the OGC Strategic Member Advisory Committee, OGC Executive Planning Committee, and special guests.
Gain insights from experts from leading organizations, including: event hosts American Red Cross, OGC Strategic Members Department of Homeland Security (DHS) / Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Natural Resources Canada (NRCan), and United States Geological Survey (USGS), as well as others from across government and industry. See the full agenda here.
Day 1 consists of panels and discussions centered around 4 topics: Disaster Response & Emergency Management; Wildfires; Climate Change & Disaster Risk Reduction; and the role that Artificial Intelligence and related technologies can play in building disaster and climate resilience. Throughout each panel, expect information on the FAIR solutions and workflows developed through OGC initiatives – such as the Disasters Pilot 2023 and the Climate Resilience Pilot – the gaps that remain between the data & tools we have and the ones we need, panelists’ successes & challenges, and audience feedback.
Day 2 provides attendees the opportunity to see working demonstrations of cutting-edge solutions for climate, disaster, and emergency resilience and response developed in OGC COSI Program Initiatives or using OGC innovations in geospatial technologies such as Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning, Earth Observation, Analysis Ready Data (ARD), Decision Ready Indicators (DRI) for emergency response, FAIR systems & data, cloud-native geospatial, and more.
Day 2 will also include a demonstration of General Dynamics Information Technology (GDIT)’s standards-based Raven mobile command-center, which collects and distributes mission-critical information at the edge. Powered by AI systems, the Raven can filter information so data-driven decisions can be made and disseminated to first responders, analysts, and decision makers in real-time.
Join us at the American Red Cross Headquarters in Washington, DC, USA, to tackle climate, disasters, and emergencies together using FAIR geospatial data and systems. A video overview of the 2022 OGC Innovation Days event is available on OGC’s YouTube channel.
For more information, including registration, agenda, venue & accommodation info, and more, visit the OGC 2023 Innovation Days webpage. The event is free for OGC Members – see this page on the OGC Portal for your discounted registration link. Sponsorship opportunities remain available, contact OGC to find out more.
The post Climate, Disaster, and Emergency Communities invited to Innovation Days 2023 appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 11:01
11:01 GeoTools Team: GeoTools 29.3 released
sur Planet OSGeoThe GeoTools team is pleased to announce the release of the latest maintenance version of GeoTools 29.3: geotools-29.3-bin.zip geotools-29.3-doc.zip geotools-29.3-userguide.zip geotools-29.3-project.zip This release is also available from the OSGeo Maven Repository and is made in conjunction with GeoServer 2.23.3 and GeoWebCache 1.23.2. We are
-
 15:00
15:00 OGC Compliance Certification Available for v2.0 of the Web Processing Service (WPS) Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the Executable Test Suite (ETS) for version 2.0 of the Web Processing Service (WPS) Standard has been approved by the OGC Membership. Products that implement the Standard and pass the tests in the ETS can now be certified as OGC Compliant.
The OGC Compliance Program offers a certification process that ensures organizations’ solutions are compliant with OGC Standards. It is a universal credential that allows agencies, industry, and academia to better integrate their solutions. OGC Compliance provides confidence that a product will seamlessly integrate with other compliant solutions regardless of the vendor that created them.
The WPS Standard supports the wrapping of computational tasks into executable processes that can be offered by a server through a web service interface and be invoked by a client application. The processes typically combine coverage, raster, vector, and/or point cloud data with well-defined algorithms to produce new information. Some of those algorithms may apply Machine Learning and other Artificial Intelligence (AI) approaches, as demonstrated by the OGC Testbed-16 initiative.
Implementers of the WPS 2.0 Standard are invited to validate their products using the new test suite, which is available now on the OGC Validator Tool. Testing involves submitting the endpoint of a WPS implementation to be assessed. The validator tool sends the appropriate requests to the endpoint of the implementation and then evaluates the responses. These tests typically take only 5-10 minutes to complete. Once a product has passed the tests, the implementer can submit an application to OGC for use of the OGC Compliant trademark on their product.
To support developers with implementation of the standard, GeoLabs ZOO-Project 2.0 and the 52°North 52N Web Processing Service 4.0.0-beta.10 product have been designated as reference implementations of the standard after the software products successfully passed the compliance tests.
More information about the OGC compliance process, and how it can benefit your organization, is available at ogc.org/compliance. Implementers of version 2.0 of the WPS Standard – or other OGC Standards – can validate their products using the OGC Validator Tool.
The post OGC Compliance Certification Available for v2.0 of the Web Processing Service (WPS) Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 14:47
14:47 Markus Neteler: GRASS GIS 8.3.1 released
sur Planet OSGeoWhat’s new in a nutshellThe GRASS GIS 8.3.1 maintenance release provides more than 60 changes compared to 8.3.0. This new patch release brings in important fixes and improvements in GRASS GIS modules and the graphical user interface (GUI) which stabilizes the new single window layout active by default.
Some of the most relevant changes include: fixes for
r.watershedwhich got partially broken in the 8.3.0 release; and a fix for installing addons on MS Windows withg.extension.Translations continue in Weblate, which automatically creates pull requests with the translated chunks. We’d like to thank the translators of all languages for their ongoing support!
Full list of changes and contributorsFor all 60+ changes, see our detailed announcement with the full list of features and bugs fixed at GitHub / Releases / 8.3.1.
Thanks to all contributors!
Software downloads Binaries/Installers download- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
Further binary packages for other platforms and distributions will follow shortly, please check at software downloads.
Source code downloadFirst time users may explore the first steps tutorial after installation.
About GRASS GIS
The Geographic Resources Analysis Support System ( [https:]] ), commonly referred to as GRASS GIS, is an Open Source Geographic Information System providing powerful raster, vector and geospatial processing capabilities. It can be used either as a stand-alone application, as backend for other software packages such as QGIS and R, or in the cloud. It is distributed freely under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL). GRASS GIS is a founding member of the Open Source Geospatial Foundation (OSGeo).
The GRASS Dev Team
The post GRASS GIS 8.3.1 released appeared first on Markus Neteler | Geospatial Analysis | Remote sensing | GRASS GIS.
-
 14:03
14:03 Oslandia: QField 3.0 release : field mapping app, based on QGIS
sur Planet OSGeoWe are very happy and enthusiasts at Oslandia to forward the QField 3.0 release announcement, the new major update of this mobile GIS application based on QGIS.
Oslandia is a strategic partner of OPENGIS.ch, the company at the heart of QField development, as well as the QFieldCloud associated SaaS offering. We join OPENGIS.ch to announce all the new features of QField 3.0.
Shipped with many new features and built with the latest generation of Qt’s cross-platform framework, this new chapter marks an important milestone for the most powerful open-source field GIS solution.
Main highlightsUpon launching this new version of QField, users will be greeted by a revamped recent projects list featuring shiny map canvas thumbnails. While this is one of the most obvious UI improvements, countless interface tweaks and harmonization have occurred. From the refreshed dark theme to the further polishing of countless widgets, QField has never looked and felt better.
The top search bar has a new functionality that allows users to look for features within the currently active vector layer by matching any of its attributes against a given search term. Users can also refine their searches by specifying a specific attribute. The new functionality can be triggered by typing the ‘f’ prefix in the search bar followed by a string or number to retrieve a list of matching features. When expanding it, a new list of functionalities appears to help users discover all of the tools available within the search bar.
QField’s tracking has also received some love. A new erroneous distance safeguard setting has been added, which, when enabled, will dictate the tracker not to add a new vertex if the distance between it and the previously added vertex is greater than a user-specified value. This aims at preventing “spikes” of poor position readings during a tracking session. QField is now also capable of resuming a tracking session after being stopped. When resuming, tracking will reuse the last feature used when first starting, allowing sessions interrupted by battery loss or momentary pause to be continued on a single line or polygon geometry.
On the feature form front, QField has gained support for feature form text widgets, a new read-only type introduced in QGIS 3.30, which allows users to create expression-based text labels within complex feature form configurations. In addition, relationship-related form widgets now allow for zooming to children/parent features within the form itself.
To enhance digitizing work in the field, QField now makes it possible to turn snapping on and off through a new snapping button on top of the map canvas when in digitizing mode. When a project has enabled advanced snapping, the dashboard’s legend item now showcases snapping badges, allowing users to toggle snapping for individual vector layers.
In addition, digitizing lines and polygons by using the volume up/down hardware keys on devices such as smartphones is now possible. This can come in handy when digitizing data in harsh conditions where gloves can make it harder to use a touch screen.
While we had to play favorites in describing some of the new functionalities in QField, we’ve barely touched the surface of this feature-packed release. Other major additions include support for Near-Field Communication (NFC) text tag reading and a new geometry editor’s eraser tool to delete part of lines and polygons as you would with a pencil sketch using an eraser.
Thanks to Deutsches Archäologisches Institut, Groupements forestiers Québec, Amsa, and Kanton Luzern for sponsoring these enhancements.
Quality of life improvementsStarting with this new version, the scale bar overlay will now respect projects’ distance measurement units, allowing for scale bars in imperial and nautical units.
QField now offers a rendering quality setting which, at the cost of a slightly reduced visual quality, results in faster rendering speeds and lower memory usage. This can be a lifesaver for older devices having difficulty handling large projects and helps save battery life.
Vector tile layer support has been improved with the automated download of missing fonts and the possibility of toggling label visibility. This pair of changes makes this resolution-independent layer type much more appealing.
On iOS, layouts are now printed by QField as PDF documents instead of images. While this was the case for other platforms, it only became possible on iOS recently after work done by one of our ninjas in QGIS itself.
Many thanks to DB Fahrwgdienste for sponsoring stabilization efforts and fixes during this development cycle.
Qt 6, the latest generation of the cross-platform framework powering QFieldLast but not least, QField 3.0 is now built against Qt 6. This is a significant technological milestone for the project as this means we can fully leverage the latest technological innovations into this cross-platform framework that has been powering QField since day one.
On top of the new possibilities, QField benefited from years of fixes and improvements, including better integration with Android and iOS platforms. In addition, the positioning framework in Qt 6 has been improved with awareness of the newer GNSS constellations that have emerged over the last decade.
Forest-themed release namesForests are critical in climate regulation, biodiversity preservation, and economic sustainability. Beginning with QField 3.0 “Amazonia” and throughout the 3.X’s life cycle, we will choose forest names to underscore the importance of and advocate for global forest conservation.
Software with service
OPENGIS.ch and Oslandia provides the full range of services around QField and QGIS : training, consulting, adaptation, specific development and core development, maintenance and assistance. Do not hesitate to contact us and detail your needs, we will be happy to collaborate : infos+qfield@oslandia.com
As always, we hope you enjoy this new release. Happy field mapping!
-
 13:59
13:59 gvSIG Team: 19th International gvSIG Conference: Communication proposals submission is open
sur Planet OSGeo
The 19th International gvSIG Conference “Connected solutions” will be held on November 29th and 30th, 2023. Within the in-person and online alternation, this year the conferences will be held as online event, which facilitates participation both in terms of presentations/workshops and attendance.
The communication proposals submission is now open, which can be sent to the email address conference-contact@gvsig.com, following the information indicated in the Communications section of the conference website.
As always, registration for the conference will be free of charge, and will be able to be done once the program has been published.
We encourage you to participate!
-
 11:20
11:20 gvSIG Team: 19as Jornadas Internacionales de gvSIG: abierto el periodo de envío de propuestas de comunicación
sur Planet OSGeo
Los días 29 y 30 de noviembre de 2023 tendrán lugar las 19as Jornadas Internacionales de gvSIG “Soluciones conectadas”. Dentro de la alternancia presencial-online, este año se realizan las jornadas en modalidad online, lo que facilita la participación tanto a nivel de ponencias/talleres como de asistencia.
Ya está abierto el periodo de envío de propuestas de comunicación, que pueden enviarse a la dirección de correo electrónico conference-contact@gvsig.com, siguiendo la información indicada en el apartado «Comunicaciones» de la web de las jornadas.
Como siempre, la inscripción a las jornadas será gratuita, y podrá realizarse una vez publicado el programa de las mismas.
¡Os animamos a participar!
-
 2:00
2:00 GeoServer Team: GeoServer 2.23.3 Release
sur Planet OSGeoGeoServer 2.23.3 release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is a maintenance release of GeoServer providing existing installations with minor updates and bug fixes. GeoServer 2.23.3 is made in conjunction with GeoTools 29.3, and GeoWebCache 1.23.2.
Thanks to Peter Smythe (AfriGIS) for making this release.
Security PatchesThis release includes security patches from projects that GeoServer depends on and is considered a recommended upgrade for production systems.
- GEOS-11030 Update jetty-server to 9.4.51.v20230217
See project security policy for more information on how security vulnerabilities are managed.
Also, another reminder of the URL check security setting that was introduced to series 2.22.x and 2.23.x (but turned off by default) and is now enabled by default for series 2.24.x. If you are not yet in a position to upgrade to 2.24.0 you may wish to enable the recommended setting already.
Release notesNew Feature:
- GEOS-11000 WPS process to provide elevation profile for a linestring
Improvement:
- GEOS-10856 geoserver monitor plugin - scaling troubles
- GEOS-11081 Add option to disable GetFeatureInfo transforming raster layers
- GEOS-11087 Fix IsolatedCatalogFacade unnecessary performance overhead
- GEOS-11089 Performance penalty adding namespaces while loading catalog
- GEOS-11090 Use Catalog streaming API in WorkspacePage
- GEOS-11099 ElasticSearch DataStore Documentation Update for RESPONSE_BUFFER_LIMIT
- GEOS-11100 Add opacity parameter to the layer definitions in WPS-Download download maps
- GEOS-11102 Allow configuration of the CSV date format
- GEOS-11114 Improve extensibility in Pre-Authentication scenarios
- GEOS-11116 GetMap/GetFeatureInfo with groups and view params can with mismatched layers/params
- GEOS-11120 Create aggregates filterFunction in OSEO to support STAC Datacube extension implementation
- GEOS-11130 Sort parent role dropdown in Add a new role
- GEOS-11142 Add mime type mapping for yaml files
- GEOS-11148 Update response headers for the Resources REST API
- GEOS-11149 Update response headers for the Style Publisher
- GEOS-11153 Improve handling special characters in the WMS OpenLayers Format
- GEOS-11155 Add the X-Content-Type-Options header
Bug:
- GEOS-10452 Use of Active Directory authorisation seems broken since 2.15.2 (LDAP still works)
- GEOS-11032 Unlucky init order with GeoWebCacheExtension gwcFacade before DiskQuotaMonitor
- GEOS-11138 Jetty unable to start cvc-elt.1.a / org.xml.sax.SAXParseException
- GEOS-11140 WPS download can leak image references in the RasterCleaner
- GEOS-11145 The GUI “wait spinner” is not visible any longer
- GEOS-11166 OGC API Maps HTML representation fail without datetime parameter
Task:
- GEOS-10248 WPSInitializer NPE failure during GeoServer reload
- GEOS-11030 Update jetty-server to 9.4.51.v20230217
- GEOS-11084 Update text field css styling to look visually distinct
- GEOS-11091 Upgrade spring-security to 5.7.10
- GEOS-11092 acme-ldap.jar is compiled with Java 8
- GEOS-11094 Bump org.hsqldb:hsqldb:2.7.1 to 2.7.2
- GEOS-11124 Update json dependency to 20230227 in geowebcache-rest
- GEOS-11141 production consideration for logging configuration hardening
For the complete list see 2.23.3 release notes.
About GeoServer 2.23 SeriesAdditional information on GeoServer 2.23 series:
- GeoServer 2.23 User Manual
- Drop Java 8
- GUI CSS Cleanup
- Add the possibility to use fixed values in Capabilities for Dimension metadata
- State of GeoServer 2.23
- GeoServer Feature Frenzy 2023
- GeoServer used in fun and interesting ways
- GeoServer Orientation
Release notes: ( 2.23.3 | 2.23.2 | 2.23.1 | 2.23.0 | 2.23-RC1 )
-
 18:16
18:16 GeoCat: Cyber Resilience Act
sur Planet OSGeoAs a small and medium business operating in Europe GeoCat BV is clearly affected by the forthcoming European Cyber Resilience Act (CRA). We are a proud open source company and are concerned about our friends and partners caught up in the uncertainty around this proposed legislation.
We applaud the goals of the CRA as security is a responsibility GeoCat handles with care on behalf of our customers and products.
GeoCat is proud of the products we offer our customers: GeoCat Live, GeoNetwork Enterprise and GeoServer Enterprise. Each of these products are offered with a clear vendor relationship, an aspect of which is the handling and communication of security vulnerabilities.
Part of the magic of free and open-source is the rich collaborations formed across industry, academia, and government working alongside non-governmental organizations and enthusiasts. We are concerned that the CRA as proposed places undue hardships on these relationships. These relationships form a network of trust, and cannot be reduced to a product relationship.
We encourage regulators to seek expert input at this time. With so much of technology based in free and open-source technology we encourage regulators to look at ways to support security priorities with a deeper understanding.
Dutch regulators are encouraged to read:
- Cyber Resilience Act
- Vrijschrift To Dutch Parliament: Eu Cyber Resilience Act Will Harm Competitiveness (Dutch)
The post Cyber Resilience Act appeared first on GeoCat B.V..
-
 16:26
16:26 From GIS to Remote Sensing: Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin update: version 8.1
sur Planet OSGeoThe Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (SCP) has been updated to version 8.1 which solves a few bugs and in particular ease the installation of required dependencies.
This update automatically tries to install the required library Remotior Sensus in the plugin directory, if it is not already installed in the QGIS environment, which allows for using the main functions of SCP.However, it is still recommended to follow the installation instructions to download the required dependencies.
Moreover, an alternative Windows installation using the OSGeo4W network installer has been added to the user manual [https:]]
Also, the user manual describes the installation in macOS [https:]]
and Linux [https:]]
With this update the installation should work in most cases.
For any comment or question, join the Facebook group or GitHub discussions about the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin.
-
 13:24
13:24 gvSIG Team: Osor Awards: gvSIG selected among the top 6 open-source projects by the European Commission
sur Planet OSGeo
We have reason to celebrate. The gvSIG project, submitted by the Generalitat Valenciana and the gvSIG Association, has been chosen by the Osor Awards jury as one of the top 6 open-source projects. Undoubtedly, this is a recognition of the highest caliber for the work carried out by these institutions and the entire gvSIG community around the project.
About Osor Awards
The European Commission’s Open Source Observatory (OSOR) has organised the EU Public Services Open Source Achievement Awards to honour and showcase the best open source solutions and initiatives created by or for the public administrations in Europe.
As the title of the Awards indicates, the Jury focused on achievements of open source solutions and initiatives: the ambitious goals, determination in overcoming challenges, contribution towards furthering democracy, transparency and active participation of citizens in creating digital infrastructures serving constituents, the impact on their communities, and effective usage of public resources and exceptional response to solving problems.
Award ceremony
The representatives of the top 6 entries and the winner of the OSOR Community Award will be invited to Brussels for the event celebrating 15 years of our Observatory – OSOR Turns 15: From Pioneering to Mainstreaming Open Technologies in Public Services on 21 November 2023.
… We’re going to Brussels!
-
 19:42
19:42 GRASS GIS: GRASS GIS 8.3.1 released
sur Planet OSGeoWhat’s new in a nutshell The GRASS GIS 8.3.1 maintenance release provides more than 60 changes compared to 8.3.0. This new patch release brings in important fixes and improvements in GRASS GIS modules and the graphical user interface (GUI) which stabilizes the new single window layout active by default. Some of the most relevant changes include: fixes for r.watershed which got partially broken in the 8.3.0 release; and a fix for installing addons on MS Windows with g. -
 2:47
2:47 XYCarto: GRASS GIS, Docker, Makefile
sur Planet OSGeoSmall example of using Docker and Makefile to implement GRASS GIS. This blog is written to be complimentary to the Github repository found here. Included in this post is a more verbose explanation of what is happening in the Github repository. Users can explore the scripts to see the underlying bits that make it each step. The intention is to help simplify the GRASS set-up and execution of processes using GRASS operations.
TL;DR
GitHub repository is here with the method and documents.
Summary
This is a basic example of setting up scripted GRASS process through a Docker image and using a
makefileto launch the process. The goal is remove the need to install GRASS on your machine and to fully containerize the process within Docker.It is assumed that users have a familiarity with Docker, Make, and GRASS.
In short, the repo is built to launch a GRASS environment and call a script with the users GRASS commands. Ideally, users should be able to clone the Github repository, build the Docker locally (or pull it), and run a simple
makecommand calling the primary script to perform the GRASS operations.Methods in the repository have been tested using Ubuntu and MacOS operating systems.
Important
This method is developed for scripting purposes and not intended for saving data in your GRASS environment. Using this method, each time the script is run the initial operation checks to see if a GRASS environment exists. If so, that environment is destroyed and a new environment is built.
Requirements
make docker
Methods
If you prefer try out the commands given below, you will need to clone the Git repo:
git clone git@github.com:xycarto/grass-docker-make.git
These are the two primary commands to set-up the GRASS, Docker, Make operations. Users will first need to build a Docker containing the GRASS installation. Inside the
makefileare all the necessary components to find the Dockerfile and build the image. I’ve tagged this build with “xycarto” (see the top of the makefile); however, you can name this whatever you choose.Build GRASS Docker
make docker-local
Run GRASS Script
With the Docker image in place, you can test if the method is working by checking the GRASS version. This
makecommand uses two scripts. First, a script is called to construct the GRASS environment and then, call the script with all your GRASS operations. The second script is launched using:grass grass/GRASS_ENV/PERMANENT --exec bash grass-script.sh
The
—execindicates the script is run within the GRASS environment giving users access to all the GRASS capabilities.GRASS needs to run within a designated projection. Included in the
makecommand is a variable to set this. Users can implement any projection here using the EPSG value. The following is building a GRASS environment in New Zealand Transverse Mercator (NZTM), EPSG:2193:make grass-project proj="2193"
This should output the GRASS version installed in the Docker.
Modifications
Users can implement any GRASS commands and methods in the
run-grass.shscript, simply by modifying the file.How this can be used
File variables can be given to the GRASS process back in the
makecommand and passing this through therun-grass.shscript. For example, say you have a example.tif file you’d like to process in GRASS. Users can add a variable to the make file calledtif. It might look like this in the makefile:grass-project: $(RUN) bash run-grass.sh $(proj) $(tif)
The call of the command looks like:
make grass-project proj=“2193" tif=example.tif
Now with the makefile modified, you need to pass the variable through to the GRASS processing. First you need to modify the
run-grass.shscript to accept the new variable frommake. This can be done by adding the following line at the top:tif=$2
Where
$2means the second argument in the command given. Therun-grass.shscript now has the tif path variable. With this, you can now pass the path to the actual GRASS script by modifying the last line like so:grass grass/GRASS_ENV/PERMANENT --exec bash grass-script.sh $tif
The
grass-script.shcan now be modified to accept thetifvariable by adding the following line at the top:tif=$1
Once you get this all set up an running, the real power comes now in a scripted method run a large collection of tifs through a GRASS process.
Let’s say you have 1000 tifs that need to run. You can list these tifs and simply develop a method like the the following:
cat list-of-tifs.txt | xargs -P 1 -t -I % make grass-project proj=“2193" tif=%
This method would sequentially process the tif list through your GRASS process.
Having a hard time following? Please feel free to contact me and I’ll see if I can help.
-
 19:00
19:00 CLIMOS and a FAIR data-to-information value chain
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The visible effects of climate change continue to grow over time, in both frequency and severity. Extreme meteorological events, such as heavy rains, severe storms, strong winds, and high temperatures, are causing extreme floods, landslides, droughts, heatwaves, wildfires, biodiversity loss, desertification and more, and severely impacting infrastructure, crops, livestock, and lives.
As such, the last three decades have seen policy initiatives put in place to try and limit the impacts of global warming, reverse land degradation/desertification, stop the loss of biodiversity, protect finite natural resources, and reduce the risks associated with environmental disasters. These initiatives are summarised under the umbrella of the United Nations Agenda 2030 and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which together aim at increasing the resilience of people and systems to the changing environmental and socioeconomic conditions. Within this framework, Climate Action (SDG 13) and particularly Health (SDG 3) are defined goals to be tackled by the international community through collaborative solutions.
Extreme weather-induced hazards and disasters certainly provide a very visible example of the impact of climate change. However, most of the mortality caused by climate change comes in less cataclysmic forms. One obvious example is the increased mortality rate during heatwaves. A less obvious example is the changing risk of exposure to disease for humans, other animals, and plants.
Changes in temperature and precipitation, combined with changes in land use and cover, are creating spatial shifts in the life-cycle dynamics of disease-transmitting vectors, such as bats, small mammals, or mosquitoes, which has resulted in changing risks of exposure to disease.
The EU project CLIMOS, which OGC is a partner, is examining one such change by focussing on diseases transmitted by sandflies. CLIMOS works towards enhancing the scientific knowledge of the parameters that affect the spread of sandflies – and thus their ability to transmit disease – in the context of a changing climate. The project calls for technical systems that can combine and process: raw data output by climate models; earth observations of ongoing meteorological events and changes to land cover; and ecological data describing the life cycles of the sandflies.
Technical systems that are able to find, access, integrate, and process data for use in building climate resilience are coming to be known as Climate Resilience Information Systems (CRIS). CRIS are already being used to develop and provide interoperable Analysis Ready Data (ARD), usually in the form of data cubes, to scientists for further processing using scientific algorithms, and/or for developing Decision Ready Indicators (DRI) that allow for clear interpretation of current events by decision makers.
The “raw data to information” value chain underpinning CRIS is made possible when the FAIR data principle is respected, that is that data and systems are developed in a manner that ensures they are Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable. CLIMOS is therefore focussing on the use of FAIR-aligned Climate Services for data assessment, scientific knowledge generation, early warning, and to better understand how meteorological conditions are increasing the risk of sand fly-borne diseases in particular areas.
As part of the CLIMOS project, the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is supporting the move toward FAIR systems for use in the emergency alert systems and data pipelines. Specifically, OGC is addressing the interoperability challenges faced when combining health, environmental, Earth observation, and climate model data. These challenges are being examined and addressed through various technical testbeds and data pilot studies that emphasise the FAIR principles, as well as within OGC Domain Working Groups. For the objectives of CLIMOS, OGC’s Climate Change Resilience, Emergency Management, and Health Domain Working Groups are each providing excellent sources of experience and knowledge related to these three aspects of the CLIMOS project.
The work of CLIMOS is an essential contribution to realise the SDG 3 goal to “Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.”
This post originally appeared on the CLIMOS Project blog.
The post CLIMOS and a FAIR data-to-information value chain appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:20
17:20 Marco Bernasocchi: QField 3.0 “Amazonia” is here – Feature-packed and super slick.
sur Planet OSGeoPièce jointe: [télécharger]
We’re so excited and proud of this latest QField version that we’ve opted for a major 3.0 version update.
Get it nowShipped with many new features and built with the latest generation of Qt’s cross-platform framework, this new chapter marks an important milestone for the most powerful open-source field GIS solution.
Main highlights
Upon launching this new version of QField, users will be greeted by a revamped recent projects list featuring shiny map canvas thumbnails. While this is one of the most obvious UI improvements, countless interface tweaks and harmonization have occurred. From the refreshed dark theme to the further polishing of countless widgets, QField has never looked and felt better.
The top search bar has a new functionality that allows users to look for features within the currently active vector layer by matching any of its attributes against a given search term. Users can also refine their searches by specifying a specific attribute. The new functionality can be triggered by typing the ‘f’ prefix in the search bar followed by a string or number to retrieve a list of matching features. When expanding it, a new list of functionalities appears to help users discover all of the tools available within the search bar.
QField’s tracking has also received some love. A new erroneous distance safeguard setting has been added, which, when enabled, will dictate the tracker not to add a new vertex if the distance between it and the previously added vertex is greater than a user-specified value. This aims at preventing “spikes” of poor position readings during a tracking session. QField is now also capable of resuming a tracking session after being stopped. When resuming, tracking will reuse the last feature used when first starting, allowing sessions interrupted by battery loss or momentary pause to be continued on a single line or polygon geometry.
On the feature form front, QField has gained support for feature form text widgets, a new read-only type introduced in QGIS 3.30, which allows users to create expression-based text labels within complex feature form configurations. In addition, relationship-related form widgets now allow for zooming to children/parent features within the form itself.
To enhance digitizing work in the field, QField now makes it possible to turn snapping on and off through a new snapping button on top of the map canvas when in digitizing mode. When a project has enabled advanced snapping, the dashboard’s legend item now showcases snapping badges, allowing users to toggle snapping for individual vector layers.
In addition, digitising lines and polygons by using the volume up/down hardware keys on devices such as smartphones is now possible. This can come in handy when digitizing data in harsh conditions where gloves can make it harder to use a touch screen.
While we had to play favourites in describing some of the new functionalities in QField, we’ve barely touched the surface of this feature-packed release. Other major additions include support for Near-Field Communication (NFC) text tag reading and a new geometry editor’s eraser tool to delete part of lines and polygons as you would with a pencil sketch using an eraser.
Thanks to Deutsches Archäologisches Institut, Groupements forestiers Québec, Amsa, and Kanton Luzern for sponsoring these enhancements.
Quality of life improvementsStarting with this new version, the scale bar overlay will now respect projects’ distance measurement units, allowing for scale bars in imperial and nautical units.
QField now offers a rendering quality setting which, at the cost of a slightly reduced visual quality, results in faster rendering speeds and lower memory usage. This can be a lifesaver for older devices having difficulty handling large projects and helps save battery life.
Vector tile layer support has been improved with the automated download of missing fonts and the possibility of toggling label visibility. This pair of changes makes this resolution-independent layer type much more appealing.
On iOS, layouts are now printed by QField as PDF documents instead of images. While this was the case for other platforms, it only became possible on iOS recently after work done by one of our ninjas in QGIS itself.
Many thanks to DB Fahrwgdienste for sponsoring stabilization efforts and fixes during this development cycle.
Qt 6, the latest generation of the cross-platform framework powering QFieldLast but not least, QField 3.0 is now built against Qt 6. This is a significant technological milestone for the project as this means we can fully leverage the latest technological innovations into this cross-platform framework that has been powering QField since day one.
On top of the new possibilities, QField benefited from years of fixes and improvements, including better integration with Android and iOS platforms. In addition, the positioning framework in Qt 6 has been improved with awareness of the newer GNSS constellations that have emerged over the last decade.
Forest-themed release names
Forests are critical in climate regulation, biodiversity preservation, and economic sustainability. Beginning with QField 3.0 “Amazonia” and throughout the 3.X’s life cycle, we will choose forest names to underscore the importance of and advocate for global forest conservation.
As always, we hope you enjoy this new release. Happy field mapping!
-
 23:51
23:51 KAN T&IT Blog: Trabajo en conjunto con el INEC de Costa Rica
sur Planet OSGeoEstamos felices de anunciarles que desde Kan vamos a trabajar codo a codo con el Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos de Costa Rica (inec.cr).
Con la adopción del Marco Geoespacial y Estadístico Global (GSGF) propuesto por la ONU en América Latina y el Caribe a través de la Comisión Económica para América Latina y el Caribe (CEPAL), pondremos en marcha un conjunto de componentes tecnológicos específicos, incluyendo un gestor estadístico, un gestor de datos geoespaciales, APIs con posibilidad de consumir información de diferentes aplicaciones y un geoportal para visualizar, navegar y comparar la información estadística de este país.Al mismo tiempo, implementaremos componentes ya existentes en la comunidad como Kobo Toolbox, GeoNode, Airflow, MapLibre, Nominatim y Metabase para ofrecer una solución integral que abarque desde la recopilación de datos en terreno hasta la publicación de la información.

Esta plataforma será una valiosa herramienta tanto para gobiernos, investigadores, empresas como para cualquier persona interesada en obtener información actualizada y confiable sobre la región.
A medida de que vayamos avanzando, les contaremos más sobre este proyecto que nos tiene muy entusiasmados.
-
 20:30
20:30 Stefano Costa: Research papers and case studies using iosacal
sur Planet OSGeoI have updated the documentation of iosacal with a new page that lists all research papers and case studies where the software gets a mention for being used.
 A collage of figures from the papers using iosacal
A collage of figures from the papers using iosacal
The list is at [https:]] and it’s longer than I thought, with 6 papers ranging from Norway to Antarctica, from the Last Glacial Maximum to the European Middle Ages.
It’s humbling to see this small piece of software find its way in so many research projects and I’m learning a lot by studying these publications.
Some authors contributed to iosacal with new features and bug fixes, and that is the most accurate metric of a healthy project that I can think of.
I’m going to add more useful content to the documentation as the main focus of the 0.7 release. In the meantime, you can continue using iosacal 0.6 in your research projects.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Calls for Participation in its Open Science Persistent Demonstrator Pilot
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) invites organizations and individuals to join the OGC Open Science Persistent Demonstrator (OSPD) Pilot. The multi-year project will support collaborative open science for the scientific community, decision-makers, and the general public. Responses are due by December 1, 2023. Funding is available for Participants.
Collaborative Open Science is essential to addressing complex challenges whose solutions lie in cross-sector integrations that leverage expertise and data from diverse domains while prioritizing integrity. By making it simple to connect data and platforms together in transparent, reusable and reproducible workflows, the OGC OSPD Pilot aims to enable innovation through collaborative open science.
OGC’s OSPD Pilot focuses on connecting geospatial and Earth Observation (EO) data and platforms to enable and demonstrate solutions that create capacity for novel research and accelerate its practical implementation.
The Pilot will produce a web portal to demonstrate how platforms operated by different organizations can be used for collaborative research and data representation, facilitate testing the compatibility of in-development data or platforms with other elements in a multi-platform workflow, and promote training in methods for collaborative, open innovation by providing learning and outreach materials.
The OSPD Pilot will produce three main elements:
- The development of a web portal that demonstrates how platforms operated by different organizations can be used for collaborative research and data representation;
- A test environment for web platforms to explore mutual use and which provides a collaboration space for existing and in-development platforms to use each other and test aspects such as reproducibility of workflows; and
- The provision of learning and outreach materials that make the Open Science platforms known and accessible to a wide range of users and enable efficient use.
The OSDP is sponsored by OGC Strategic Members the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Agency (NASA), who will provide vision and leadership throughout the initiative.
The OGC Open Science Persistent Demonstrator Pilot will be conducted under OGC’s Collaborative Solutions and Innovation (COSI) Program, a collaborative, agile, and hands-on prototyping and engineering environment where sponsors and OGC members come together to address location interoperability challenges while validating international open standards. To learn about the benefits of sponsoring an OGC COSI Program Initiative such as this, visit the OGC COSI Program webpage.
More information on OGC’s OPSD Pilot, including the CFP document and how to respond, is available on the OGC Open Science Persistent Demonstrator Pilot webpage. Responses to the CFP are due by December 1, 2023.
The post OGC Calls for Participation in its Open Science Persistent Demonstrator Pilot appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 4:00
4:00 EOX' blog: VirES for (not only) Swarm - 2023 update
sur Planet OSGeoIt has been a while since the last blog post about VirES for Swarm, but don't let that make you think the level of activity has dropped. The service has moved from strength to strength and enjoys a continually growing number of users, a steady addition of features and datasets, and excitement about ... -
 1:46
1:46 From GIS to Remote Sensing: Managing input bands using the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin: the Band set tab
sur Planet OSGeoThis is the first of a series of video tutorials focused on the tools of the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (SCP).In this tutorial, the Band set tab is illustrated, which allows for managing input bands.You can find more information in the user manual at this link.
Following the video tutorial.
For any comment or question, join the Facebook group or GitHub discussions about the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin.
-
 17:34
17:34 Webinar: Location Innovation Academy for NMCA
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The online Location Innovation Academy recently launched to provide online training material for geospatial data management. It currently offers 12 e-learning modules in three clusters. These materials are designed to help government agencies, particularly national mapping organizations, make the most of their data and digital infrastructure.
On Thursday, 26th October, 2023 at 11:00 – 12:30 CET, OGC and GEOE3 will host a webinar that aims to serve as an introduction to the Academy for National Mapping and Cadastral Agencies (NMCA), and will focus on the integration of climate and meteorological data into data portals used and provided by NMCA.
Additionally, anyone who wishes to use materials from the online academy in their own training courses will learn the information needed to navigate the academy platform and its core content. Teachers, professors, coaches, consultants, and other professionals providing training in geoinformatics, spatial planning processes, and related fields are therefore also encouraged to attend.
During these demonstrations, training materials for the use of OGC climate resilience application packages and for integration of meteorological data into portals managed by NMCA will be presented as examples out of the GEOE3 project.
For more information about the Academy, or to enroll in a free course, visit the Location Innovation Academy website.
Topics: Integration of Meteorological Data; Climate Application Packages
Time: Thursday, 26th October. 11:00 – 12:30 CET
Registration: Click here for registration
Virtual Room: Dial-in info will be provided after registration.
Language: English

The post Webinar: Location Innovation Academy for NMCA appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 4:00
4:00 GeoServer Team: Introducing GeoSpatial Techno with a Video Tutorial
sur Planet OSGeoThis is a community blog post introducing Geospatial Techno, along with a sample of one of their GeoServer training videos.
GeoSpatial Techno is a startup focused on geospatial information that is providing e-learning courses to enhance the knowledge of geospatial information users, students, and other startups. The main approach of this startup is providing quality, valid specialized training in the field of geospatial information.
( YouTube | LinkedIn | Reddit | Facebook | X )
Getting to know OGC web services and GeoServer softwareThe course guides you in using GeoServer software to create geospatial web services, styles and publish them step by step simply and practically. Now, before delving into OGC web services, it is important to familiarize yourself with the various types of services.
In this session, we introduced you to the basics of the OGC web services and GeoServer software. If you want to access the complete tutorial, simply click on the link.
I would highly appreciate it if you could subscribe to my channel and share it with your friends to help spread this tutorial. By subscribing, you will gain complete access to the training video, which will enable you to enhance your skills. Moreover, sharing it with your friends guarantees that they can also benefit from this valuable resource. Thank you for your support.
What is Service?A collection of operations, accessible through an interface, that allows a user to invoke a behavior of value to the user.
What are Web Services?Web services are internet-based applications that can perform a wide range of functions, from simple tasks to complex business processes.
What are GeoSpatial Web Services?GeoSpatial web services are online platforms that offer access to and analyze geographical information. They aim to overcome the lack of compatibility between different geospatial systems.
Why do you need standard web services?Standard web services provide a common platform for communication between modern-day business applications that use different programming languages. This enables convenient interaction regardless of development language.
What is OGC?The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is an international organization that promotes the use of open standards to make geospatial information and services to be “FAIR”, which stands for Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable. This goal applies to various areas such as data sharing, data processing, sensor web, and the Internet of Things.
What are OGC Web Services?OGC Web Services (OWS) are a set of standards that allow for seamless integration of various online geoprocessing and location services. With OWS, users can access and utilize services such as the Web Map Service (WMS), Web Feature Service (WFS), Web Coverage Service (WCS), and Web Map Tile Service (WMTS).
WMS enables users to retrieve and obtain detailed information on maps of geospatial data. WFS allows for data manipulation operations on geographic features, including querying, creating, modifying, and deleting features. WCS provides access to raster datasets like elevation models and remote sensing imagery. WMTS serves pre-rendered or computed map tiles over the internet.
These services provide an interoperable framework for accessing, integrating, analyzing, and visualizing online geodata sources, sensor-derived information, and geoprocessing capabilities.
What is GeoServer?GeoServer is a Java-based server that allows users to view and edit geospatial data. Using open standards set forth by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), GeoServer allows for great flexibility in map creation and data sharing.
Open and Share Your Spatial DataGeoServer is a powerful open-source tool for displaying spatial information through maps in various formats. The tool integrates OpenLayers, a free mapping library, for easy and quick map generation. Moreover, It supports standards like WMS, WFS, WCS, and WMTS, enabling data sharing, editing, and easy integration with web and mobile applications. With modular functionality and extensions, GeoServer offers extensive processing options. For example, the Web Processing Service (WPS) extension provides a wide range of processing options, and users can even create their extensions.
Use Free and Open Source SoftwareGeoServer is a free and open-source software that brings down the financial barrier to using GIS products. It is released every six months with new features, bug fixes, and improvements, providing a quick turnaround time. This transparent process often leads to faster advancements compared to closed software solutions. By using GeoServer, organizations can avoid software lock-in and save money on support contracts in the future.
Integrate With Mapping APIsGeoServer is a versatile software that can integrate with popular mapping applications like Google Maps and Microsoft Bing Maps. It can also connect with traditional GIS architectures such as ESRI ArcGIS. OpenLayers and Leaflet are recommended as complementary tools to GeoServer for web mapping needs.
Join the CommunityGeoServer has an active global community of users and developers, offering support through email lists. The software has a fixed release cycle and public issue tracker, ensuring transparency and regular updates. Commercial support is also available. Overall, using GeoServer means being part of a supportive community.
-
 17:00
17:00 Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) published as official OGC Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) Standard v1.0 has been approved by the OGC Membership for adoption as an official OGC Standard. COG, as an OGC Standard, formalizes existing practices already implemented by the community, such as the GDAL library or the COG explorer and other implementations.
COG allows for the efficient streaming and partial downloading of imagery and grid coverage data on the web, and enables fast data visualization and geospatial processing workflows. COG-aware applications can efficiently stream/download only the parts of the information they need to visualize or process web-based data. With so much remote sensing imagery available in cloud storage facilities, the benefits of optimizing their visualization and processing will be widespread. COG is one of the preferred formats used in catalogs conforming to the SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC) specification, and sits alongside other emerging cloud-optimized formats of relevance to OGC, such as Zarr, COPC, and GeoParquet.
The COG Standard specifies how TIFF files can be organized in a way that favors the extraction of convenient parts of the data at the needed resolution while remaining compatible with traditional TIFF readers. It also specifies how to use HTTP (or [HTTPS)] to transmit only the part of information needed without downloading the complete file.
The OGC COG Standard depends on the TIFF specification and the OGC GeoTIFF Standard. For large files, it depends on the BigTIFF specification. The standard takes advantage of some existing characteristics of the TIFF specification and the existing HTTP Range Request specification (IETF RFC 7233) and does not modify them in any way.
The early work for crafting this OGC Standard was undertaken in the Open-Earth-Monitor Cyberinfrastructure (OEMC) project, which received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation program under grant agreement number 101059548 and in the All Data 4 Green Deal – An Integrated, FAIR Approach for the Common European Data Space (AD4GD) project, which received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation program under grant agreement number 101061001.
This work was followed by an activity within OGC’s Testbed-17 that formally specified COG requirements in the OGC Testbed-17: Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF specification Engineering Report. The lessons from the initiatives were then used to inform the standardization of COG by the OGC Membership.
OGC Members interested in staying up to date on the progress of this standard, or contributing to its development, are encouraged to join the GeoTIFF Standards Working Group (SWG) via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about participating in this SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
As with any OGC standard, the open Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) Standard v1.0 is free to download and implement.
The post Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) published as official OGC Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 4:00
4:00 EOX' blog: Sentinel-2 cloudless 2022
sur Planet OSGeoIntroducing the latest marvel in Earth observation: Sentinel-2 Cloudless, the pinnacle of usability clarity in satellite imagery. This newest version takes your visual exploration to unprecedented heights, delivering pristine, cloud-free views of our planet with breathtaking detail and accuracy. Ev ... -
 20:58
20:58 Markus Neteler: GRASS GIS 8.3.0 released
sur Planet OSGeoWhat’s new in a nutshellThe GRASS GIS 8.3.0 release provides more than 360 changes compared to the 8.2 branch. This new minor release brings in many fixes and improvements in GRASS GIS modules and the graphical user interface (GUI) which now has the single window layout by default. Some of the most relevant changes include: support for parallelization in three raster modules, new options added to several temporal modules, and substantial clean-up of
g.extension, the module that allows the installation of add-ons. The GUI also received a lot of attention with many fixes and items reorganised. We have also adopted the Clang format and indented most of the C code accordingly. A lot of effort was put into cleaning up the C/C++ code to fix almost all compiler warnings.Translations have been moved from Transifex to Weblate, which automatically creates pull requests with the translated chunks. We’d like to thank the translators of all languages for their long term support!
Also, docker images have been updated and moved from the mundialis to the OSGeo organization at https://hub.docker.com/r/osgeo/grass-gis/.
We have carried out quite some work in the GitHub Actions: we added support for “pre-commit” in order to reduce unnecessary runs of the automated checks, there were notable improvements in the code checking section and we have activated renovatebot to automatically maintain GitHub Actions.
Last but not least, we have significantly improved the automated release creation to reduce maintainer workload and we have gained nine new contributors! Welcome all!!
Full list of changes and contributorsFor all 360+ changes, see our detailed announcement with the full list of features and bugs fixed at GitHub / Releases / 8.3.0.
Thank you all contributors!!
Download and test! Binaries/Installers download- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
Further binary packages for other platforms and distributions will follow shortly, please check at software downloads.
Source code downloadFirst time users may explore the first steps tutorial after installation.
About GRASS GIS
The Geographic Resources Analysis Support System ( [https:]] ), commonly referred to as GRASS GIS, is an Open Source Geographic Information System providing powerful raster, vector and geospatial processing capabilities. It can be used either as a stand-alone application, as backend for other software packages such as QGIS and R, or in the cloud. It is distributed freely under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL). GRASS GIS is a founding member of the Open Source Geospatial Foundation (OSGeo).
The GRASS Dev Team
The post GRASS GIS 8.3.0 released appeared first on Markus Neteler | Geospatial Analysis | Remote sensing | GRASS GIS.
-
 1:13
1:13 GeoTools Team: GeoTools 30.0 released
sur Planet OSGeoThe GeoTools team is pleased to announce the release of the latest stable version of GeoTools 30.0: geotools-30.0-bin.zip geotools-30.0-doc.zip geotools-30.0-userguide.zip geotools-30.0-project.zip This release is also available from the OSGeo Maven Repository and is made in conjunction with GeoServer 2.24.0, GeoWebCache 1.24.0 and MapFish Print v2 -
 4:00
4:00 GeoServer Team: GeoServer 2.24.0 Release
sur Planet OSGeoGeoServer 2.24.0 release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is a stable release of GeoServer recommended for production use. GeoServer 2.24.0 is made in conjunction with GeoTools 30.0, mapfish-print-v2 2.3.0 and GeoWebCache 1.24.0.
Thanks to Peter Smythe (AfriGIS) and Jody Garnett (GeoCat) for making this release.
Thanks to everyone who helped test the release candidate: JP Motaung & Nicolas Kemp, Georg Weickelt, Peter Smythe, Tobia Di Pisa, and Giovanni Allegri.
We would like to thank our 2023 sponsors North River Geographic Systems Inc and How 2 Map for their financial assistance.
Keeping GeoServer sustainable requires a long term community commitment. If you were unable to contribute time testing the release candidate, sponsorship options are available via OSGeo.
Upgrade NotesGeoServer strives to maintain backwards compatibility allowing for a smooth upgrade experience.
We have one minor change to share in this release:
-
URL Checks: The url check security setting is now enabled by default.
In GeoServer 2.22.5 and 2.23.2 this setting was available for use, but was turned off by default. If you are not yet in a position to upgrade to 2.24.0 you may wish to enable the recommended setting.
This release addresses security vulnerabilities and is considered an essential upgrade for production systems.
- CVE-2023-43795 WPS Server Side Request Forgery
- CVE-2023-41339 Unsecured WMS dynamic styling sld=url parameter affords blind unauthenticated SSRF
See project security policy for more information on how security vulnerabilities are managed.
IAU authority support and EPSG assumption removalThe new gs-iau extension module provides support for planetary CRSs, sourced from the International Astronomical Union. This allows users to manage GIS data over the Moon, Mars, or even the Sun, with well known, officially supported codes.
In addition to that, many bug fixes occurred in the management of CRSs and their text representations (plain codes, URL, URIs) so that the EPSG authority is no longer assumed to be the only possibility, in a variety of places, such as, for example, GML output. The code base has seen this assumption for twenty long years already, and while we made a good effort to eliminate the assumption, it could be still lurking in some places. Please test and let us know.
To learn more about this extension please visit the user-guide documentation. Thanks to Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions) for working on this activity.
- GSIP-219 - Multiple CRS authority support, planetary CRS
- GEOS-11075 IAU authority : planetary CRS support
- GEOS-11001 Support other CRS authorities in WFS
- GEOS-11002 Support other CRS authorities in WMS
- GEOS-11056 Support other CRS authorities in WCS
- GEOS-11064 Support other CRS authorities in WPS
- GEOS-11066 Support other CRS authorities in importer
- GEOS-11076 SRSList should show authorities other than EPSG, if available
- GEOS-10970 CatalogBuilder cannot handle CRS in authorities other than EPSG
- GEOS-10971 XStreamPersister cannot save CRS references using authorities other than EPSG
- GEOS-10972 Resource page CRS editors would not work with authorities other than EPSG
The printing extension has seen big changes - with a host of new functionality developed by GeoSolutions over the years. With this update the printing module can now be used out-of-the-box by GeoNode and MapStore (no more customization required).
This update covers the release of MapFish Print 2.3.0 (and restores website user-guide).
GeoServer documentation has been updated with configuration options covering the new functionality.
- Max number of columns configuration for multi column legends
- Simple colored box icon in legends
- Explicit support of GeoServer CQL_FILTER parameter (also with layers merge support): wiki
- Legend fitting
- Don’t break legend items
- Reorder legends block in columns
- Images content
- Dynamic images page
- Multipage legends
- Custom intervals in ScalebarBlock
- Clustering Support wiki
- HTML rendering in text blocks
- Extra Pages
- Group Rendering in attribute blocks
- Skip rendering of pages
- Automatic X-Forwarded-For
- Parsing of Base64 encoded images
Thanks to GeoSolutions for adding functionality to mapfish-print for the GeoNode project. Shout out to Tobia Di Pisa and Giovanni Allegra for integration testing. Jody Garnett (GeoCat) was responsible for updating the mapfish print-lib for Java 11 and gathering up the functionality from different branches and forks. And integrating the updated configuration instructions with the GeoServer User Guide.
- GEOS-11159 Update mapfish-print-lib 2.3.0
The previous 2.23 series added a new Check URL facility under the Security menu, but it was turned off by default, for backwards compatibility reasons. This functionality allows administrators to manage OGC Service use of external resources.
This has been included in GeoServer 2.22.x and 2.23.x series for backwards compatibility.
Backwards compatibility note:: This functionality is turned ON by default from GeoServer 2.24.0 onwards.
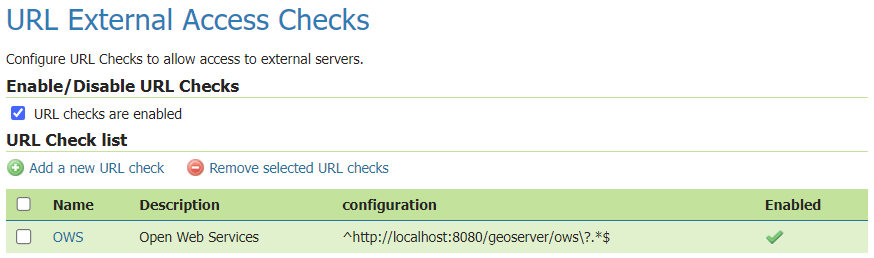
For information and examples on how to use the URL Check page, visit user guide documentation.
- GSIP 218 - Control remote HTTP requests sent by GeoTools \ GeoServer
- GEOS-10949 Control remote resources accessed by GeoServer
- GEOS-11048 Improve URL checking
This release follows a revised security policy. Our existing “responsible disclosure policy” has been renamed, the practice is now called “coordinated vulnerability disclosure.” Last year we enabled GitHub private vulnerability reporting, we will now use these facilities to issue CVE numbers.
Coordinated vulnerability disclosure
Disclosure policy:
- The reported vulnerability has been verified by working with the geoserver-security list
- GitHub security advisory is used to reserve a CVE number
- A fix or documentation clarification is accepted and backported to both the “stable” and “maintenance” branches
- A fix is included for the “stable” and “maintenance” downloads (released as scheduled, or issued via emergency update)
- The CVE vulnerability is published with mitigation and patch instructions
This represents a balance between transparency and participation that does not overwhelm participants. Those seeking greater visibility are encouraged to volunteer with the geoserver-security list; or work with one of the commercial support providers who participate on behalf of their customers.
This change has already resulted in improved interaction with security researchers.
Thanks to Jody Garnett (GeoCat) for this proposal on behalf of GeoCat Live customers.
Developer updates Internal refactor to remove “org.opengis” package usageThe GeoTools project moved away from using the
org.opengispackage after complaints from OGC GeoAPI working group representatives, using the same package name. Interfaces have been moved to theorg.geotool.apipackage, along with some general clean up.While this does not affect GeoServer users directly, it’s of consequence for those that have installations with custom, home grown plugins that might have to be migrated as a consequence. For those, the GeoTools project offers a migration guide, along with a refactoring script that might perform the migration for you, or else, get you close to a working point. GeoServer itself has been migrated using these scripts, with minimal manual intervention.
For more details, and access to the migration script, please see the GeoTools 30 upgrade guide.
Thanks to Jody Garnett (GeoCat), Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions), and Ian Turton (ASTUN Technologies) for all the hard work on this activity. We would also like to thank the Open Source Geospatial Foundation for setting up a cross-project activity and financial support to address this requested change.
- GEOS-11070 Upgrading to GeoTools 30.x series, refactor to
org.geotools.apiinterfaces
While not strictly part of this release, it’s interesting to know about some community module advances that can be found only in the the 2.24.x series.
Two extensions are no longer actively supported and are now available as community modules:
- GEOS-10960 Downgrade imagemap module to community
- GEOS-10961 Downgrade xslt extension to community
The following community modules have been removed (due to lack of interest):
- GEOS-10962 Remove wms-eo community module
- GEOS-10963 Remove SAML community module
- GEOS-10966 Remove importer-fgdb community module
- GEOS-10967 Remove teradata community module
- GEOS-10977 Remove wmts-styles community module
- GEOS-10978 Remove nsg-wmts community module
- GEOS-10984 Remove ows-simulate community module
The OGC API community module keeps improving. In particular, thanks to the GeoNovum sponsorship, GeoSolutions made the OGC API Features module pass the OGC CITE compliance tests, for the “core” and “CRS by reference” conformance classes. Along with this work, other significant changes occurred:
- Made the API version number appear in the service path, easing future upgrades
- Support for configurable links, required to get INSPIRE download service compliance.
In addition to that, the new “search” experimental conformance class allows to POST complex searches against collections, as a JSON document, in a way similar to the STAC API.
Those interested in this work are encouraged to contact Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions).
- GEOS-10924 Support JSON-FG draft encoding in OGC API - Features
- GEOS-11045 Implement proposal “OGC API - Features - Part n: Query by IDs”
- GEOS-10882 Add an option to remove trailing slash match in OGC APIs
- GEOS-10887 Add angle brackets to OGC API CRS Header
- GEOS-10892 Allow configuring custom links for OGC API “collections” and single collection resources
- GEOS-10895 Make OGC API CITE compliant even if the trailing slash is disabled: landing page exception
- GEOS-11058 Support other CRS authorities in OGC APIs
- GEOS-10909 Don’t link from OGC API Features to WFS 2.0 DescribeFeatureType output, if WFS is disabled
- GEOS-10954 Split ogcapi community module package into single functionality packages
For folks working with very large catalogues some improvement from cloud native geoserver are now available to reduce startup time.
Thanks to Gabriel Roldan for folding this improvement into a community module for the rest of the GeoServer community to enjoy.
- GEOS-11049 Community module “datadir catalog loader”
The GeoServer Access Control List project is an independent application service that manages access rules, and a GeoServer plugin that requests authorization limits on a per-request basis.
Gabriel Roldan is the contact point for anyone interested in this work.
The vector mosaic and FlatGeoBuf modules sport significant performance improvementsFlatGeoBuf is a “performant binary encoding for geographic data”, a single file format that also manages to be cloud native and include a spatial index. GeoServer provides access to this format thought the WFS FlatGeobuf output format, which not only can write the format, but also read it as a standard data store.
The Vector Mosaic datastore supports creation of mosaics made of single file vector data, useful in situations where the access to data is targeted to sub-pages of a larger data set (e.g., data for a single time, or a single customer, or a single data collect, out of a very large uniform set of vectors) and the database storage for it has become either too slow, or too expensive.
These two modules make a great combo for those in need to handle very large vector datasets, by storing the FlatGeoBuf on cheap storage.
In particular, the FlatGeoBuf module saw speed improvements that made it the new “fastest vector format” for cases where one needs to display a large data set, all at once, on screen (PostGIS remains the king of the hill for anything that needs sophisticated filtering instead).
For reference, we have timed rendering 4 million tiny polygons out of a precision farming collect, using a 7 classes quantile based SLDs. Here is a tiny excerpt of the map:
And here are the timings to render the full set of polygons, putting them all on screen, at the same time, with a single GetMap request:
- PostGIS, 113 seconds
- Shapefile, 41 seconds
- Flatgeobuf, 36 seconds
The tuning is not complete, more optimizations are possible. Interested? Andrea Aime is the contact point for this work.
Release notes(Including the changes made in 2.24-RC, the release candidate)
Improvement:
- GEOS-11114 Improve extensibility in Pre-Authentication scenarios
- GEOS-11130 Sort parent role dropdown in Add a new role
- GEOS-11142 Add mime type mapping for yaml files
- GEOS-11148 Update response headers for the Resources REST API
- GEOS-11149 Update response headers for the Style Publisher
- GEOS-10926 Community Module Proxy-Base-Ext
- GEOS-10934 CSW does not show title/abstract on welcome page
- GEOS-10973 DWITHIN delegation to mongoDB
- GEOS-10999 Make GeoServer KML module rely on HSQLDB instead of H2
- GEOS-11005 Make sure H2 dependencies are included in the packages of optional modules that still need it
- GEOS-11059 Map preview should not assume EPSG authority
- GEOS-11081 Add option to disable GetFeatureInfo transforming raster layers
- GEOS-11087 Fix IsolatedCatalogFacade unnecessary performance overhead
- GEOS-11090 Use Catalog streaming API in WorkspacePage
- GEOS-11099 ElasticSearch DataStore Documentation Update for RESPONSE_BUFFER_LIMIT
- GEOS-11100 Add opacity parameter to the layer definitions in WPS-Download download maps
- GEOS-11102 Allow configuration of the CSV date format
- GEOS-11116 GetMap/GetFeatureInfo with groups and view params can with mismatched layers/params
Bug:
- GEOS-11138 Jetty unable to start cvc-elt.1.a / org.xml.sax.SAXParseException
- GEOS-11140 WPS download can leak image references in the RasterCleaner
- GEOS-11145 The GUI “wait spinner” is not visible any longer
- GEOS-8162 CSV Data store does not support relative store paths
- GEOS-10452 Use of Active Directory authorisation seems broken since 2.15.2 (LDAP still works)
- GEOS-10874 Log4J: Windows binary zip release file with log4j-1.2.14.jar
- GEOS-10875 Disk Quota JDBC password shown in plaintext
- GEOS-10899 Features template escapes twice HTML produced outputs
- GEOS-10903 WMS filtering with Filter 2.0 fails
- GEOS-10921 Double escaping of HTML with enabled features-templating
- GEOS-10922 Features templating exception on text/plain format
- GEOS-10928 Draft JSON-FG Implementation for OGC API - Features
- GEOS-10936 YSLD and OGC API modules are incompatible
- GEOS-10937 JSON-FG reprojected output should respect authority axis order
- GEOS-10958 Update Spotbugs to 4.7.3
- GEOS-10981 Slow CSW GetRecords requests with JDBC Configuration
- GEOS-10985 Backup Restore of GeoServer catalog is broken with GeoServer 2.23.0 and StAXSource
- GEOS-10993 Disabled resources can cause incorrect CSW GetRecords response
- GEOS-11015 geopackage wfs output builds up tmp files over time
- GEOS-11016 Docker nightly builds use outdated GeoServer war
- GEOS-11033 WCS DescribeCoverage ReferencedEnvelope with null crs
- GEOS-11060 charts and mssql extension zips are missing the extension
Task:
- GEOS-11134 Feedback on download bundles: README, RUNNING, GPL html files
- GEOS-11141 production consideration for logging configuration hardening
- GEOS-11091 Upgrade spring-security to 5.7.10
- GEOS-11094 Bump org.hsqldb:hsqldb:2.7.1 to 2.7.2
- GEOS-11103 Upgrade Hazelcast version to 5.3.x
- GEOS-10248 WPSInitializer NPE failure during GeoServer reload
- GEOS-10904 Bump jettison from 1.5.3 to 1.5.4
- GEOS-10907 Update spring.version from 5.3.25 to 5.3.26
- GEOS-10941 Update ErrorProne to 2.18
- GEOS-10987 Bump xalan:xalan and xalan:serializer from 2.7.2 to 2.7.3
- GEOS-10988 Update spring.version from 5.3.26 to 5.3.27 and spring-integration.version from 5.5.17 to 5.5.18
- GEOS-11010 Upgrade guava from 30.1 to 32.0.0
- GEOS-11011 Upgrade postgresql from 42.4.3 to 42.6.0
- GEOS-11012 Upgrade commons-collections4 from 4.2 to 4.4
- GEOS-11018 Upgrade commons-lang3 from 3.8.1 to 3.12.0
- GEOS-11019 Upgrade commons-io from 2.8.0 to 2.12.0
- GEOS-11020 Add test scope to mockito-core dependency
- GEOS-11062 Upgrade [httpclient] from 4.5.13 to 4.5.14
- GEOS-11063 Upgrade [httpcore] from 4.4.10 to 4.4.16
- GEOS-11067 Upgrade wiremock to 2.35.0
- GEOS-11080 Remove ASCII grid output format from WCS
- GEOS-11084 Update text field css styling to look visually distinct
- GEOS-11092 acme-ldap.jar is compiled with Java 8
For the complete list see 2.24.0 release notes.
About GeoServer 2.24 SeriesAdditional information on GeoServer 2.24 series:
-
-
 20:18
20:18 From GIS to Remote Sensing: Basic Land Cover Classification Using the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin
sur Planet OSGeoThis is the first tutorial of the new Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin version 8. This tutorial describes the essential steps for the classification of a multispectral image (i.e., a modified Copernicus Sentinel-2 image):- Define the Band set and create the Training Input File
- Create the ROIs
- Create a Classification Preview
- Create the Classification Output
Following the video of this tutorial.
The detailed steps of this tutorial are described in the user manual, at the following link [https:]]
I am going to write other tutorials to describe the available classification algorithms, and the other tools of the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin.
For any comment or question, join the Facebook group or GitHub discussions about the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin.
-
 12:12
12:12 GRASS GIS: Apply Now for New Mentoring Program
sur Planet OSGeoThe GRASS GIS project is launching a new mentoring program to help students, researchers, and software developers integrate GRASS GIS into their projects. Mentoring will be provided free of charge by experienced GRASS developers in a one-on-one setting allowing for remote and asynchronous communication. Mentors will work with participants to select the most appropriate and efficient tools and techniques to run and integrate GRASS tools into the participants’ workflow and provide advice and feedback during the implementation.
-
 16:52
16:52 A recap of the 127th OGC Member Meeting, Singapore
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)From September 25-29, 2023, more than 100 geospatial experts from around the world converged in Singapore to attend OGC’s 127th Member Meeting, with another 100+ attending online. As always, big thanks go out to our dedicated members that either attended in-person, or juggled lives across multiple timezones to attend virtually.
Sponsored by OGC Principal Member, the Singapore Land Authority (SLA), the meeting was themed “Building future standards for the next generation of geospatial experts.” Once again, the Member Meeting was held in conjunction with the Singapore Geospatial Festival 2023 operated by SLA’s GeoWorks.
Alongside the usual assortment of Standards Working Group (SWG) and Domain Working Group (DWG) meetings, the Member Meeting also saw several special sessions, including: a two-part Data Quality Workshop; a session on Modeling of Humanities’ Spatio-Temporal Data; a Digital Twins special session; a session on the OGC Academy; a Connecting Land and Sea special session; an Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) ad hoc; and a meeting of the OGC Asia Forum.
Monday evening’s welcome reception celebrated Simple Features’ 25th birthday with a suitably delicious cake and an enthusiastic rendition of “Happy Birthday.” Simple Features, which is jointly published with ISO, is OGC’s earliest standard and describes how to model the location of “features” (a geometric representation of anything of interest) on a 2-dimensional space representing the surface of a planet. And of course there was the usual Wednesday night “VIP Dinner” (held at the delicious Red House Seafood), where Wuhan University received an OGC Community Impact Award, and a Diversity Luncheon held on Thursday.
 OGC Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons, leads the celebrations for Simple Features’ 25th birthday.
Themes from the week
OGC Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons, leads the celebrations for Simple Features’ 25th birthday.
Themes from the week
As is befitting of the location in Singapore, with its advanced modeling of the whole nation, across the entirety of the Member Meeting were presentations related to Digital Twins – twins not only of the built environment, but for vegetation, the ocean, and the subsurface. Several Working Groups regularly include discussion on Digital Twins related to their scope, especially the Urban Digital Twins DWG. Related topics regarding the Metaverse and Interoperable Simulation and Gaming also continue regular appearances at OGC meetings.
Marine and coastlines play an important role in economies and climate resilience strategies alike. OGC has a long-running pilot project on marine geospatial infrastructure, and we continue to refine models for describing and managing the coastal land-sea interface. We expect this work to be extended to the topics of ITS and logistics in the coming years, too.
A Kick-off and a Joint OpeningThe OGC Member Meeting started on Monday, but as it was held jointly with the Singapore Geospatial Festival, the joint opening wasn’t until Tuesday. Monday, then, kicked off with a brief welcome session before the ever-popular Today’s Innovations, Tomorrow’s Technologies and Future Directions session.
The topic of this meeting’s Future Directions session was Geospatial Artificial Intelligence. Dr. Gobe Hobona, OGC’s Director of Product Management, opened with an overview of where this topic fits in the context of previous sessions. He was then followed by three presentations:
- Kyoung-Sook Kim from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science & Technology (AIST) presented a Design Standardization Roadmap for GeoAI.
- Peter Baumann, Dimitar Misev, and Otoniel Campos of Constructor University (formerly Jacobs University) presented on Scalable Datacube-Enabled AI Infrastructure Based on Open Standards.
- Amey Godse and Sunil Shah of Duality Robotics presented on Building Digital Site Twins Using Geospatial Data and Artificial Intelligence.
The speakers then participated in a panel fielding audience questions, including their views on the fundamental scope of the AI domain in a geospatial context, and what types of machine learning need OGC’s attention and which may be less relevant. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The joint Opening session on Tuesday featured keynote remarks from Colin Low, Chief Executive, SLA, and myself. The Guest of Honor was Dr. Mohamad Maliki Bin Osman, Minister in the Prime Minister’s Office, Second Minister for Education & Foreign Affairs. The session also featured presentations from local students who had performed impressive geospatial projects in their primary schools. It finished with a panel on “Geospatial: Enriching Minds, Empowering Lives,” which was also the key theme for the Singapore Geospatial Festival.
 The theme of the Member Meeting was “Building future standards for the next generation of geospatial experts.”
Meeting Special Sessions
The theme of the Member Meeting was “Building future standards for the next generation of geospatial experts.”
Meeting Special Sessions
The week continued with its usual array of SWG and DWG meetings, interspersed with several special sessions, outlined below.
The OGC Data Quality DWG held two sessions to comprise a workshop covering a breadth of data quality topics. The first session focused on the work of ISO/TC 211 on data quality measures and a registry to be hosted by OGC. The second session included presentations on the data quality requirements and considerations for a variety of types of geospatial data, including 3D and imagery. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The session on Modeling of Humanities’ Spatio-Temporal Data was organized by participants in the HumSpatial Consortium, in which OGC participates, to address the complexities of representing “named places” in geospatial technologies. Presentations were given by scholars and practitioners from the humanities research and government sectors heavily involved with place-names and other types of geospatial data. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
Several sessions over the course of the week included presentations related to Digital Twins, often in the context of other domains, such as Artificial Intelligence or Data Quality. A dedicated special session for Digital Twins was organized to demonstrate different information types and practices and facilitate discussion on the relative meaning/relationship between digital twins, the metaverse, and the industrial metaverse. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The OGC Academy is an information portal for distributing OGC knowledge related to the work of the Consortium and general geospatial interoperability. The web-based resources are under development with an estimated completion in 2026. Content is continuously refreshed. This session discussed capacity building and the academy more broadly. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The OGC Marine DWG organized a follow-up session to the one hosted last year in Singapore on “Connecting Land and Sea” to highlight activities in the OGC Federated Marine Spatial Data Infrastructure Pilot as well as work from OGC members around the world. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) ad hoc session highlighted work in ISO/TC 204, with whom OGC maintains a liaison, and explored the next steps for related work in OGC. Attendees generally accepted that ITS work intersected several OGC Working Groups and that a new effort to refine the road network model developed in TC 204 would be suitable for OGC activities. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
At each OGC Member Meeting, one or more local forums meet to present and discuss topics of regional interest. On Friday of the Member Meeting, the OGC Asia forum offered a short history on the forum and five presentations from across the region. OGC Members can access the presentations and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
 Winston Yap from the National University of Singapore’s Urban Analytics Lab presents during the Digital Twins Special Session.
Closing and Important Things
Winston Yap from the National University of Singapore’s Urban Analytics Lab presents during the Digital Twins Special Session.
Closing and Important Things
The Member Meeting’s Closing session began with the Important Things session and my rapid, 15-minute summary of the entire meeting week that included slides and content from a large number of Working Group sessions. OGC Members can access the presentation and a recording on this page in the OGC Portal.
The Important Things session then proceeded with two discussion topics:
- “Is the ‘fundamental model’ of geospatial 2D, 3D, 4D, or more D?” with consideration to whether the minimum number of dimensions is necessary, or whether all dimensions should just be assumed.
- “The need to establish a policy for the governance of building blocks” where the TC concluded that more discrete definitions are needed for “building blocks” and other registered items that act as useful components in geospatial architecture.
Notes from the session were recorded in the Etherpad “Important-Things-2023-09”, which is available to OGC Members via the Portal.
The formal Closing Plenary then followed, which focuses on Working Group presentations and voting. The session advanced a number of Standards, SWGs, and documents toward vote or publication, so keep your eye on our news page, or subscribe to the “Standards updates” topic on the OGC Mailing List to get notifications sent straight to your inbox.
Thank youOur 127th Member Meeting was yet another memorable meeting. It’s so great to see OGC Members discuss, collaborate, and drive technology and standards development forward in support of some of the biggest issues facing humanity. Once again, a sincere thank you to our members for investing their time and energy, as well as their dedication to making OGC the world’s leading and most comprehensive community of location experts.
Be sure to join us at TU Delft, Netherlands, on March 25-29, 2024, for our 128th Member Meeting. Registration and further info will be available soon on ogcmeet.org. Sponsorship opportunities are also available – contact us for more info. You can subscribe to the “Events” and other topics on the OGC Mailing List to stay up to date on all aspects of OGC, including when registration goes live for our Member Meetings.
In the meantime, don’t miss our 2023 Innovation Days event, December 5-7 in Washington, DC, USA. The multi-day event brings together policy makers, program decision-makers, and other experts in geospatial to showcase climate, emergency, and disaster management & resilience solutions that scale from local to global impacts.
 Attendees of the 127th OGC Member Meeting in Singapore, 2023.
Attendees of the 127th OGC Member Meeting in Singapore, 2023.The post A recap of the 127th OGC Member Meeting, Singapore appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 4:00
4:00 EOX' blog: Data Gravity, the Source Cooperative and hopeful thoughts...
sur Planet OSGeoTL;DR understand the cost drivers in your "open data" strategy, long-term don't neglect the ecosystem gravitating around the actual data you can outsource data promotion but not data governance allow a neutral cooperative to track uptake and share analytics The term data gravity describes the observ ... -
 4:00
4:00 Camptocamp: Camptocamp at GéoDataDays 2023
sur Planet OSGeoPièce jointe: [télécharger]
Held in Reims, France, GéoDataDays 2023 was a major event in the world of geomatics and digital mapping. -
 2:45
2:45 From GIS to Remote Sensing: Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin version 8 officially released
sur Planet OSGeoI am glad to announce the release of the new version 8 (codename "Infinity") of the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (SCP) for QGIS.
This new version is based on a completely new Python processing framework that is Remotior Sensus, which expands the processing capabilities of SCP, also allowing for the creation of Python scripts.
The following video provides an introduction to the SCP tools.
Read more » -
 3:35
3:35 Sean Gillies: Bear 100 recap
sur Planet OSGeoA week ago I started the Bear 100 Endurance Run. I did not finish. This was my first DNF. I'm still trying to figure out what went wrong and evaluate how I responded.
To recap: I rolled into the sixth aid station, Tony Grove, mile 51, at 9:59 p.m. I made a head to toe gear change. Underwear, pants, hat, socks, and shoes. Diaper ointment lube on my feet and privates. Ate potatoes and chicken noodle soup and refilled my bottles. I spent too much time there, but this was going to be my main stop before dawn, and I wanted to get properly set up for 8 hours of plugging through the night. I left at 10:43 p.m.
Somewhere around mile 59, descending into Franklin Basin, my left ankle stopped working, and I limped into the Franklin Basin aid station (mile 62). After 15 minutes of triage, I decided to quit. I had no flexibility or stability in my left foot, and continuing seemed pointless.
What happened? I couldn't remember a single major incident. I'd had a number of little wobbles earlier in the day and the descent from Tony Grove was pretty rough. I certainly picked up a little damage along the way. And I'd sprained this ankle four weeks ago. Maybe it wasn't strong enough to go 100 miles. It's possible that I fell asleep on my feet at 1:30 a.m. and rolled it. I was certainly sleepy enough at some points. Either the accumulation of stress was too much for my ankle, or an acute injury happened while I was checked out. Or both. I don't know for sure.
I'm disappointed. Otherwise, things were going well. My gear choices were solid. I was eating and drinking well enough. Other than one toenail lost to kicking a rock, my feet were fine, no hotspots or blisters. My ankle was swollen for several days, but I didn't go far enough to wreck my quads or hips. Sigh.
I will try this again.
More about the race, photos, stories, etc, soon.
-
 11:00
11:00 OGC and the International Data Spaces Association sign Memorandum of Understanding
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) and the International Data Spaces Association (IDSA) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that outlines how they will together contribute to a flourishing data economy through the creation and development of standards for data spaces that ensure sovereign, interoperable, and trusted data sharing.
“As the number of available data sources continues to grow, the challenge of integrating them into high-value products becomes ever greater,” commented OGC Chief Technology Innovation Officer, Ingo Simonis, Ph.D. “In order to develop effective solutions for cross-border data integration, international collaboration is critical. As such, OGC is eager to work with IDSA to tackle this task together.”
“Committed to driving digital transformation, IDSA champions economic growth, innovation, and a cohesive data-sharing approach,” said Silvia Castellvi, Director of Research & Standardization at IDSA. “Partnering with OGC ensures our standards align and resonate. Enhancing features, like the geolocation of IDS Connectors, not only advances our standard but boosts its appeal for future developers and users.”
OGC is an international non-profit consortium aiming to make geospatial (location) information and data services FAIR – Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable. IDSA is an international non-profit association that follows a user-driven approach to create a global standard for international data spaces and interfaces based on sovereign data sharing.
The MoU seeks to align activities between the two organizations so that OGC and IDSA Standards can work in tandem. This will be achieved in part through joint participation in potential future projects and initiatives, particularly in the areas of global supply chains, intelligent transport, and smart city data spaces.
Projects in global supply chains and intelligent transport may include developing solutions that support the monitoring of shipping routes, tracking freight, sharing ocean currents and weather data, and more. Projects in smart city data spaces could focus on improving data sharing from business and technical perspectives, and could include data ranging from traffic to population migration.
The two organizations have already identified several ongoing or completed projects relevant to their work together, including: Divine, Flexigrobots, DEMETER, ATLAS & AgriDataValue, Iliad, AD4GD, OGC Rainbow, and others.
About IDSA
The International Data Spaces Association (IDSA) is on a mission to create the future of the global, digital economy. Its 140+ member companies and institutions have created the International Data Spaces (IDS) standard: a secure system of sovereign and trusted data sharing in which all participants can realize the full value of their data. IDS enables new smart services and innovative business processes to work across companies and industries, while ensuring that the control of data remains in the hands of data providers. We call this data sovereignty.
Visit internationaldataspaces.org for more informationPress contact:
Nora Grass
+49 162 2104263
nora.gras@internationaldataspaces.orgThe post OGC and the International Data Spaces Association sign Memorandum of Understanding appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 21:29
21:29 SIG Libre Uruguay: IV Convención Científica Internacional UCLV 2023
sur Planet OSGeo
La Universidad Central “Marta Abreu” de Las Villas, Institución de Excelencia de la Educación Superior en Cuba, convoca a la IV Convención Científica Internacional de Ciencia, Tecnología y Sociedad UCLV 2023, bajo el lema “Ciencia e Innovación para el Desarrollo Sostenible.”
Podrán participar investigadores, académicos, docentes, directivos, empresarios, decisores de políticas de gobierno, estudiantes y otros actores sociales, implicados en la actividad de ciencia e innovación y protección del medio ambiente, además, contaremos con la presentación de conferencias magistrales de expertos de reconocido prestigio internacional y nacional, así como se desarrollarán otras actividades científicas desde una perspectiva multidisciplinar e intersectorial.
Se contará tambien con la modalidad de participación virtual, facilitando a través de la plataforma la transmisión en vivo de actividades que se especificarán en el programa del evento.
El encuentro se desarrollará del 13 al 17 de noviembre de 2023, en el destino turístico Cayos de Villa Clara: Santa María, Cuba.

Destacamos especialmente el II Simposio Internacional sobre «Generación y Transferencia de Conocimiento para la Transformación Digital» SITIC2023, donde se desarrollarán un número importante de actividades: conferencias, curso, talleres. A continuación, la agenda
-
 17:00
17:00 CoverageJSON v1.0 Adopted as OGC Community Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that version 1.0 of CoverageJSON has been approved by the OGC Membership for adoption as an official OGC Community Standard. CoverageJSON enables the development of interactive visualizations that display and manipulate spatio-temporal data within a web browser.
The key design goals for CoverageJSON are simplicity, machine and human readability, and efficiency in the storage and use of complex data.
Coverages and collections of coverages can be encoded using CoverageJSON. Coverage data may be gridded or non-gridded, and data values may represent continuous values (such as temperature) or discrete categories (such as classes of land cover).
This OGC Community Standard was an outcome of the European Union project “Maximizing the Exploitation of Linked Open Data in Enterprise and Science” (MELODIES), which ran from 2013 to 2016, and was released under a Creative Commons 4.0 License by the University of Reading. There are several widely-used open source implementations and libraries available. Furthermore, CoverageJSON is one of the encodings supported by the OGC API – Environmental Data Retrieval Standard.
CoverageJSON is based on the popular JavaScript Object Notation (JSON), and provides an effective, efficient format that’s friendly to web and application developers and consistent with the OGC API family of Standards.
CoverageJSON supports the efficient transfer of usable quantities of data from big data stores to lightweight clients, such as browsers and mobile applications. This enables straightforward local manipulation of the data by scientists and other users.
The simplest and most common use-case is to embed all the data values of all variables in a Coverage object within the CoverageJSON document to create a self-contained, standalone, document that supports the use of very simple clients.
Another simple use case is to put data values for each variable (parameter) in separate array objects in separate CoverageJSON documents that are linked from a parent CoverageJSON object. This is useful for a multi-variable dataset, such as one with temperature, humidity, wind speed, etc., to be recorded in separate files. This allows the client to load only the variables of interest.
A sophisticated use case is to use tiling objects, where the data values are partitioned spatially and temporally, so that a single variable’s data values would be split among several documents. A simple example of this use case is encoding each time step of a dataset into a separate file, but the tiles could also be divided spatially, like a tiled map server implementation.
As with any OGC Standard, the OGC CoverageJSON Community Standard is free to download and implement. Interested parties can learn more about, view, and download the Standard from OGC’s CoverageJSON Community Standard Page.
The post CoverageJSON v1.0 Adopted as OGC Community Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 20:45
20:45 QGIS Blog: Call for Proposals: QGIS Website Overhaul 2023/2024
sur Planet OSGeo Background
Background
Our web site ( [https:]] ) dates back to 2013, it is time for a revision!
As well as modernizing the look and feel of the site, we want the content to be updated to represent changes in the maturity of the project.
We want to appeal to new audiences, especially business and NGO decision makers (in particular the experience for the front pages), whilst still maintaining appeal to grass roots users (especially the lower level pages which contain many technical details and community collaboration notes).
We want to enhance our fund raising efforts through a site that encourages people to contribute to, as well as take from, the project.
 Existing effort
Existing effort
First some key links:
- Current web site: [https:]
- Design for new web site landing page: [https:]]
- Design for new web site (figma): [https:]]
- Code for new web site (what we have built so far): [https:]]
- Plugins web site: [https:]]
- QGIS Documentation Site: [https:]]
- QGIS User Manual: [https:]]
- QGIS Server Manual: [https:]]
- Gentle Introduction to GIS: [https:]]
- QGIS Python Cookbook: [https:]]
- QGIS C++ API Documentation: [https:]]
- QGIS Python API Documentation: [https:]]
- QGIS Certification and Changelog: [https:]]
The above websites were created with a mix of technologies:
- Sphinx (rst)
- Doxygen
- Custom Django Apps
It will not be possible to unify the technology used for all of the above sites, but we want all of the web sites to have a cohesive appearance and the navigation flow between them to be seamless. For the main website at [https:]] and its child pages, we want to re-implement the site to provide a new experience – according to the design we have laid out in our figma board. Note that we want to follow this design. Some small tweaks will be fine but we are not looking for a ‘from scratch’ re-implementation of our design.
This will be our website for the next 10 years – you need to hand it over to us in a way that we can continue working on it and maintaining it without your intervention.
We are calling for proposals to help us with this migration as per the phases described below.
Phase 1?: Project planning Timeline
Timeline Proposed site structure
Proposed site structure
- What content will be kept
- What will be removed
- What is new to be added
- Keep front page as starting point
- Suggest tweaks if needed
- Establish a clear vocabulary of page types
- Second and third level page design
- Special pages such as
- Download
- Release countdown
- Donation / sustaining members
- Gallery
- and any other you identify as non-standard second/third level
- Guidance and standards for producing visuals like screenshots etc. For example, how we present QGIS screenshots in a flattering way.
- Establish a plan for auxiliary sites:
- Plugins.qgis.org
- Api.qgis.org
- Docs.qgis.org
- etc. (see intro for more exhaustive list)
- Iterative review and feedback from the QGIS web team should be incorporated from biweekly check in calls.
Phase 2?: Content migration of the main site Outcome: We have a clear roadmap and design guide for migrating all of our websites to a consistent unified experience.
Outcome: We have a clear roadmap and design guide for migrating all of our websites to a consistent unified experience. During this phase the contractor will focus on migrating the content of the main site to the new platform.
There will be an iterative review and feedback from the QGIS web team should be incorporated from biweekly check-in calls.
Phase 3?: Auxiliary sites migrations Outcome: [https:]] new site goes live! (Target date end of February 2024)
Outcome: [https:]] new site goes live! (Target date end of February 2024)This is out of scope of the current call for proposals but should be part of the overall planning process:
This would be a collaborative process involving a QGIS funded web developer and the consultant.
Iterative review and feedback from the QGIS web team should be incorporated from biweekly check in calls.
 Outcome: Auxiliary sites goes live with a cohesive look and feel to match the main site.
Outcome: Auxiliary sites goes live with a cohesive look and feel to match the main site. What we will provide
What we will provide
- Maps and screenshots, videos, animations (with inputs from design team)
- Inputs in terms of content review
 Qualification criteria
Qualification criteria
 Must have an established track record of website design and content creation.
Must have an established track record of website design and content creation. Individuals or companies equally welcome to apply.
Individuals or companies equally welcome to apply. Any potential conflict of interest should be declared in your application.
Any potential conflict of interest should be declared in your application. Discussions will happen in English, with live discussions as well as written communication via issues or Pull request. Being reasonably fluent in English and understand the soft skills required to interact in a community project will be more than appreciated
Discussions will happen in English, with live discussions as well as written communication via issues or Pull request. Being reasonably fluent in English and understand the soft skills required to interact in a community project will be more than appreciated Payment milestones
Payment milestones
10 % Kick off
40 % Phase 1 Completion
50 % Phase 2 Completion
 Indicative budget
Indicative budget
We would like to point you to the QGIS Annual Budget so that you have a sense of our broad financial means (i.e. we will not be able to afford proposals in excess of €25,000 for phase 1+2).
 Technology choices and IP:
Technology choices and IP:
- Must be wholly based on Open Source tooling (e.g. javascript, css, web frameworks)
- Needs to be ideally implemented in Hugo (or Sphinx)
- Must produce a static web site (except for existing django based sites)
- Publication and development workflow will follow standard pull request / review process via our GitHub repositories
- Mobile friendly
- Site will be english only – any auto-translation tooling that can be added so that users can trivially see an auto-translated version of the site will be considered favourably.
 Proposal submission
Proposal submission
Your proposal should consist of no more than 5 pages (include links to relevant annexes if needed) covering the following:
- Overview of yourself / your organization
- Delivery timeline
- Team composition
- Budget for each phase
- Examples of prior work
- Bonus things to mention if relevant: GIS experience & working with Open Source projects
Please send your proposal to finance@qgis.org by October 29nd 2023 midnight, anywhere on earth.
-
 2:49
2:49 GeoTools Team: GeoTools 30-RC released
sur Planet OSGeoThe GeoTools team is pleased to share the availability GeoTools 30-RC :geotools-30-RC-bin.zip geotools-30-RC-doc.zip geotools-30-RC-userguide.zip geotools-30-RC-project.zip org.opengis package removalThe main novelty in this release is the renaming of all "org.opengis" packages into "org.geotools.api" ones, to satisfy a request coming from OGC members that manage the "GeoAPI" project, using the -
 21:53
21:53 From GIS to Remote Sensing: Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin version 8 release date and dependency installation
sur Planet OSGeoThis post is to announce that the new version 8 (codename "Infinity") of the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (SCP) for QGIS will be released the 8th of October 2023.This new version is based on a completely new Python processing framework that is Remotior Sensus, which will expand the processing capabilities of SCP, also allowing for the creation of Python scripts.
The SCP requires Remotior Sensus, GDAL, NumPy and SciPy for most functionalities. Optionally, scikit-learn and PyTorch are required for machine learning. GDAL, NumPy and SciPy should already be installed along with QGIS.It might be useful to illustrate the installation steps of these dependencies before SCP is released.Read more » -
 17:58
17:58 Fernando Quadro: Verificações de URL no GeoServer
sur Planet OSGeoA versão 2.24.x do GeoServer traz entre suas novidades as verificações de acesso externo de URL que permite controlar as verificações executadas em URLs fornecidas pelo usuário que o GeoServer usará para acessar recursos remotos.
Atualmente, as verificações são realizadas nas seguintes funcionalidades:
- Solicitações WMS GetMap, GetFeatureInfo e GetLegendGraphic com folhas de estilo SLD remotas (parâmetro SLD)
- Ícones remotos referenciados por estilos (o acesso aos ícones no diretório de dados é sempre permitido)
- Solicitações WMS GetMap e GetFeatureInfo no modo de representação de recursos (parâmetros REMOTE_OWS e REMOTE_OWS_TYPE)
- Entradas remotas WPS, como solicitações GET ou POST
Para criar as regras de verificação, o GeoServer utiliza expressões regulares. Na internet existem sites disponíveis que irão te ajudar a definir um padrão de expressão regular Java (linguagem que o GeoServer é desenvolvido) válido. Essas ferramentas podem ser usadas para interpretar, explicar e testar expressões regulares. Por exemplo:
– [https:]] (habilitar o tipo Java 8)
1. Configuração de verificações de URL
Navegue até a página Dados > Verificações de URL para gerenciar e configurar verificações de URL.
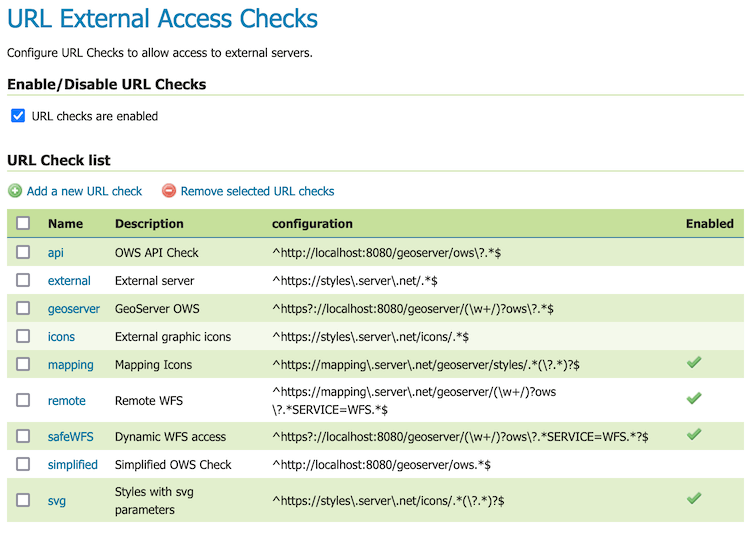
Tabela de verificações de URL
Use as opções Ativar/Desativar para habilitar este recurso de segurança:
- Quando a caixa de seleção de verificações de URL está habilitada, as verificações de URL são realizadas para limitar o acesso do GeoServer a recursos remotos, conforme descrito acima. A ativação de verificações de URL é recomendada para limitar a interação normal dos protocolos Open Web Service usados ??para ataques de Cross Site Scripting.
- Quando a caixa de seleção está desabilitada, as verificações de URL NÃO são habilitadas, o GeoServer recebe acesso irrestrito a recursos remotos. Desativar verificações de URL não é uma configuração segura ou recomendada.
2. Adicionando uma verificação baseada em expressão regular
Os botões para adicionar e remover verificações de URL podem ser encontrados na parte superior da lista de verificação de URL.
Para adicionar uma verificação de URL, pressione o botão Adicionar nova verificação. Você será solicitado a inserir os detalhes da verificação de URL (conforme descrito abaixo em Editando uma verificação).
3. Removendo uma verificação
Para remover uma verificação de URL, marque a caixa de seleção ao lado de uma ou mais linhas na lista de verificação de URL. Pressione o botão Remover verificações de URL selecionadas para remover. Você será solicitado a confirmar ou cancelar a remoção. Pressionar OK para remover as verificações de URL selecionadas.
4. Editando uma verificação
As verificações de URL podem ser configuradas, com os seguintes parâmetros para cada verificação:
- Nome: Nome da verificação, utilizado para identificá-lo na lista.
- Descrição: Descrição da verificação, para referência posterior.
- Expressão regular: Expressão regular usada para corresponder aos URLs permitidos
- Habilitado: Caixa de seleção para ativar ou desativar a verificação
Veja abaixo como é a tela de configuração:
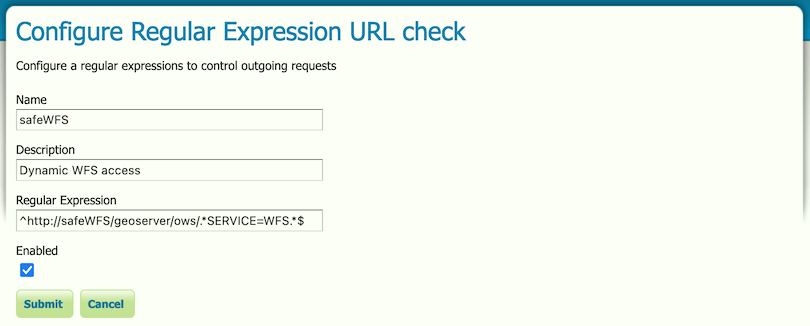
Tela de configuração de verificação de URL
5. Testando verificações
O formulário Testar verificações permite que uma URL seja verificada, informando se o acesso é permitido ou não.
Pressione o botão Testar URL para realizar as suas verificações. Se pelo menos uma verificação corresponder ao URL, ele será permitido e o teste indicará a verificação que permite o acesso. Caso contrário, será rejeitado e o teste indicará que nenhuma verificação de URL foi correspondente.

Tela de teste de verificações de URL
Fonte: GeoServer Documentation
-
 23:20
23:20 Fernando Quadro: GeoServer ACL
sur Planet OSGeoA versão 2.24.x do GeoServer traz entre suas novidades o GeoServer ACL (Access Control List), um sistema de autorização avançado.
Ele consiste em um serviço independente que gerencia regras de acesso e um plugin do GeoServer que solicita limites de autorização por solicitação.
Como administrador, você usará o GeoServer ACL para definir regras que concedem ou negam acesso a recursos publicados com base nas propriedades da solicitação de serviço, como credenciais do usuário, o tipo de serviço OWS (OGC Web Services) e as camadas solicitadas.
Essas regras podem ser tão abertas quanto conceder ou negar acesso a espaços de trabalho inteiros do GeoServer, ou tão granulares quanto especificar quais áreas geográficas e atributos de camada permitir que um usuário ou grupo de usuários específico veja.
Como usuário, você executará solicitações ao GeoServer, como WMS GetMap ou WFS GetFeatures, e o mecanismo de autorização baseado no ACL limitará a visibilidade dos recursos e conteúdos das respostas àqueles que correspondem às regras que se aplicam às propriedades da solicitação e as credenciais do usuário autenticado.
GeoServer ACL não é um provedor de autenticação. É um gerenciador de autorização que usará as credenciais do usuário autenticado, sejam elas provenientes de HTTP básico, OAuth2/OpenID Connect ou qualquer mecanismo de autenticação que o GeoServer esteja usando, para resolver as regras de acesso que se aplicam a cada solicitação específica.
GeoServer ACL é Open Source, nascido como um fork do GeoFence. Como tal, segue a mesma lógica para definir regras de acesso a dados e acesso administrativo. Portanto, se você estiver familiarizado com o GeoFence, será fácil raciocinar como o GeoServer ACL funciona.
Fonte: GeoServer ACL Project
-
 17:00
17:00 Wuhan University receives OGC Community Impact Award
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) has announced Wuhan University, represented by Professor Peng Yue, as the latest recipient of the OGC Community Impact Award. The award was presented at the VIP Dinner of the 127th OGC Member Meeting in Singapore.
The Community Impact Award is given by OGC to highlight and recognize those members of the OGC Community who, through their exceptional leadership, volunteerism, collaboration, and investment, have had a positive impact on the wider geospatial community.
“Wuhan University and Professor Peng Yue exemplify the mission of OGC through their combined efforts in technical leadership and international consensus building,” commented OGC Chief Standards Officer, Scott Simmons. “Their recent contributions toward standardization in AI were inclusive of the breadth of OGC membership and will prove truly useful for the geospatial community.”
Wuhan University has, and continues to, make an impact within the OGC Community through their active leadership, international collaboration, and engagement across numerous OGC Collaborative Solutions and Innovation Program (COSI) Initiatives, Working Groups, Member Meetings, and the OGC China Forum. Professor Peng Yue was also the primary lead on the newly published Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence (Part 1) Standard.
The OGC Community Impact award highlights the importance of collaboration, volunteering time and energy, advancing technologies and standards, raising awareness, and helping solve critical issues across the geospatial community. Wuhan University exemplifies all of these qualities in their work to drive innovation and standards for AI/ML and associated training data, and their efforts in leading the OGC Community in China.
The post Wuhan University receives OGC Community Impact Award appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 17:00
17:00 OGC Adopts Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence Conceptual Model as Official Standard
sur Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC)The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is excited to announce that the OGC Membership has approved the OGC Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence (TrainingDML-AI) Part 1: Conceptual Model for adoption as an official OGC Standard. The Standard defines the conceptual model for standardized geospatial training data for Machine Learning.
Training data plays a fundamental role in Earth Observation (EO) Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning (AI/ML) applications, especially Deep Learning (DL). It is used to train, validate, and test AI/ML models. Understanding the source and applicability of training data allows for better understanding of the results of AI/ML operations.
To maximize the interoperability and re-usability of geospatial training data, the TrainingDML-AI Standard defines a model and encodings consistent with the OGC Standards baseline to exchange and retrieve the training data via the Web. Part 1 of the Standard contains the Conceptual Model, as well as example JSON encodings. Future Parts of the Standard will cover other encodings.
Additionally, the Standard provides detailed metadata for formalizing the information model of training data. This includes but is not limited to the following aspects:
- How the training data is prepared, such as provenance and quality;
- How to specify different metadata used for different ML tasks;
- How to differentiate the high-level training data information model and extended information models specific to various ML applications;
- How to describe the version, license, and training data size;
- How to introduce external classification schemes and flexible means for representing ground-truth labeling.
OGC Members interested in staying up to date on future progress of this standard, or contributing to its development, are encouraged to join the Training Data Markup Language for AI Standards Working Group via the OGC Portal. Non-OGC members who would like to know more about participating in this SWG are encouraged to contact the OGC Standards Program.
As with any OGC standard, the open OGC Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence (TrainingDML-AI) Part 1: Conceptual Model Standard is free to download and implement.
The post OGC Adopts Training Data Markup Language for Artificial Intelligence Conceptual Model as Official Standard appeared first on Open Geospatial Consortium.
-
 23:21
23:21 KAN T&IT Blog: Análisis de calidad de información geoespacial. BID Perú.
sur Planet OSGeoEn el marco del convenio con el Banco Interamericano de Desarrollo sede Perú (BID Perú), se llevó a cabo el proyecto de análisis de calidad de información geoespacial generados en el contexto del programa “Apoyo a la Plataforma Nacional de Ciudades Sostenibles y Cambio Climático en Lima” para el Ministerio de Ambiente de la República de Perú (MINAM). Este proyecto consistió en realizar el control de calidad de más de 400 capas de información geoespacial en función de los requerimientos establecidos en la familia de normas ISO 19100 que apuntan a regular y a normalizar la generación de información geoespacial con el objetivo de garantizar su interoperabilidad. El objetivo final de este trabajo fue aportar al proceso de mejora de la calidad e interoperabilidad de los datos al Plan Nacional de Adaptación al Cambio Climático (NAP, por sus siglas en inglés) en Perú.
El NAP consiste en un exhaustivo documento en donde se plasman los principales lineamientos para planificar la implementación de medidas diseñadas específicamente para reducir los riesgos derivados del impacto del cambio climático. A su vez, este documento pretende ser una fuente de información disponible para la toma de decisiones a nivel gubernamental en torno a ésta problemática. En este sentido, entre los objetivos que persigue el NAP, se presentan los siguientes:
1: Integrar y articular diversos instrumentos de gestión: Estrategia Regional de Cambio Climático, NDC y Planes Locales de Adaptación al Cambio Climático.
2: Desarrollar un análisis de riesgos climáticos a nivel nacional y regional para 5 áreas temáticas: Agua, Bosques, Agricultura, Pesca y Acuicultura y Salud; y para 4 amenazas clave: movimientos en masa, inundaciones, cambio en las condiciones de aridez y retroceso glaciar.
3: Actualizar las medidas de adaptación establecidas en cada uno de los instrumentos de gestión, de acuerdo con las necesidades de las poblaciones y los ecosistemas.
Para llevar a cabo el proceso de revisión y control de calidad de la información generada en este contexto, se trabajó en conjunto con las empresas productoras de la información geoespacial y en constante comunicación con representantes del BID Perú. Estas empresas habían sido convocadas por el Ministerio de Ambiente de Perú en convenio con BID y la organización World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) con el objetivo de analizar y generar información para: el “Plan de Adaptación Costera para el Área Metropolitana de Lima (AML)”, los “Estudios base sobre riesgo de desastres por riesgos naturales y crecimiento urbano en el AML” y los “Estudios de análisis urbanístico, prefactibilidad y diseños constructivos para acciones estratégicas de accesibilidad, multimodalidad y desarrollo orientado al transporte en el Sistema Integrado de Transporte (SIT) de Lima y Callao”. Toda la información geoespacial generada en el marco de estos tres productos fue el objeto de análisis de la consultoría realizada por Kan.
La premisa que guió el desarrollo de este proyecto fue alcanzar un nivel de calidad del dato óptimo que permitiera a los organismos disponibilizar la información producida garantizando el libre acceso, la interoperabilidad, la confiabilidad y la calidad.
En primera instancia se presentaron requisitos para la presentación de la información para asegurar el libre acceso. En este sentido, se solicitó que la información pudiera ser consultada a través de software libres, para que pudieran ser consumidos sin necesidad de pagar una licencia para hacerlo, siendo el formato “geopackage” el indicado para cumplir esta condición.
El análisis de la información se basó en una metodología específica desarrollada por el equipo SIG de Kan, fundamentada en las normas 19115-3, 19139, 19110 y 19157 que hacen referencia a los formatos e implementación de metadatos, a la catalogación de objetos geográficos y a la calidad del dato, respectivamente. Todo el contenido de estas normas se plasmaron en matrices analíticas que luego fueron aplicadas a cada una de las capas de información. Estas matrices permitieron relevar el estado de la información en relación a: la completud de sus metadatos, formatos de interoperabilidad de la información, calidad del dato, referencias sobre su linaje, uso y propósito, su consistencia lógica y topológica, el análisis de sus atributos, entre otros puntos. En total, se establecieron seis categorías de análisis:
A: Compatibilidad del conjunto de datos
B: Interoperabilidad del conjunto de datos
C: Interoperabilidad conjunto de metadatos
D: Interoperabilidad – Metadatos de la capa
E: Compatibilidad de la capa
F: Calidad del dato
Para cada categoría se definieron una serie de elementos de análisis que en total suman 47 ítems. El objetivo final de esta revisión fue cuantificar la usabilidad de la información geográfica producida, estableciendo un rango de usabilidad. Este rango va entre -1 y 1, siendo los valores cercanos a -1 aquellos que incumplen en más de un 50% los elementos establecidos para el análisis y los valores cercanos a 1 aquellos que cumplen en más de un 50% los elementos. De esta forma se obtuvo un resultado parcial de usabilidad por capa y un resultado global de usabilidad para el conjunto de datos. Luego de haber realizado el análisis, se confrontaron los resultados obtenidos con lo establecido por las normas, de esta manera se creó un documento de recomendaciones y sugerencias para la mejora de la calidad e interoperabilidad del dato.
Este proyecto permitió conocer la calidad de la información generada en el proyecto e identificar aquellos aspectos posibles de mejorar para garantizar la interoperabilidad de la información. Luego de este proceso de análisis, las empresas aplicaron las recomendaciones y sugerencias realizadas por el equipo SIG de Kan con el que alcanzaron un nivel óptimo de calidad del dato.

-
 4:00
4:00 GeoServer Team: GeoServer 2.24-RC Release
sur Planet OSGeoGeoServer 2.24-RC release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is a release candidate intended for public review and feedback, made in conjunction with GeoTools 30-RC, GeoWebCache 1.24-RC, mapfish-print-v2 2.3-RC and geofence-3.7-RC.
Thanks to Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions) and Jody Garnett (GeoCat) for working on making this release candidate.
Release candidate public testing and feedbackTesting and providing feedback on releases is part of the open-source social contract. The development team (and their employers and customers) are responsible for sharing this great technology with you.
The collaborative part of open-source happens now - we ask you to test this release candidate in your environment and with your data. Try out the new features, double check if the documentation makes sense, and most importantly let us know!
If you spot something that is incorrect or not working do not assume it is obvious and we will notice. We request and depend on your email and bug reports at this time. If you are working with commercial support your provider is expected to participate on your behalf.
Keeping GeoServer sustainable requires a long term community commitment. If you are unable to contribute time, sponsorship options are available via OSGeo.
IAU authority support and EPSG assumption removalThe new gs-iau extension module provides support for planetary CRSs, sourced from the International Astronomical Union. This allows to manage GIS data over the Moon, Mars, or even the Sun, with well known, officially supported codes.
In addition to that, many bug fixes occurred in the management of CRSs and their text representations (plain codes, URL, URIs) so that the EPSG authority is no longer assumed to be the only possibility, in a variety of places, such as, for example, GML output. The code base has seen this assumption for twenty years long, and while we made a good effort to eliminate the assumption, it could be still lurking in some places. Please test and let us know.


To learn more about this extension please visit the user-guide documentation. Thanks to Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions) for working on this activity.
- GSIP-219 - Multiple CRS authority support, planetary CRS
- GEOS-11075 IAU authority : planetary CRS support
- GEOS-11001 Support other CRS authories in WFS
- GEOS-11002 Support other CRS authorities in WMS
- GEOS-11056 Support other CRS authorities in WCS
- GEOS-11064 Support other CRS authorities in WPS
- GEOS-11066 Support other CRS authorities in importer
- GEOS-11076 SRSList should show authorities other than EPSG, if available
- GEOS-10970 CatalogBuilder cannot handle CRS in authorities other than EPSG
- GEOS-10971 XStreamPersister cannot save CRS references using authorities other than EPSG
- GEOS-10972 Resource page CRS editors would not work with authorities other than EPSG
The printing extension has seen big changes - with a host of new functionality developed by GeoSolutions over the years. With this update the printing module can now be used out-of-the-box by GeoNode and MapStore (no more customization required).
- Max number of columns configuration for multi column legends
- Simple colored box icon in legends
- Explicit support of Geoserver CQL_FILTER parameter (also with layers merge support)
- Legend fitting
- Don’t break legend items
- Reorder legends block in columns
- Images content
- Dynamic images page
- Multipage legends
- Custom intervals in ScalebarBlock
- Clustering Support
- HTML rendering in text blocks
- Extra Pages
- Group Rendering in attribute blocks
- Skip rendering of pages
- Automatic X-Forwarded-For
- Parsing of Base64 encoded images
Thanks to GeoSolutions for adding functionality to mapfish-print for the GeoNode project. Jody Garnett (GeoCat) was responsible for updating the mapfish print-lib for Java 11 and gathering up the functionality from different branches and forks.
- GEOS-11132 mapfish-print-v2 2.3-RC
This release adds a new Check URL facility under the Security menu. This allows administrators to manage OGC Service use of external resources.

For information and examples on how to use the URL Check page, visit user guide documentation.
- GSIP 218 - Control remote HTTP requests sent by GeoTools \ GeoServer
- GEOS-10949 Control remote resources accessed by GeoServer
- GEOS-11048 Improve URL checking
The GeoTools project moved away from using the “org.opengis” package after complaints from OGC GeoAPI working group representatives, using the same package name. Interfaces have been moved to the “org.geotool.api” package, along with some general clean up.
While this does not affect GeoServer users directly, it’s of consequence for those that have installation with custom, home grown plugins that might have to be migrated as a consequence. For those, the GeoTools project offers a migration guide, along with a refactoring script that might perform the migration for you, or else, get you close to a working point. GeoServer itself has been migrated using these scripts, with minimal manual intervention.
For more details, and access to the migration script, please see the GeoTools 30 upgrade guide.
Thanks to Jody Garnett (GeoCat), Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions), and Ian Turton (ASTUN Technologies) for all the hard work on this activity. We would also like to thank the Open Source Geospatial Foundation for setting up a cross-project activity and financial support to address this requested change.
- GEOS-11070 Upgrading to GeoTools 30.x series, refactor to org.geotools.api interfaces
While not strictly part of this release, it’s interesting to know about some community module advances that can be found only in the the 2.24.x series.
Two extensions are no longer actively supported and are now available as community modules:
- GEOS-10960 Downgrade imagemap module to community
- GEOS-10961 Downgrade xslt extension to community
The following community modules have been removed (due to lack of interest):
- GEOS-10962 Remove wms-eo community module
- GEOS-10963 Remove SAML community module
- GEOS-10966 Remove importer-fgdb community module
- GEOS-10967 Remove teradata community module
- GEOS-10977 Remove wmts-styles community module
- GEOS-10978 Remove nsg-wmts community module
- GEOS-10984 Remove ows-simulate community module
The OGC API community module keeps improving. In particular, thanks to the GeoNovum sponsorship, GeoSolutions made the OGC API Features module pass the OGC CITE compliance tests, for the “core” and “CRS by reference” conformance classes. Along with this work, other significant changes occurred:
- Made the API version number appear in the service path, easing future upgrades
- Support for configurable links, required to get INSPIRE download service compliance.
In addition to that, the new “search” experimental conformance class allows to POST complex searches against collections, as a JSON document, in a way similar to the STAC API.


Those interested in this work are encouraged to contact Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions).
- GEOS-10924 Support JSON-FG draft encoding in OGC API - Features
- GEOS-11045 Implement proposal “OGC API - Features - Part n: Query by IDs”
- GEOS-10882 Add an option to remove trailing slash match in OGC APIs
- GEOS-10887 Add angle brackets to OGC API CRS Header
- GEOS-10892 Allow configuring custom links for OGC API “collections” and single collection resources
- GEOS-10895 Make OGC API CITE compliant even if the trailing slash is disabled: landing page exception
- GEOS-11058 Support other CRS authorities in OGC APIs
- GEOS-10909 Don’t link from OGC API Features to WFS 2.0 DescribeFeatureType output, if WFS is disabled
- GEOS-10954 Split ogcapi community module package into single functionality packages
For folks working with very large catalogues some improvement from cloud native geoserver are now available to reduce startup time.
Thanks to Gabriel Roldan for folding this improvement into a community module for the rest of the GeoServer community to enjoy.
- GEOS-11049 Community module “datadir catalog loader”
The GeoServer Access Control List project is an independent application service that manages access rules, and a GeoServer plugin that requests authorization limits on a per-request basis.
Gabriel Roldan is the contact point for anyone interested in this work.
The vector mosaic and FlatGeoBuf modules sport significant performance improvementsFlatGeoBuf is a “A performant binary encoding for geographic data”, a single file format that also manages to be cloud native and include a spatial index. GeoServer provides access to this format thought the WFS FlatGeobuf output format, which not only can write the format, but also read it as a standard data store.
The Vector Mosaic datastore supports creation of mosaics made of single file vector data, useful in situations where the access to data is targeted to sub-pages of a larger data set (e.g., data for a single time, or a single customer, or a single data collect, out of a very large uniform set of vectors) and the database storage for it is become either too slow, or too expensive.
These two modules make a great combo for those in need to handle very large vector datasets, by storing the FlatGeoBuf on cheap storage.
In particular, the FlatGeoBuf module saw speed improvements that made it the new “fastest vector format” for cases where one needs to display a large data set, all at once, on screen (PostGIS remains the king of the hill for anything that needs sophisticated filtering instead).
For reference, we have timed rendering 4 million tiny polygons out of a precision farming collect, using a 7 classes quantile based SLDs. Here is a tiny excerpt of the map:

And here are the timings to render the full set of polygons, putting them all on screen, at the same time, with a single GetMap request:
- PostGIS, 113 seconds
- Shapefile, 41 seconds
- Flatgeobuf, 36 seconds
The tuning is not complete, more optimizations are possible. Interested? Andrea Aime is the contact point for this work.
Release notesNew Feature:
- GEOS-10992 Make GWC UI for disk quota expose HSQLDB, remove H2, automatically update existing installations
- GEOS-11000 WPS process to provide elevation profile for a linestring
Improvement:
- GEOS-10926 Community Module Proxy-Base-Ext
- GEOS-10934 CSW does not show title/abstract on welcome page
- GEOS-10973 DWITHIN delegation to mongoDB
- GEOS-10999 Make GeoServer KML module rely on HSQLDB instead of H2
- GEOS-11005 Make sure H2 dependencies are included in the packages of optional modules that still need it
- GEOS-11059 Map preview should not assume EPSG authority
- GEOS-11081 Add option to disable GetFeatureInfo transforming raster layers
- GEOS-11087 Fix IsolatedCatalogFacade unnecessary performance overhead
- GEOS-11090 Use Catalog streaming API in WorkspacePage
- GEOS-11099 ElasticSearch DataStore Documentation Update for RESPONSE_BUFFER_LIMIT
- GEOS-11100 Add opacity parameter to the layer definitions in WPS-Download download maps
- GEOS-11102 Allow configuration of the CSV date format
- GEOS-11116 GetMap/GetFeatureInfo with groups and view params can with mismatched layers/params
Bug:
- GEOS-8162 CSV Data store does not support relative store paths
- GEOS-10452 Use of Active Directory authorisation seems broken since 2.15.2 (LDAP still works)
- GEOS-10874 Log4J: Windows binary zip release file with log4j-1.2.14.jar
- GEOS-10875 Disk Quota JDBC password shown in plaintext
- GEOS-10899 Features template escapes twice HTML produced outputs
- GEOS-10903 WMS filtering with Filter 2.0 fails
- GEOS-10921 Double escaping of HTML with enabled features-templating
- GEOS-10922 Features templating exception on text/plain format
- GEOS-10928 Draft JSON-FG Implementation for OGC API - Features
- GEOS-10936 YSLD and OGC API modules are incompatible
- GEOS-10937 JSON-FG reprojected output should respect authority axis order
- GEOS-10958 Update Spotbugs to 4.7.3
- GEOS-10981 Slow CSW GetRecords requests with JDBC Configuration
- GEOS-10985 Backup Restore of GeoServer catalog is broken with GeoServer 2.23.0 and StAXSource
- GEOS-10993 Disabled resources can cause incorrect CSW GetRecords response
- GEOS-11015 geopackage wfs output builds up tmp files over time
- GEOS-11016 Docker nightly builds use outdated GeoServer war
- GEOS-11033 WCS DescribeCoverage ReferencedEnvelope with null crs
- GEOS-11060 charts and mssql extension zips are missing the extension
Task:
- GEOS-11091 Upgrade spring-security to 5.7.10
- GEOS-11094 Bump org.hsqldb:hsqldb:2.7.1 to 2.7.2
- GEOS-11103 Upgrade Hazelcast version to 5.3.x
- GEOS-10248 WPSInitializer NPE failure during GeoServer reload
- GEOS-10904 Bump jettison from 1.5.3 to 1.5.4
- GEOS-10907 Update spring.version from 5.3.25 to 5.3.26
- GEOS-10941 Update ErrorProne to 2.18
- GEOS-10987 Bump xalan:xalan and xalan:serializer from 2.7.2 to 2.7.3
- GEOS-10988 Update spring.version from 5.3.26 to 5.3.27 and spring-integration.version from 5.5.17 to 5.5.18
- GEOS-11010 Upgrade guava from 30.1 to 32.0.0
- GEOS-11011 Upgrade postgresql from 42.4.3 to 42.6.0
- GEOS-11012 Upgrade commons-collections4 from 4.2 to 4.4
- GEOS-11018 Upgrade commons-lang3 from 3.8.1 to 3.12.0
- GEOS-11019 Upgrade commons-io from 2.8.0 to 2.12.0
- GEOS-11020 Add test scope to mockito-core dependency
- GEOS-11062 Upgrade [httpclient] from 4.5.13 to 4.5.14
- GEOS-11063 Upgrade [httpcore] from 4.4.10 to 4.4.16
- GEOS-11067 Upgrade wiremock to 2.35.0
- GEOS-11080 Remove ASCII grid output format from WCS
- GEOS-11084 Update text field css styling to look visually distinct
- GEOS-11092 acme-ldap.jar is compiled with Java 8
For the complete list see 2.24-RC release notes.
About GeoServer 2.24 SeriesAdditional information on GeoServer 2.24 series:
- Control remote HTTP requests sent by GeoTools/GeoServer
- Multiple CRS authority support, planetary CRS
Release notes: ( 2.24-RC )
-
 1:06
1:06 Sean Gillies: Bear 100 race week
sur Planet OSGeoThis is it, race week. Wednesday I'm flying to Salt Lake City and driving to Logan. Friday before dawn I'm headed up the trail to Bear Lake.
Week ~5 was a rest week at the end of a big training block. I biked and ran for less than 4 hours. Week ~4 I ran for 12 hours, 53 miles, and 8,500 feet of elevation gain. Much of that was above 10,000 feet in Rocky Mountain National Park, my go-to for accessible high country. I ran up to Granite Pass, 12,100 feet, just below the Longs Peak boulder field, and test drove the gels that will be served at the Bear 100. Spring Energy's Awesome Sauce is good! I could eat them all day. Spring's Speednut product is a bit harder for me to stomach. One of those every few hours might be all I can take.
At the end of week ~4 I did some volunteering at the Black Squirrel Trail Half-Marathon, a race I've run several times. I helped park cars in the pre-race darkness and get first-timers pointed toward registration and the starting line. I saw the Milky Way in the clear, dark early morning sky. I caught up with the race directors, Nick and Brad, and saw other friends in the first mile of the course. Volunteering at events is always needed and fun. I recommend it.
In week ~3, I ran for 9.5 hours, 42 miles, and 5,700 feet. In the interest of fine tuning, I went out in the heat of the day and took my poles. In week ~2, last week, I got the new COVID vaccination and did less running and more yoga and body-weight strength and mobility exercise. Split squats with dumbbells made me sore, but I am over it now.
Where am I at now, in week ~1? I think I have enough experience and adequate training this year to finish. Three events of 40 miles, including one overnight, and one at very high elevation. The heart palpitations that were troubling me last year almost never occur now. I'm well over my most recent sinus infection. I've got all the gear I need and am physically and psychologically prepared for hot weather, cold weather, and rain or snow. The race will have more food than I can eat along the way and will deliver my five drop bags to aid stations and the finish line. I don't have a crew or pacer for the run, but think I'll be fine without. Reality is that it's harder to have these as you get older. Your family is busy and your friends are busy with their own families. I'm shy, but not shy about forming small ad-hoc teams on the trail, so I expect to be fine on that front.
The Bear 100 Endurance Run starts with 5,000 feet of climbing in the first 10 miles. I can do this. At least it's at the beginning and not the end. That leaves only 17,000 feet for the last 90 miles. I'm joking about this to keep my spirits up. This will be super hard, a big bump up from my hardest week of training, and I'll need to go even deeper into the unknown than I've done at the Never Summer 100K. I'm ready to see what happens out there.
The one thing that's concerning me is that I have a persistent ache in my right foot. Yesterday I went out for an hour in my Nike Terra Kiger's to see if I might want to bring them along as a shoe option. The answer is no: they don't have enough padding for my foot in its current condition. I feel worse today than yesterday. There's at least a small chance that I have a bone stress problem. The pain and swelling is right on the "N-spot". I'm not going to let this stop me from starting and will see how it goes on Friday. I've got a pretty high pain threshold and will be stashing some ibuprofen in my later drop bags. Cold rain and cold, numb feet, if the forecast holds, might help, too. How is that for positive thinking?
If you want to follow along on Friday and Saturday, the live tracking should be at [https:]] . My bib number is 314. That website currently shows last year's race. I expect that this year's progress will be shown on Friday morning.
-
 20:10
20:10 Sean Gillies: Status update
sur Planet OSGeoI'm pausing my job search and open source work to focus on next weekend's adventure. Forgive me if I don't respond before October 5-6. After I'm back I'll be prioritizing the job search over open source. Not for long, I hope!
-
 22:29
22:29 QGIS Blog: QGIS Grant Programme 2023 Update
sur Planet OSGeoThanks to our generous donors and sustaining members, we are in the wonderful position to be able to further extend our 2023 Grant Programme and to fund two additional projects that came in very close 5th and 6th in the voting results:
- QEP#261 Cachable provider metadata API — or how to
 the QGIS loading times
the QGIS loading times - QEP#236 Unification of all geometric and topological verification methods
On behalf of the QGIS.ORG project, I would like to thank everyone who helped with the fund raising and everyone who stepped up and joined our donor and sustaining membership programme.

- QEP#261 Cachable provider metadata API — or how to
-
 19:39
19:39 GeoSolutions: FREE Webinar: MapStore for Local Governments – Cleveland Metroparks Case Study
sur Planet OSGeoYou must be logged into the site to view this content.